Kubernetes 实践 主要记录一些自己的一些部署实践。
1 目标
最近在看 TiDB 的 Multi Kubernetes 集群部署方案,TiDB 本身是灵活扩容的分布式数据库,因此部署前需要确保 Multi Kubernetes 之间服务的连通性。
Kubernetes 中,IP 是虚拟以及不持久的,各个服务之间是靠 Domain 相互访问的。因此,Multi Kubernetes 之间的连通性关键就在于:
- 物理网络连通 - 所有方案最基本的,就是底层的网络可以联通。
- DNS 解析 - 因为服务之间靠 Domain 访问,因此访问另一个集群的服务时,DNS 要能够解析为另一个集群的 Pod IP。
2 物理网络连通
Multi Kubernetes 之间物理网络的连通不同场景有着不同的方案。
- 使用 EKS 时,不同 VPC 下的 EKS 集群都过 VPC Peering 连接,实现物理网络的连通性。
- 使用 GKE 时,GKE 集群之间网络就是联通的。
- 其他自己部署的 Multi Kubernetes 集群,可能需要 Tunnel 来构建物理网络。可以参考下项目 submariner-io/submariner。
物理网络连通的最终的效果就是,一个 Kubernetes 集群的 Pod,是能够 “访问” 到另一个 Kubernetes 集群的 Pod 的。
Note
最理想的网络互通,应该是多个 Kubernetes 集群处于同一个网络,不过这应该就是一个 Kubernetes 集群了,而不是两个了。
在这之下,两个 Kubernetes 集群之间能够 “直接”(不需要通过 NodePort 映射)相互访问。就像两个不同的网段,中间有路由器来连通这两个网段。
而这个 “路由器” 有着多种的实现了:例如最直接的,Cluster1 网络 -> Node1 -> Node2 -> Cluster2 网络,中间通过 NodePort 来转发。
3 DNS
3.1 DNS 解析流程
无论是 Pod DNS 还是 Service DNS,其解析都由 CoreDNS 负责。所以一个 Cluster 要访问另一个 Cluster 的服务时,其期望的步骤为:
-
Cluster1 Pod -> Cluster1 CoreDNS
Cluster1 Pod 发送 DNS 请求到 Cluster1 CoreDNS。
-
Cluster1 CoreDNS -> Cluster2 CoreDNS
Cluster1 CoreDNS 判断请求的 Domain 是 Cluster2 的,因此转发给 Cluster2 CoreDNS 解析。
因为物理网络是连通的,所以转发是可以成功的。
-
Cluster2 CoreDNS -> Cluster1 CoreDNS
Cluster2 CoreDNS 接受到请求后,解析 Domain,回复对应 Cluster2 Pod IP 给 Cluster1 CoreDNS。
因为物理网络是连通的,所以回复是可以成功的。
-
Cluster1 CoreDNS -> Cluster1 Pod
Cluster1 CoreDNS 将解析结果回复给 Cluster1 Pod。
-
Cluster1 Pod -> Cluster2 Pod
因为物理网络是连通的,所以访问是可以成功的。
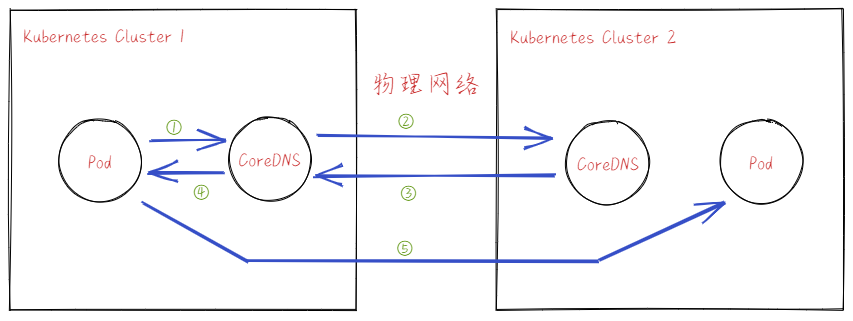
当然,我们 CoreDNS 能够包含所有 Cluster 的记录,那么可能可以加速解析的流程。目前不清楚可不可以这样配置,或者有没有这样的实现。
Note
注意,上述中直接访问跨 Kubernetes 访问 Service 是可能无法联通的,猜想两种情况:
- Service IP 与 Pod 网络不是一个平面的,那么如果 Cluster1 Pod 发出的包无法被路由到 Cluster2 中(除非配置好路由规则,例如 AWS GCP 的 Route)。
- Service IP 与 Pod 网络是一个平面的,Cluster1 Pod 发出的数据包能够路由到 Cluster2 中,由 Cluster2 中的 kube-proxy 根据 Service IP 成功转发了。
所以,问题的关键还是在于数据包能否路由到 Cluster2 网络中。
3.2 配置 CoreDNS
基于上面的流程,有两个关键的问题:
- 如何判断请求的 Domain 是 Cluster2 的?
