介绍 Kubernetes 源码中 Volume 相关的实现(不包含 CSI 相关实现)。
Volume 的基本概念见 Kubernetes - 存储设计。
1 Base Interface
在 Kubernetes - 存储设计 中看到,各个存储插件都围绕这 Volume Plugin 的概念展开。这里我们先看一下 Interface 的抽象。
1.1 VolumePlugin Interface
在源码实现中,Volume Plugin 概念对应的就是 VolumePlugin Interface,其定义了最基本的存储插件应该支持接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
type Spec struct {
Volume *v1.Volume
PersistentVolume *v1.PersistentVolume
ReadOnly bool
InlineVolumeSpecForCSIMigration bool
Migrated bool
}
// VolumePlugin is an interface to volume plugins that can be used on a
// kubernetes node (e.g. by kubelet) to instantiate and manage volumes.
type VolumePlugin interface {
// Init 初始化 plugin
Init(host VolumeHost) error
// Name 返回 plugin name
// 命名方式为 "example.com/volume","kubernetes.io" 由 kubernete 内置 Volume 预留使用
GetPluginName() string
// GetVolumeName 基于 spec 返回一个唯一的 volume name 或者 id
// 对于 Attach 与 Detach 操作会传递该 name 来让 plugin 识别 volume
GetVolumeName(spec *Spec) (string, error)
// CanSupport 返回 plugin 是否支持该 spec
CanSupport(spec *Spec) bool
// RequiresRemount 表明 plugin 是否支持 volume 的重新挂载
RequiresRemount(spec *Spec) bool
// NewMounter 创建一个 Mounter
NewMounter(spec *Spec, podRef *v1.Pod, opts VolumeOptions) (Mounter, error)
// NewUnmounter 创建一个 UnMounter
NewUnmounter(name string, podUID types.UID) (Unmounter, error)
// ConstructVolumeSpec 由 volume name 得到一个 spec
ConstructVolumeSpec(volumeName, volumePath string) (*Spec, error)
// SupportsMountOption 表明是否支持挂载选项
SupportsMountOption() bool
// SupportsBulkVolumeVerification checks if volume plugin type is capable
// of enabling bulk polling of all nodes. This can speed up verification of
// attached volumes by quite a bit, but underlying pluging must support it.
SupportsBulkVolumeVerification() bool
}
|
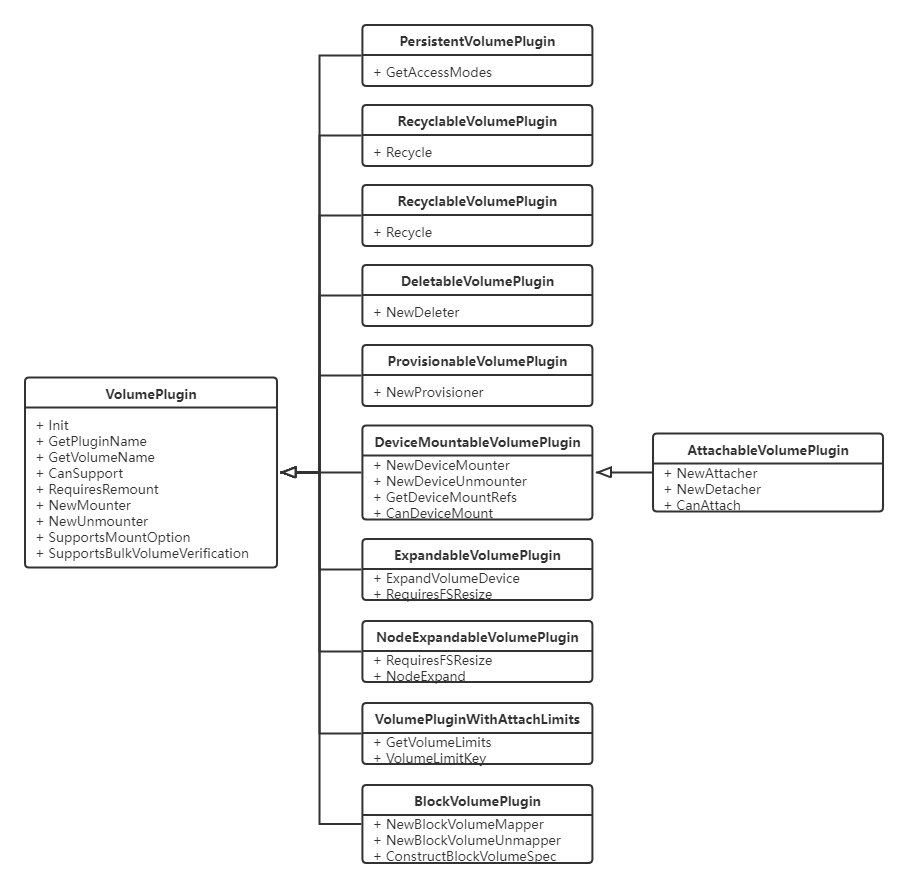
在 VolumePlugin 之上,根据支持的功能不同衍生了更多的 Plugin Interface。包括:
PersistentVolumePlugin - Volume 支持保存持久数据RecyclableVolumePlugin - 支持 Recycle VolumeDeletableVolumePlugin - 支持 Delete VolumeProvisionableVolumePlugin - 支持 Provision VolumeDeviceMountableVolumePlugin - 需要先挂载 Device,才可以将 Volume 挂载给 PodAttachableVolumePlugin - 需要先 Attach 到 Node,再挂载 Device,才可以将 Volume 挂载给 PodExpandableVolumePlugin - Volume 支持从控制面触发 ExpandNodeExpandableVolumePlugin - Volume 支持 Node 触发 ExpandVolumePluginWithAttachLimits - 限制 Node 能够 Attach Volume 的数量BlockVolumePlugin - 支持 Block Volume
