1 概述
Kubernetes Scheduler 负责了 Schedule + Eviction + Preemption 三个功能。Scheduler 本质上也是一个 Controller,监听着 Pod 和 Node 等资源,出现事件时尝试执行调度操作。
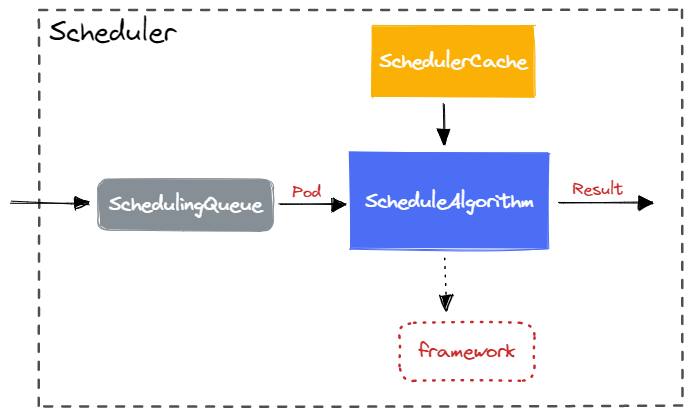
目前,Scheduler 的架构如下:

- SchedulingQueue 保存需要等待调度的 Pod;
- SchedulerCache 是对 Pod 以及 Node 信息的本地缓存;
- ScheduleAlgorithm 抽象了 Schedule() 算法接口,为 Pod 选择一个合适的 Node;
- Framework 是用于扩展 ScheduleAlgorithm 的抽象;
2 SchedulingQueue
SchedulingQueue 用于暂存 Unscheduled Pods,Scheduler 会每次从 SchedulingQueue 中获取一个 Pod 进行调度。
2.1 队列实现
SchedulingQueue 通过三种队列实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
type PriorityQueue struct {
// activeQ is heap structure that scheduler actively looks at to find pods to
// schedule. Head of heap is the highest priority pod.
activeQ *heap.Heap
// podBackoffQ is a heap ordered by backoff expiry. Pods which have completed backoff
// are popped from this heap before the scheduler looks at activeQ
podBackoffQ *heap.Heap
// unschedulableQ holds pods that have been tried and determined unschedulable.
unschedulableQ *UnschedulablePodsMap
// ...
}
|
- ActiveQueue 保存所有等待调度的 Pod;
- UnscheduledQueue 保存当前不可调度的 Pod 但稍后会尝试重调度的 Pod;
- PodBackoffQueue 保存多次调度失败的 Pod,等候后续重试的 Pod;
2.1.1 ActiveQueue
ActiveQueue 存储所有等待调度的 Pod,基于 Heap 实现。每次取出优先级最高的 Pod。
Pod 之间的比较函数使用 Framework 函数 QueueSortFunc() 返回 QueueSort 插件的 Less() 函数,默认使用 Priority + AddTimestamp 进行排序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
type QueueSortPlugin interface {
Plugin
Less(*QueuedPodInfo, *QueuedPodInfo) bool
}
// 默认的 PrioritySort 插件
type PrioritySort struct{}
func (pl *PrioritySort) Less(pInfo1, pInfo2 *framework.QueuedPodInfo) bool {
// 优先使用 Priority 排序,如果相等使用 AddTimestamp 排序
p1 := corev1helpers.PodPriority(pInfo1.Pod)
p2 := corev1helpers.PodPriority(pInfo2.Pod)
return (p1 > p2) || (p1 == p2 && pInfo1.Timestamp.Before(pInfo2.Timestamp))
}
|
2.1.2 PodBackoffQueue
PodBackoffQueue 存储多次调度失败的 Pod,也是基于 Heap 实现。每次取出 Backoff 时间最小的 Pod。Pod 比较函数如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
func (p *PriorityQueue) podsCompareBackoffCompleted(podInfo1, podInfo2 interface{}) bool {
pInfo1 := podInfo1.(*framework.QueuedPodInfo)
pInfo2 := podInfo2.(*framework.QueuedPodInfo)
bo1 := p.getBackoffTime(pInfo1)
bo2 := p.getBackoffTime(pInfo2)
return bo1.Before(bo2)
}
|
每个 Pod Backoff 时间基于调度次数增长:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
func (p *PriorityQueue) getBackoffTime(podInfo *framework.QueuedPodInfo) time.Time {
duration := p.calculateBackoffDuration(podInfo)
backoffTime := podInfo.Timestamp.Add(duration)
return backoffTime
}
func (p *PriorityQueue) calculateBackoffDuration(podInfo *framework.QueuedPodInfo) time.Duration {
duration := p.podInitialBackoffDuration
for i := 1; i < podInfo.Attempts; i++ {
// Use subtraction instead of addition or multiplication to avoid overflow.