- 如何配置 CoreDNS 转发请求?
这些都需要通过 CoreDNS 配置来实现,先看参考文档 Customizing DNS Service 知晓如何配置 CoreDNS。
从 K8s 学习 - 2 - Service 我们知晓,Kubernetes 中的 Domain 分为 Pod 与 Service。
- Pod Domain
<pod_ip>.<namespace>.pod.<clust-domain><pod_ip>.<depolyment/daemonset_name>.svc.<cluster_domain><hostname>.<subdomain>.<namespace>.svc.<cluster_domain>
- Service Domain
<service>.<namespace>.svc.<cluster_domain>
因为 DNS 解析是将 Domain 从后向前按照域解析的,所以最简单的方式就是:将 Multi Kubernetes 的 Cluster Domain 设置为不同的,然后配置 CoreDNS 转发。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: coredns
namespace: kube-system
data:
Corefile: |
.:53 {
# default..
}
<target-cluster-domain>:53 { # <-- 指向对端的 Kubernetes Cluster Domain
errors
cache 30
forward . <target-coredns-ip>
}
|
- 除了自己集群的域名解析外,对于 “<target-cluster-domain>” 的域名解析都转发给了对应集群的 CoreDNS。
改变 Kubernetes 集群的 Cluster Domain 方式:部署 Cluster 时,通过 kubelet 参数 -cluster-domain=<default-local-domain> 配置。
不过,改变 Cluster Domain 方式需要在部署 Cluster 时配置,如果你已经部署了 Cluster,这可能就不太方便了。这种情况下,Multi Kubernetes Cluster Domain 都是 “cluster.local”,所以我们要在更前面的域上来区分,自然是 “<namespace>"。
例如,你的 Pod 要访问另一个 Cluster 的 Pod:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: coredns
namespace: kube-system
data:
Corefile: |
.:53 {
# default..
}
<target-namespace>.svc.cluster.local:53 { # <-- 指向对端 Kubernetes 服务的 namespace
errors
cache 30
forward . <target-coredns-ip>
}
|
可以想到,这种访问匹配的范围更小,更重要的是,这使得 Multi Cluster 之间的 namespace 不应该重复。
4 AWS 上的实践
4.1 创建 EKS 集群
先建立两个 EKS 集群,需要注意两个集群 VPC CIDR 不要不覆盖。
1
2
3
|
$ eksctl create cluster --name test-cluster --with-oidc --ssh-access --managed --region us-west-2 --instance-types m5.xlarge --nodes 3
$ eksctl create cluster --name test-cluster-2 --with-oidc --ssh-access --managed --region us-west-2 --instance-types m5.xlarge --nodes 3 --vpc-cidr 10.0.0.0/16
|
查询下两个 EKS 集群信息,后面需要用到:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
$ eksctl get cluster test-cluster
NAME VERSION STATUS CREATED VPC SUBNETS SECURITYGROUPS
test-cluster 1.20 ACTIVE 2021-09-30T11:53:19Z vpc-0409bd99d5e2b6f5b subnet-00d1a0abdaf60021b,subnet-0a9fca73d25257d90,subnet-0aee90db41909f538,subnet-0c81d647b53fe567a,subnet-0dcd3f3da03b5e767,subnet-0f80939acbdda6357 sg-00985dc11204cfeda
$ eksctl get cluster test-cluster-2
NAME VERSION STATUS CREATED VPC SUBNETS SECURITYGROUPS
test-cluster-2 1.20 ACTIVE 2021-09-30T12:19:39Z vpc-0e35ec388cb70e7fc subnet-012fa5481e326aafc,subnet-0586d236d85ed6893,subnet-0d5695aa8970fea2d,subnet-0d61b543c82d94d14,subnet-0d740e2366cf2778f,subnet-0def1a48342d72d32 sg-0d914515ffd1173b5
|
我们创建了同 Region 下不同 VPC 两个 EKS 集群,不同 Region 下后续操作也是一样的。
后续操作中,各个资源的 1、2 分别代表对应集群的资源。k1 与 k2 分别代表对应集群的 kubectl 操作(通过 –kubeconfig 参数)。