看几个 Interface 为例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
// DeletableVolumePlugin 表示支持 Delete 操作的 Volume Plugin
type DeletableVolumePlugin interface {
VolumePlugin
NewDeleter(spec *Spec) (Deleter, error)
}
// ProvisionableVolumePlugin 表示支持 Provisioner 操作的 Volume Plugin
type ProvisionableVolumePlugin interface {
VolumePlugin
NewProvisioner(options VolumeOptions) (Provisioner, error)
}
// AttachableVolumePlugin 表示支持 Attach/Detach 操作的 Volume Plugin
type AttachableVolumePlugin interface {
DeviceMountableVolumePlugin
NewAttacher() (Attacher, error)
NewDetacher() (Detacher, error)
CanAttach(spec *Spec) (bool, error)
}
// DeviceMountableVolumePlugin 表示支持 Mount/Unmount 操作的 Volume Plugin
type DeviceMountableVolumePlugin interface {
VolumePlugin
NewDeviceMounter() (DeviceMounter, error)
NewDeviceUnmounter() (DeviceUnmounter, error)
GetDeviceMountRefs(deviceMountPath string) ([]string, error)
CanDeviceMount(spec *Spec) (bool, error)
}
|
用一个类图总结一下:

可以看到,上面 VolumePlugin 相关 Interface 除了提供基础的信息查询接口外,不直接提供实际的操作 Volume 的接口,而是返回 Mounter 这样的 Interface。
1.2 Control Interface
源码中将提供 Mount / Provision 具体操作接口单独抽成了一个个 Interface,我们现称之为 Control Interface。
Why
个人猜想还是为了复用,例如不同的 Plugin 可能大部分 Volume 操作都是不同的,但是一些例如 SetUp 这样的接口大部分实现都是一样的,因此能够通过返回同一个 Mounter 实例来复用逻辑。
将 Control 逻辑抽象为 Interface 是一个很常见的设计方式。
Control Interface 包括:
Mounter
CanMount() - SetUp() 调用前检查所需的组件(例如插件程序)是否准备好SetUp() 与 SetUpAt() - 为 Pod 准备好对应的 Volume 目录
Unmounter
TearDown() 与 TearDownAt() - 移除为 Pod 准备的 Volume 目录
CustomBlockVolumeMapper
SetUpDevice() - 为 Pod 准备好 DeviceMapPodDevice() - 将 Device 映射给 Pod
CustomBlockVolumeUnmapper
TearDownDevice() - 移除为 Pod 准备好的 DeviceUnmapPodDevice() - 取消 Device 映射
Provisioner
Provision() - 创建一个 Volume
Deleter
Attacher
Attach() - Attach Volume 到 Node 上VolumesAreAttached() - 返回 Node 上的 attached Volume
Detacher
DeviceMounter
MountDevice() - 将 attached Volume 挂载到一个全局目录
DeviceUnmounter
UnmountDevice() - 取消 attached Volume 的全局目录挂载
来看几个 Control Interface:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
|
// Volume represents a directory used by pods or hosts on a node. All method
// implementations of methods in the volume interface must be idempotent.
type Volume interface {
// GetPath 返回 volume 需要的挂载路径
GetPath() string
// MetricsProvider 提供统计接口
MetricsProvider
}
// Mounter 接口为 Pod 提供 Volume 对应的目录
type Mounter interface {
Volume
// CanMount 优先于 Setup 调用,用于检查当前环境是否包含能够 Mount 的组件
CanMount() error
// SetUp 为 Pod 提供 Volume 的目录,目录路径由自己决定
SetUp(mounterArgs MounterArgs) error
// SetUpAt 为 Pod 提供 Volume 的目录,目录路径由 dir 指定
SetUpAt(dir string, mounterArgs MounterArgs) error
// GetAttributes 返回 Volume 的属性
GetAttributes() Attributes
}
// Unmounter interface provides methods to cleanup/unmount the volumes.
type Unmounter interface {
Volume
// TearDown 取消为 Pod 提供的目录
TearDown() error
// TearDown 取消为 Pod 提供的指定目录
TearDownAt(dir string) error
}
// BlockVolumeMapper interface is a mapper interface for block volume.
type BlockVolumeMapper interface {
BlockVolume
}
type Provisioner interface {
// Provision 创建一个 Volume
Provision(selectedNode *v1.Node, allowedTopologies []v1.TopologySelectorTerm) (*v1.PersistentVolume, error)
}
type Deleter interface {
Volume
// Deleter 移除一个 Volume
Delete() error
}
type Attacher interface {
DeviceMounter
// Attach Volume 到指定的 Node 上
Attach(spec *Spec, nodeName types.NodeName) (string, error)
// VolumesAreAttached 查询 Node 上的 attached Volume
VolumesAreAttached(specs []*Spec, nodeName types.NodeName) (map[*Spec]bool, error)
// WaitForAttach 等待 attach 结束
WaitForAttach(spec *Spec, devicePath string, pod *v1.Pod, timeout time.Duration) (string, error)
}
type DeviceMounter interface {
// GetDeviceMountPath 返回 Node 上 Volume 对应的块设备路径
GetDeviceMountPath(spec *Spec) (string, error)
// MountDevice 将 Volume 对应的块设备挂载到一个全局的目录(不提供给 Pod)
MountDevice(spec *Spec, devicePath string, deviceMountPath string, deviceMounterArgs DeviceMounterArgs) error
}
type Detacher interface {
DeviceUnmounter
// Detach Volume 在指定的 Node
Detach(volumeName string, nodeName types.NodeName) error
}
type DeviceUnmounter interface {
// UnmountDevice 取消 Volume 对应块设备的挂载
UnmountDevice(deviceMountPath string) error
}
|
2 Volume Plugin 的管理
当我们有了 VolumePlugin 及相关的 Interface 后,Kubernetes 就需要实现如果管理多个 Volume Plugin 了。
2.1 VolumePluginMgr 类
所有的 VolumePlugin 会注册到 VolumePluginMgr 对象中管理。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
type VolumePluginMgr struct {
mutex sync.RWMutex
plugins map[string]VolumePlugin // 静态注册的 VolumePlugin
prober DynamicPluginProber
probedPlugins map[string]VolumePlugin // probe 探测出的 VolumePlugin
loggedDeprecationWarnings sets.String
Host VolumeHost
}
|