4.2 构建网络
EKS 中 Pod 是 Host Network,与 Node 在同一个网络中。AWS VPC 中各个 Subnet 网络是互通的,因此我们只需要构建 VPC 之间的网络互通。
需要创建与配置以下 AWS 资源:
- VPC Peering - 连接 VPC 之间的网络
- Route Table - 能够将流量正确的转发到另一个 VPC
- ACL - 流量到达 Subnet 能够通过 ACL
- Security Group - 流量到达每个 Instance 能够通过 Security Group
Note
要使用 VPC Peering 连通 VPC,这些资源都是需要配置的。
4.2.1 创建 VPC Peering
Create VPC Peering,构建 VPC1 连通 VPC2。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
$ aws ec2 create-vpc-peering-connection \
--vpc-id vpc-0409bd99d5e2b6f5b \
--peer-vpc-id vpc-0e35ec388cb70e7fc
{
"VpcPeeringConnection": {
"AccepterVpcInfo": {
"OwnerId": "385595570414",
"VpcId": "vpc-0e35ec388cb70e7fc",
"Region": "us-west-2"
},
"ExpirationTime": "2021-10-07T12:53:36+00:00",
"RequesterVpcInfo": {
"CidrBlock": "192.168.0.0/16",
"CidrBlockSet": [
{
"CidrBlock": "192.168.0.0/16"
}
],
"OwnerId": "385595570414",
"PeeringOptions": {
"AllowDnsResolutionFromRemoteVpc": false,
"AllowEgressFromLocalClassicLinkToRemoteVpc": false,
"AllowEgressFromLocalVpcToRemoteClassicLink": false
},
"VpcId": "vpc-0409bd99d5e2b6f5b",
"Region": "us-west-2"
},
"Status": {
"Code": "pending-acceptance",
"Message": "Pending Acceptance by 385595570414"
},
"Tags": [],
"VpcPeeringConnectionId": "pcx-094a1149b32ef0c05"
}
}
|
Accept VPC Peering,完成 VPC Peering 构建。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
$ aws ec2 accept-vpc-peering-connection \
--vpc-peering-connection-id pcx-094a1149b32ef0c05
{
"VpcPeeringConnection": {
"AccepterVpcInfo": {
"CidrBlock": "10.0.0.0/16",
"CidrBlockSet": [
{
"CidrBlock": "10.0.0.0/16"
}
],
"OwnerId": "385595570414",
"PeeringOptions": {
"AllowDnsResolutionFromRemoteVpc": false,
"AllowEgressFromLocalClassicLinkToRemoteVpc": false,
"AllowEgressFromLocalVpcToRemoteClassicLink": false
},
"VpcId": "vpc-0e35ec388cb70e7fc",
"Region": "us-west-2"
},
"RequesterVpcInfo": {
"CidrBlock": "192.168.0.0/16",
"CidrBlockSet": [
{
"CidrBlock": "192.168.0.0/16"
}
],
"OwnerId": "385595570414",
"PeeringOptions": {
"AllowDnsResolutionFromRemoteVpc": false,
"AllowEgressFromLocalClassicLinkToRemoteVpc": false,
"AllowEgressFromLocalVpcToRemoteClassicLink": false
},
"VpcId": "vpc-0409bd99d5e2b6f5b",
"Region": "us-west-2"
},
"Status": {
"Code": "provisioning",
"Message": "Provisioning"
},
"Tags": [],
"VpcPeeringConnectionId": "pcx-094a1149b32ef0c05"
}
}
|
4.2.2 Route Table 添加 Route 项
为了 VPC 之间的连通性,需要向各个 VPC 的 Route Table 添加 Route 项,转发数据包到 VPC Peering。
先查询两个 VPC 对应的 Route Table ID。
1
2
3
|
$ aws ec2 describe-route-tables --filters Name=vpc-id,Values=vpc-0409bd99d5e2b6f5b
$ aws ec2 describe-route-tables --filters Name=vpc-id,Values=vpc-0e35ec388cb70e7fc