大多数 Controller 需要使用 Volume Plugin 时,就会调用 Find 函数来查找对应的 Plugin。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
|
// FindPluginBySpec 查找能够支持 spec 的 VolumePlugin
func (pm *VolumePluginMgr) FindPluginBySpec(spec *Spec) (VolumePlugin, error) {
pm.mutex.RLock()
defer pm.mutex.RUnlock()
if spec == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("could not find plugin because volume spec is nil")
}
// 调用静态注册的 VolumePlugin.CanSupport() 函数筛选
matches := []VolumePlugin{}
for _, v := range pm.plugins {
if v.CanSupport(spec) {
matches = append(matches, v)
}
}
// 进行一次 Probe Plugin
pm.refreshProbedPlugins()
// 调用动态注册的 VolumePlugin.CanSupport() 函数筛选
for _, plugin := range pm.probedPlugins {
if plugin.CanSupport(spec) {
matches = append(matches, plugin)
}
}
// 没有任何 Volume Plugin 能够处理
if len(matches) == 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("no volume plugin matched")
}
// 多个 Volume Plugin 能够处理
if len(matches) > 1 {
matchedPluginNames := []string{}
for _, plugin := range matches {
matchedPluginNames = append(matchedPluginNames, plugin.GetPluginName())
}
return nil, fmt.Errorf("multiple volume plugins matched: %s", strings.Join(matchedPluginNames, ","))
}
// 返回唯一的 Volume Plugin
// Issue warning if the matched provider is deprecated
pm.logDeprecation(matches[0].GetPluginName())
return matches[0], nil
}
// FindPluginByName 通过 plugin name 查找 Volume Plugin
func (pm *VolumePluginMgr) FindPluginByName(name string) (VolumePlugin, error) {
// ...
}
func (pm *VolumePluginMgr) FindPersistentPluginBySpec(spec *Spec) (PersistentVolumePlugin, error) {
// ...
}
// 其他各个类型的 VolumePlugin ...
|
2.2 如何注册 Volume Plugin
不同类型的 Volume Plugin 有着不同的注册方式:
- In-Tree Plugin 在代码中直接注册到
VolumePluginMgr 中。
- FlexVolume 通过 DynamicPluginProber 动态探测,探测后注册到
VolumePluginMgr 中。
- CSI 是内置了一个 Plugin 实现,用以创建 PVC 与 VolumeAttacment 等资源,靠 Controller 异步的处理。在 Node 上通过 socket 的方式进行动态的注册到 Kubelet 中。
2.2.1 DynamicPluginProber 接口
FlexVolume 是由 DynamicPluginProber 接口进行 Probe 后,以动态方式注册。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
type ProbeEvent struct {
Plugin VolumePlugin // VolumePlugin that was added/updated/removed. if ProbeEvent.Op is 'ProbeRemove', Plugin should be nil
PluginName string
Op ProbeOperation // The operation to the plugin
}
type DynamicPluginProber interface {
Init() error
// If an error occurs, events are undefined.
Probe() (events []ProbeEvent, err error)
}
|
调用 Probe() 会去插件目录查找插件的可执行文件,并创建 flexVolumePlugin 类,flexVolumePlugin 即实现了 VolumePlugin 接口,可以注册到 VolumePluginMgr 中。
插件目录
Probe() 接口查找的目录格式为 <plugindir>/<vendor~driver>/<driver>,<plugindir> 在 Kubelet 由参数 --volume-plugin-dir 指定,在 Controller Manager 由参数 --flex-volume-plugin-dir。
默认为路径 /usr/libexec/kubernetes/kubelet-plugins/volume/exec。
DynamicPluginProber 周期性进行 Probe() 操作,注册新发现的 flexVolumePlugin,移除不存在的 flexVolumePlugin。
当调用 flexVolumePlugin 的操作接口(NewMounter、NewAttacher 等),会转发调用各个可执行文件的命令。例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
$ ./uds
Usage:
flexvoldrv [command]
Available Commands:
help Help about any command
init Flex volume init command.
mount Flex volume unmount command.
unmount Flex volume unmount command.
version Print version
|
2.2.2 CSI Plugin 的注册
见 K8s 实现 - CSI 实现
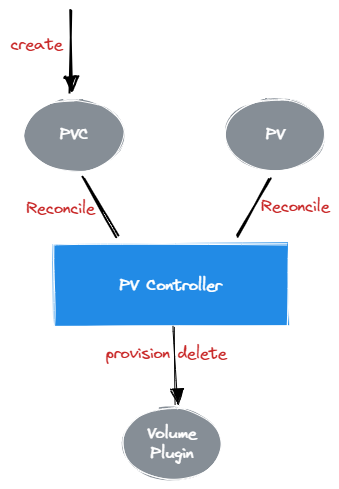
3 PV Controller
PV Controller 主要负责 PV 与 PVC 的绑定,并负责了 PV 的创建与销毁。
PV Controller 就是一个 Controller,监听着 PV 与 PVC 的事件,并对应进行 PV 与 PVC 的协调处理。

3.1 触发逻辑
所有的 Event 会走最终的 Reconcile 函数:
- PV Event:走
syncVolume 处理
- PVC Event:走
syncClaim() 进行处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
func (ctrl *PersistentVolumeController) updateVolume(volume *v1.PersistentVolume) {
// 更新 Store
new, err := ctrl.storeVolumeUpdate(volume)
if err != nil {
}
if !new {
return
}
// 执行 sync
err = ctrl.syncVolume(volume)
if err != nil {
// log
}
}
func (ctrl *PersistentVolumeController) updateClaim(claim *v1.PersistentVolumeClaim) {
// 更新 Store
new, err := ctrl.storeClaimUpdate(claim)
if err != nil {
}
if !new {
return
}
// 执行 sync
err = ctrl.syncClaim(claim)
if err != nil {
// log
}
}
|
3.2 Reconcile PV
Reconcile 主要负责了 PV 的状态更新,以及 PV 的回收。而 PV 创建与绑定相关都是由后续的 PVC 的控制循环处理。
大部分的逻辑都是围绕着 PV 与 PVC 是否绑定,以及 PVC 的状态来判断的。其中,通过 PV.Spec.ClaimRef == nil 判断是否绑定 PVC,通过 PV.Spec.ClaimRef.UID 判断具体绑定到哪个 PVC。
-
ClaimRef == nil
表明 PV 还未绑定 PVC,那么更新 PV Phase 为 Available。
-
ClaimRef != nil && ClaimRef.UID == “"
表明 PV 是为某个 PVC 预留的,那么更新 PV Phase 为 Available,不走尝试绑定 PVC 的逻辑。
-
ClaimRef != nil && ClaimRef.UID != “"
-
PVC Exist
PV 与 PVC 相互绑定,那么更新 PV Phase 为 Bound。
-
PVC not Exist
说明 PVC 已经被删除了,那么更新 PV Phase 为 Released。根据 PV ReclaimPolicy 决定是否执行删除:
- Retain - 不执行任何操作
- Recycle - 调用 Volume Plugin 回收 Volume,并解除 PV 与 PVC 绑定