|
添加 Route 项,匹配另一个集群网段,路由到 VPC Peering。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
$ aws ec2 create-route \
--route-table-id rtb-058ae03476f0eb62d \
--destination-cidr-block 10.0.0.0/16 \
--vpc-peering-connection-id pcx-094a1149b32ef0c05
{
"Return": true
}
$ aws ec2 create-route \
--route-table-id rtb-03e1023998c139fea \
--destination-cidr-block 192.168.0.0/16 \
--vpc-peering-connection-id pcx-094a1149b32ef0c05
{
"Return": true
}
|
4.2.3 配置 ACL 与 Security Group
接着配置 ACL 与 Security Group,让数据包不被防火墙所拦截。
eksctl 创建 VPC 时没有配置 ACL,因此默认的 ACL 允许所有的进出流量,所以不需要配置。
Instance 的默认 Security Group 是禁止所有的,eksctl 添加了 Node 节点的白名单,我们需要加入另一个 Cluster 网段的 Rule。
EKS 会让其下 Instance 共用一个 Security Group(eksctl get cluster 时得到),所以我们只需要配置一个 Security Group 即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
$ aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress \
--group-id sg-01cde04b3896f32df \
--protocol all \
--cidr 10.0.0.0/16
$ aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress \
--group-id sg-06cbf88ed5d56bd18 \
--protocol all \
--cidr 192.168.0.0/16
|
Note
这里的 Security Group ID 部署 eksctl get cluster 命令得到的,eksctl get cluster 得到是控制面的 Security Group。
4.3 Kubernetes DNS 配置
到这里,我们的物理连通性构建好了,接下来就是对于 Cluster 中的 DNS 配置了。因为 EKS 集群部署没有修改 Cluster Domain 的方式(也可能是我没找到),如 3.2 配置 CoreDNS 所说,我们使用 namespace 来区分 Domain。
我们先要知道 Cluster1 与 Cluster2 中各个 CoreDNS Pod 的 IP,这样才能配置 CoreDNS 转发。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
$ k1 get pods -n kube-system -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
coredns-86d9946576-72gcv 1/1 Running 0 112m 192.168.95.166 ip-192-168-85-158.us-west-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
coredns-86d9946576-tk9nk 1/1 Running 0 112m 192.168.4.66 ip-192-168-24-153.us-west-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
$ k2 get pods -n kube-system -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
coredns-86d9946576-79zvs 1/1 Running 0 87m 10.0.76.0 ip-10-0-77-8.us-west-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
coredns-86d9946576-tqcbh 1/1 Running 0 87m 10.0.91.141 ip-10-0-77-8.us-west-2.compute.internal <none> <none>
|
接着配置 CoreDNS1 与 CoreDNS2,通过对应的 ConfigMap 来配置 Corefile。配置后,CoreDNS 会自动重新加载配置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
$ k1 edit -n kube-system cm coredns
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
# ...
data:
Corefile: |
.:53 {
# default...
}
cluster-2.svc.cluster.local:53 {
log
errors
cache 30
forward . 10.0.76.0 10.0.91.141
}
$ k2 edit -n kube-system cm coredns
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
# ...
data:
Corefile: |
.:53 {
# default...
}
cluster-1.svc.cluster.local:53 {
log
errors
cache 30
forward . 10.0.76.0 10.0.91.141
}
|
这配置表明了,在创建服务时部署在 Cluster1 的 “cluster-1” namespace 与 Cluster2 的 “cluster-2” namespace 时,域名解析才能正常。
4.4 测试
OK,一切都完成了,我们来简单的测试下。我们在 Cluster1 部署一个 busybox Pod,用于等会访问 Cluster2 Service 使用。
1
|
$ k1 apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/master/hack/testdata/recursive/pod/pod/busybox.yaml
|
在 Cluster2 部署一个 Service,Service 将消息转发到百度。需要注意,一定要部署在 “cluster-2” namespace。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: proxy-to-baidu
namespace: cluster-2
spec:
ports:
- name: baidu
port: 8888
protocol: TCP
type: ExternalName
externalName: www.baidu.com # <-- 转发
|
测试下域名解析,可以看到域名解析到了百度的域名了,说明跨 Kubernetes 联通了!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
$ k1 exec busybox1 -- nslookup proxy-to-baidu.cluster-2.svc.cluster.local
Server: 10.100.0.10
Address: 10.100.0.10:53
proxy-to-baidu.cluster-2.svc.cluster.local canonical name = www.baidu.com
www.baidu.com canonical name = www.a.shifen.com
www.a.shifen.com canonical name = www.wshifen.com
|
5 GCP 上的实践
5.1 创建 VPC Network
GCP 与 AWS 不同,其 VPC 是一个虚拟的全球的概念,其下的 Subnet 是天然的跨 Region 联通的。因此,物理网络我们不需要过多的配置使其联通。
先创建一个自定义子网的 VPC:
1
|
$ gcloud compute networks create ${network_name} --subnet-mode=custom
|
在新创建的 VPC 网络下创建两个个 Subnet,注意各个 Subnet 的 IP 地址范围不能相互重叠。每个 Subnet 还包含了后续 Kubernetes 要使用的 Pod 与 Service 的 IP 地址范围。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
$ gcloud compute networks subnets create ${subnet_1} \
--region=${region_1} \
--network=${network_name} \
--range=10.0.0.0/16 \
--secondary-range pods=10.10.0.0/16,services=10.100.0.0/16
$ gcloud compute networks subnets create ${subnet_1} \
--region=${region_1} \
--network=${network_name} \
--range=10.2.0.0/16 \
--secondary-range pods=10.12.0.0/16,services=10.102.0.0/16
|
5.2 创建 GKE 集群
创建两个 Region 级别的 GKE 集群:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
$ gcloud beta container clusters create ${cluster_1} \
--region ${region_1} --num-nodes 1 \
--network ${network_name} --subnetwork ${subnet_1} \
--cluster-dns clouddns --cluster-dns-scope vpc \
--cluster-dns-domain ${cluster_domain_1}
--enable-ip-alias \
--cluster-secondary-range-name=pods --services-secondary-range-name=services
$ gcloud beta container clusters create ${cluster_2} \
--region ${region_2} --num-nodes 1 \
--network ${network_name} --subnetwork ${subnet_2} \
--cluster-dns clouddns --cluster-dns-scope vpc \
--cluster-dns-domain ${cluster_domain_2}
--enable-ip-alias \
--cluster-secondary-range-name=pods --services-secondary-range-name=services
|
一些重要的参数:
--network 与 --subnetwork 指定了加入的 Subnet;-cluster-dns clouddns 和 --cluster-dns-scope vpc 参数使用了 Cloud DNS 服务,以实现跨 Kubernetes 的 DNS 解析;--cluster-dns-domain ${cluster_domain_1} 定义了域名解析使用的 Cluster Domain,也就是我们需要为 Pod 配置的;--cluster-secondary-range-name=pods --services-secondary-range-name=services 指定了 Pod 与 Service 使用的 IP 地址范围;
5.3 配置 Firewall
最后一步就是配置 GKE 集群节点应用的 Firewall。默认情况,创建 GKE 集群会创建默认本集群 Pod 访问的 Firewall(见文档 自动创建的防火墙规则),因此集群见 Pod 相互访问是不允许的。
先找到集群用于 Pod 见通信的 Firewall rules。
1
2
3
|
$ gcloud compute firewall-rules list --filter='name~gke-${cluster_1}-.*-all'
NAME NETWORK DIRECTION PRIORITY ALLOW DENY DISABLED
gke-${cluster_1}-b8b48366-all ${network} INGRESS 1000 tcp,udp,icmp,esp,ah,sctp False
|
更新该防火墙规则,设置 source range 为所有集群的 Pod 网络的 IP 地址范围:
1
|
$ gcloud compute firewall-rules update gke-${cluster_1}-b8b48366-all --source-ranges 10.10.0.0/16,10.11.0.0/16
|
6 Kind 上的实践
6.1 创建 Kubernetes 集群
编写 Kind Cluster 配置文件。因为 Kind 支持配置 kubeadm 的配置,所以可以设置两个集群的 cluster domain。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
$ cat cluster-1.yaml
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
networking:
podSubnet: 10.10.0.0/16
serviceSubnet: 10.40.0.0/16
nodes:
- role: control-plane
- role: worker
- role: worker
kubeadmConfigPatches:
- |
kind: ClusterConfiguration
networking:
dnsDomain: "cluster-1.com"
$ cat cluster-2.yaml
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
networking:
podSubnet: 10.20.0.0/16
serviceSubnet: 10.50.0.0/16
nodes:
- role: control-plane
- role: worker
- role: worker
kubeadmConfigPatches:
- |
kind: ClusterConfiguration
networking:
dnsDomain: "cluster-2.com"
|
创建两个集群 cluster-1 cluster-2。
1
2
|
$ kind create cluster --config cluster-1.yaml --name cluster-1
$ kind create cluster --config cluster-2.yaml --name cluster-2
|
WARN
操作时,发现如果 network.podSubnet 设置为 10.0.0.0/16 之外的网段,Kind 的 CNI 无法部署成功。
6.2 构建网络
整个网络数据包的流转为:Pod A -> Node A -> Node B -> Pod B。其中 Pod -> Node 之间的网络是连通的,所以我们需要解决的关键问题就是 Node A -> Node B 的数据包转发。
Kind 创建的多个集群都是在一个 Docker Bridge Network,因此 Node 之间的网络是天然联通的。
因此,我们只需要在 Node 上添加路由项,使之能够正确转发发往对方集群的数据包。我们为所有 Node 添加指向另一个集群下的 Node 的路由,路由基于 Node 的 Pod CIDR。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
# 找到 每个 node 的 IP 与 PodCIDR
$ kubectl --context kind-cluster-1 get node -ojsonpath='{range .items[*]} {.metadata.name}{"\t"} {.spec.podCIDR}{"\t"} {.status.addresses[0].address}{"\n"} {end}'
cluster-1-control-plane 10.10.0.0/24 172.19.0.2
cluster-1-worker 10.10.2.0/24 172.19.0.4
cluster-1-worker2 10.10.1.0/24 172.19.0.3
$ kubectl --context kind-cluster-2 get node -ojsonpath='{range .items[*]} {.metadata.name}{"\t"} {.spec.podCIDR}{"\t"} {.status.addresses[0].address}{"\n"} {end}'
cluster-2-control-plane 10.20.0.0/24 172.19.0.7
cluster-2-worker 10.20.2.0/24 172.19.0.5
cluster-2-worker2 10.20.1.0/24 172.19.0.6