- Delete - 调用 Volume Plugin 删除 Volume,并删除 PV 对象
-
PVC Bind Miss
这种情况是指 PV 绑定了 PVC,但是对应的 PVC 绑定的并不是该 PV。也就是说,PV 与 PVC 绑定不对称。那么会解除 PV 的绑定,允许情况下还会删除 PV。
具体代码见 Kubernetes 源码 syncVolume 函数。
3.3 Reconcile PVC
Reconcile PVC 负责 PVC 与 PV 的绑定,以及一些情况下根据 StorageClass 创建 PV。
控制逻辑分为了两个分支:
-
PVC.Anno[pv.kubernetes.io/bind-completed] Exist
表明 PVC 已绑定 PV,这时候主要是检查 PV 与 PVC 的绑定关系是否正常
-
PVC.Spec.VolumeName == “"
说明绑定关系丢失了,那么更新 PVC Phase 为 Lost。
-
PVC.Spec.VolumeName != “" && PV not Exist
说明绑定的 PV 不存在,那么更新 PVC Phase 为 Lost。
-
PVC.Spec.VolumeName != “" && PV Exist && PV.Spec.ClaimRef == nil
说明 PV 还未绑定到 PVC,那么执行绑定操作。
-
PVC Bind Miss
这种情况是指 PVC 绑定了 PV,但是对应的 PV 绑定的并不是该 PVC,也就是说,PV 与 PVC 绑定不对称。那么会更新 PVC Phase 为 Lost。
具体代码见 Kubernetes 源码 syncBoundClaim 函数。
-
PVC.Anno[pv.kubernetes.io/bind-completed] not Exist
表明 PVC 还未绑定 PV。
-
PVC.Spec.VolumeName != “"
表示创建 PVC 时就选择了特定需要绑定的 PV,那么执行绑定操作。
-
PVC.Spec.VolumeName == “"
表示也不知道绑定哪个 PV,那么就会尝试寻找一个已有的 PV。
-
PV Founded
已有 PV 可以满足 PVC,那么执行绑定操作。s
-
PV not Founded && PVC.Spec.StorageClassName != “"
无法使用已有的 PV,那么调用 Volume Plugin 接口尝试创建一个 PV。
-
PV not Founded && PVC.Spec.StorageClassName == “"
无法使用已有 PV,也不能自己创建一个,设置 PVC Phase 为 Pending,啥也不做了。
具体代码见 Kubernetes 源码 syncUnboundClaim 函数。
4 AttachDetach Controller
PV Controller 负责了 PV 与 PVC。当 PVC 绑定并被 Pod 使用后,就会由 AttachDetach Controller 负责将其 Attach 到 Node 上。同样,AttachDetach Controller 也负责将 Volume 从 Node 上 Detach。
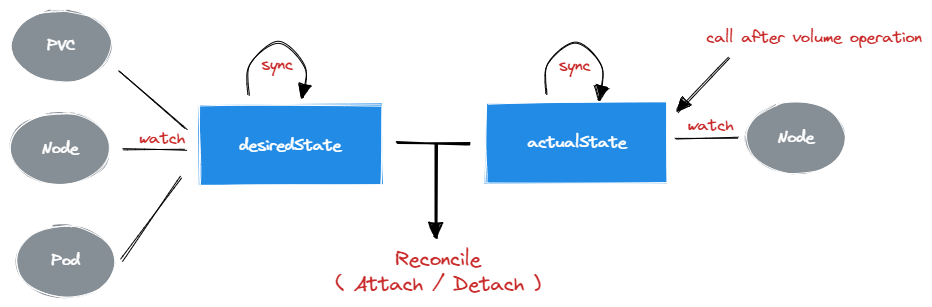
整体 AttachDetach Controller 还是基于 Controller 模式,不过与正常的 Controller 编写方式不同,AttachDetach Controller 围绕着两个 Map 的数据进行 Reconcile:
desiredStateOfWorld - 代表着各个 Volume 的期望状态;actualStateOfWorld - 代表着各个 Volume 的实际状态;

因此,AttachDetach Controller 的核心逻辑可以分为三个部分:
- 根据 PVC 与 Pod 更新
desiredStateOfWorld
- 根据 Node 更新
actualStateOfWorld
- 对比
actualStateOfWorld 与 desiredStateOfWorld 进行 Reconcile
4.1 更新 desiredStateOfWorld
desiredStateOfWorld 记录 Volume 的期望状态,即哪些 Volume 需要 Attach 到哪些 Node。
所有的 Volume 的期望状态来自于 Pod 的 Spec 定义,对应的以下情况会更新 desiredStateOfWorld:
-
Watch PVC 的 Add/Update 事件
对于已经绑定到 PV 的 PVC(Phase == Bound && Spec.VolumeName != “"),找到对应的 Pod ,调用 ProcessPodVolumes()。
-
Watch Node 的 Add/Update/Delete 事件
对于 Delete 事件,删除对应 Node 的记录。
对于 Add/Update 事件,遍历 Node 上所有的 Pod,调用 ProcessPodVolumes()。
-
Watch Pod 的 Add/Update/Delete 事件,以及周期性遍历所有 Pod
根据 Pod 调用 ProcessPodVolumes()。
-
启动时第一次,以及周期性遍历所有 Pod
根据 Pod 调用 ProcessPodVolumes()。
可以看到,大部分都是调用同一个函数 ProcessPodVolumes() 进行处理。该函数参数很简单,提供 Pod 以及对应的行为 (add/delete) 即可。
1
2
3
4
|
func ProcessPodVolumes(pod *v1.Pod, addVolumes bool,
desiredStateOfWorld cache.DesiredStateOfWorld, volumePluginMgr *volume.VolumePluginMgr,
pvcLister corelisters.PersistentVolumeClaimLister, pvLister corelisters.PersistentVolumeLister,
csiMigratedPluginManager csimigration.PluginManager, csiTranslator csimigration.InTreeToCSITranslator)
|
ProcessPodVolumes() 函数会遍历 Pod 的 Spec.Volumes,找到对应的 Volume Spec,更新 desiredStateOfWorld。
具体源码见 Kubernetes 的 ProcessPodVolumes() 函数。
4.2 更新 actualStateOfWorld
actualStateOfWorld 记录 Volume 的当前状态,即 Node 上的 Attached Volume。
状态更新来自于:
大部分处理都会调用函数 processVolumesInUse() 进行处理。该函数参数包括 NodeName 以及 Node.Status.VolumesInUse。
1
2
|
func (adc *attachDetachController) processVolumesInUse(
nodeName types.NodeName, volumesInUse []v1.UniqueVolumeName)
|
函数逻辑也很简单,遍历 Volume 更新 actualStateOfWorld 中状态。
具体见源码中的 processVolumesInUse() 函数 以及 sycn() 函数。
4.3 Reconcile
核心的 Reconcile 中就是围绕着 actualStateOfWorld 与 desiredStateOfWorld 中的状态,进行实际的操作。
-
desiredStateOfWorld[Volume] Exist && actualStateOfWorld[Volume] Unattached
表明 Volume 存在于 desiredStateOfWorld,但是 actualStateOfWorld 中对应的状态为 Unattached。
那么就调用 Volume Plugin 执行 Attach Volume 操作。
-
desiredStateOfWorld[Volume] not Exist && actualStateOfWorld[Volume] Attached
表明 Attached Volume 存在于 actualStateOfWorld,但是不存在于 desiredStateOfWorld。
那么就调用 Volume Plugin 执行 Detach Volume 操作。
具体见源码中的 reconcile() 函数。
5 Kubelet 如何处理 Volume
Provision/Delete 与 Attach/Detach 都是在 Kubernetes 控制面处理,Volume 在 Node 上涉及的 Mount/Unmount 与 SetUp/TearDown 就是由 Kubelet 处理了。
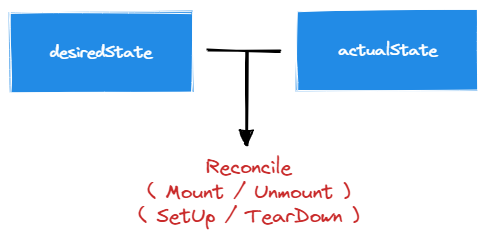
Kubelet 中的实现也是依赖于两个 Map 进行 Reconcile:
desiredStateOfWorld - 代表着各个 Volume 的期望状态;actualStateOfWorld - 代表着各个 Volume 的实际状态;

5.1 Reconcile
Kubelet 中的 Reconcile 就是负责 Volume 的 Mount/Unmount 与 SetUp/TearDown,整体逻辑分为三部分:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
func (rc *reconciler) reconcile() {
// Unmounts are triggered before mounts so that a volume that was
// referenced by a pod that was deleted and is now referenced by another
// pod is unmounted from the first pod before being mounted to the new
// pod.