# 给节点添加路由项
$ for node in cluster-1-control-plane cluster-1-worker cluster-1-worker2 ; do docker exec ${node} ip route add 10.20.0.0/24 via 172.19.0.7; done
$ for node in cluster-1-control-plane cluster-1-worker cluster-1-worker2 ; do docker exec ${node} ip route add 10.20.2.0/24 via 172.19.0.5; done
$ for node in cluster-1-control-plane cluster-1-worker cluster-1-worker2 ; do docker exec ${node} ip route add 10.20.1.0/24 via 172.19.0.6; done
$ for node in cluster-2-control-plane cluster-2-worker cluster-2-worker2 ; do docker exec ${node} ip route add 10.10.0.0/24 via 172.19.0.2; done
$ for node in cluster-2-control-plane cluster-2-worker cluster-2-worker2 ; do docker exec ${node} ip route add 10.10.2.0/24 via 172.19.0.4; done
$ for node in cluster-2-control-plane cluster-2-worker cluster-2-worker2 ; do docker exec ${node} ip route add 10.10.1.0/24 via 172.19.0.3; done
|
Note
这里尝试过给宿主机上的 kind 的 Bridge 网卡添加路由来转发,而不用为每个 Node 设置路由。但是,这样设置好后发现 UDP ICMP 数据包是可以互通的,但是 TCP 连接无法成功。还不清楚原因。
下图总结了目前构建的网络:
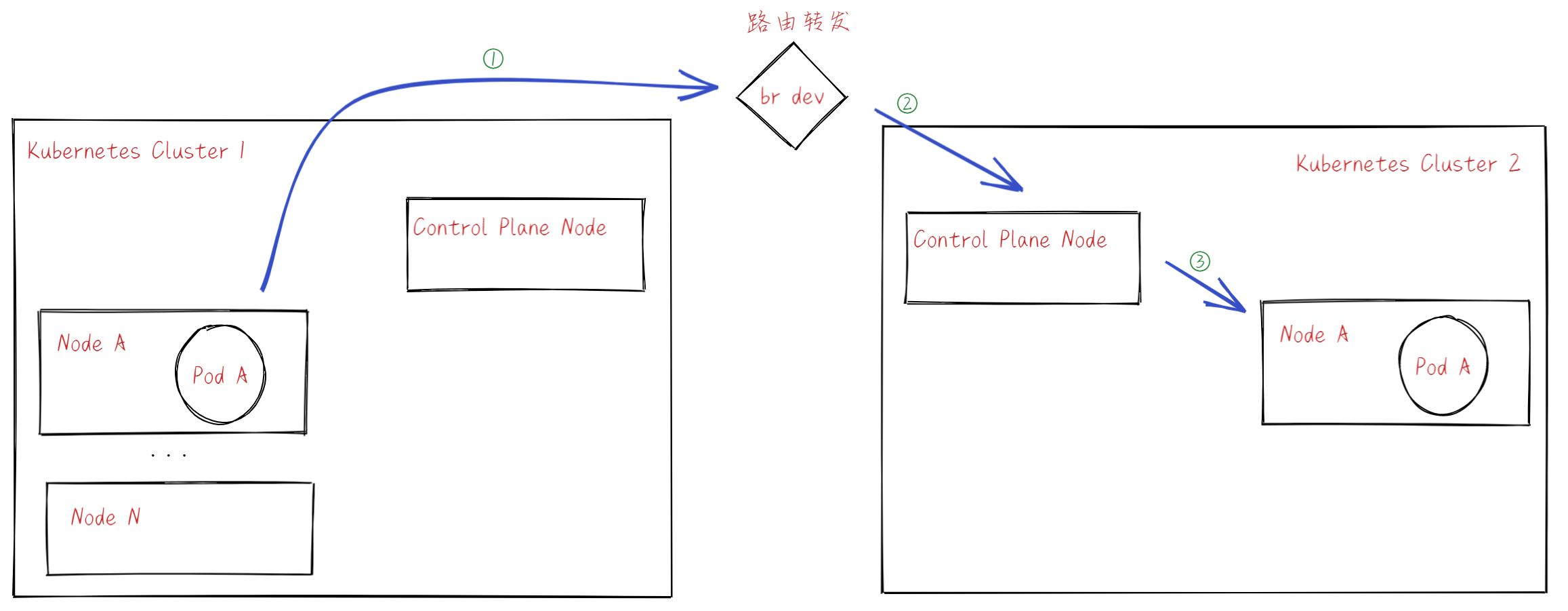
- Pod A 发送数据包,走 default 路由,由 Bridge 网卡处理。
- 根据路由,将数据包转发给 Control Plane Node。
- Control Plane Node 转发给 Node A,后发送到 Pod A。
Note
Kind 网络中,某个集群 Pod 访问其他集群时,数据包会被 Node 进行 SNAT。因此,在某些需要使用源 IP(例如证书 host 配置)时,需要注意。
6.3 Kubernetes DNS 配置
DNS 配置与 AWS 中的 DNS 配置类似,不过因为设置了两个集群的 cluster domain,所以可以直接使用 cluster domain 配置 CoreDNS。
先看两个集群的 CoreDNS Pod IP。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
$ kubectl --context kind-cluster-1 get pods -n kube-system -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
coredns-558bd4d5db-7kjdt 1/1 Running 0 65m 10.10.0.3 cluster-1-control-plane <none> <none>
coredns-558bd4d5db-lb46f 1/1 Running 0 65m 10.10.0.2 cluster-1-control-plane <none> <none>
$ kubectl --context kind-cluster-2 get pods -n kube-system -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
coredns-558bd4d5db-b8c46 1/1 Running 0 64m 10.20.0.2 cluster-2-control-plane <none> <none>
coredns-558bd4d5db-w9p8g 1/1 Running 0 64m 10.20.0.3 cluster-2-control-plane <none> <none>
|
接着配置 CoreDNS1 与 CoreDNS2,通过对应的 ConfigMap 来配置 Corefile。配置后,CoreDNS 会自动重新加载配置。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
$ kubectl --context kind-cluster-1 edit -n kube-system cm coredns
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
# ...
data:
Corefile: |
.:53 {
# default...
}
cluster-2.com:53 {
errors
cache 30
forward . 10.20.0.2 10.20.0.3 # -> 对方集群的 CoreDNS Pod IP
}
$ kubectl --context kind-cluster-2 edit -n kube-system cm coredns
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
# ...
data:
Corefile: |
.:53 {
# default...
}
cluster-1.com:53 {
errors
cache 30
forward . 10.10.0.2 10.10.0.3 # -> 对方集群的 CoreDNS Pod IP
}
|
参考