rc.unmountVolumes()
// Next we mount required volumes. This function could also trigger
// attach if kubelet is responsible for attaching volumes.
// If underlying PVC was resized while in-use then this function also handles volume
// resizing.
rc.mountAttachVolumes()
// Ensure devices that should be detached/unmounted are detached/unmounted.
rc.unmountDetachDevices()
}
|
5.1.1 unmountVolumes
unmountVolumes 函数中执行 TearDown Volume 参数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
func (rc *reconciler) unmountVolumes() {
// 遍历当前节点所有的 mounted volume
for _, mountedVolume := range rc.actualStateOfWorld.GetAllMountedVolumes() {
// 检查该 volume 与 pod 是否存在于 desiredStateOfWorld
if !rc.desiredStateOfWorld.PodExistsInVolume(mountedVolume.PodName, mountedVolume.VolumeName) {
// 进行 unmount volume 操作(底层调用的是 VolumePlugin.TearDown)
err := rc.operationExecutor.UnmountVolume(
mountedVolume.MountedVolume, rc.actualStateOfWorld, rc.kubeletPodsDir)
if err != nil &&
!nestedpendingoperations.IsAlreadyExists(err) &&
!exponentialbackoff.IsExponentialBackoff(err) {
// Ignore nestedpendingoperations.IsAlreadyExists and exponentialbackoff.IsExponentialBackoff errors, they are expected.
// Log all other errors.
klog.ErrorS(err, mountedVolume.GenerateErrorDetailed(fmt.Sprintf("operationExecutor.UnmountVolume failed (controllerAttachDetachEnabled %v)", rc.controllerAttachDetachEnabled), err).Error())
}
if err == nil {
klog.InfoS(mountedVolume.GenerateMsgDetailed("operationExecutor.UnmountVolume started", ""))
}
}
}
}
|
5.1.2 mountAttachVolumes
mountAttachVolumes 函数中负责执行 Mount 与 SetUp/MountDevice 操作。
-
desiredStateOfWorld[Volume] Exist && actualStateOfWorld[Volume] Unattached
表明 Volume 还未被 Mount,那么调用 Volume Plugin 的 Mount 操作。
-
desiredStateOfWorld[Volume] Exist && actualStateOfWorld[Volume] Unmounted
表明 Volume 还未被 Setup,那么调用 Volume Plugin 的 SetUp 操作。
具体见源码中的 mountAttachVolumes 函数。
5.1.3 unmountDetachDevices
unmountDetachDevices 函数中负责执行 Unmount Volume 操作解除全局目录挂载。另外,允许情况下还可能执行 Detach Volume 操作。
具体见源码中的 unmountDetachDevices 函数。
总结
围绕着 Kubernetes - 存储设计 所提到的 Volume 操作,对应的实现为:
参考