if duration > p.podMaxBackoffDuration-duration {
return p.podMaxBackoffDuration
}
duration += duration
}
return duration
}
|
2.1.3 UnscheduledQueue
UnscheduledQueue 存储暂时调度失败的 Pod。因为暂时调度失败每个 Pod 时刻都有可能变为可调度,因此使用 Map 而不是 Heap 实现。
2.2 Pod 流转
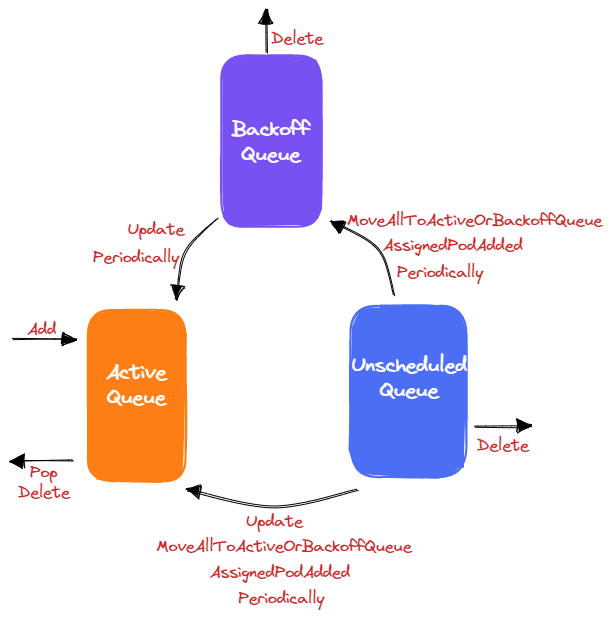
SchedulingQueue 提供队列操作接口,使得每个 Pod 会在三个队列中流转:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
type SchedulingQueue interface {
Add(pod *v1.Pod) error
Activate(pods map[string]*v1.Pod)
AddUnschedulableIfNotPresent(pod *framework.QueuedPodInfo, podSchedulingCycle int64) error
Pop() (*framework.QueuedPodInfo, error)
Update(oldPod, newPod *v1.Pod) error
Delete(pod *v1.Pod) error
MoveAllToActiveOrBackoffQueue(event framework.ClusterEvent, preCheck PreEnqueueCheck)
AssignedPodAdded(pod *v1.Pod)
AssignedPodUpdated(pod *v1.Pod)
// ...
}
|
-
Add - 将新的 Pod 添加到 ActiveQueue。
-
Activate - 将已入对的 Pod 添加到 ActiveQueue,从 UnscheduledQueue 与 PodBackoffQueue 中移除。
-
AddUnschedulableIfNotPresent - 将调度失败的 Pod 添加到 UnscheduledQueue 与 PodBackoffQueue(前提 Pod 不存在任何 Queue)。
如果集群资源最近变动过,那么表明 Pod 有可能可以重新调度成功,那么会将 Pod 加入 PodBackoffQueue。否则,Pod 加入 UnscheduledQueue,等待低频率的重试。
-
Pop - 阻塞等待从 ActiveQueue 中返回优先级最高的 Pod,不会操作 UnscheduledQueue 与 PodBackoffQueue。
-
Update - 更新 Pod 信息。由于 Pod 有更新,可能可以重新调度成功。因此,会从 UnscheduledQueue 与 PodBackoffQueue 中移除 Pod,添加到 ActiveQueue。
-
Delete - 从三个队列中删除 Pod。
-
MoveAllToActiveOrBackoffQueue - 将 UnscheduledQueue 中的所有 Pod 移动到 ActiveQueue 和 PodBackoffQueue。如果 Pod 已经大于 Backoff 时间,那么就会放到 ActiveQueue,否则放在 PodBackoffQueue 等待重试。
-
AssignedPodAdded 与 AssignedPodUpdated - 在某个 Pod 绑定 Node 后,由于 Affinity 调度机制的存在,将依赖该 Pod 的其他 Pod 从 UnscheduledQueue 中移动到 ActiveQueue 与 PodBackoffQueue。
除了 SchedulingQueue 提供的接口可以移动 Pod 外,SchedulingQueue 会运行两个协程周期性的移动 Pod:
- 周期性遍历 PodBackoffQueue,将到达 Backoff 时间的 Pod 移动到 ActiveQueue;
- 周期性遍历 UnscheduledQueue,将长时间未调度的 Pod 移动到 ActiveQueue 与 PodBackoffQueue;
整体的流程方式如下图。可以看到,除了 Delete 外,普通的队列功能 Add 与 Pop 都是操作的 ActiveQueue,而 PodBackoffQueue 与 UnscheduledQueue 是用于将 Pod 按照可调度可能性进行分类存储。

Why
这种方式类似于数据的 “冷热” 分离存储,使得能够更快的获取出被调度可能性更高的 Pod。
至于 Scheduler 如何调用 SchedulingQueue 接口的,后续再说明。
3 SchedulerCache
SchedulerCache 为 Scheduler 的本地 Pod/Node 信息的缓存数据库。为 Scheduler 提供 Node 信息,并提供了绑定 Pod 与 Node 的方法。
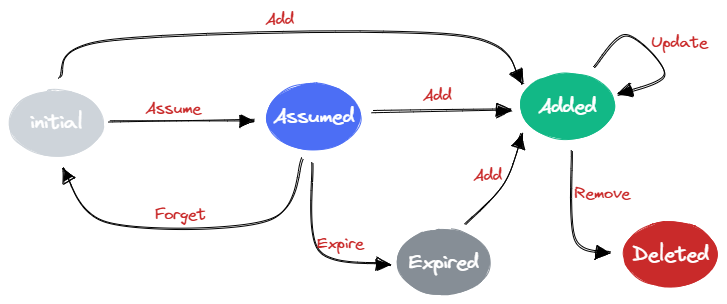
3.1 Pod State
Cache 中的 Pod 有着一个内部的状态机,状态如下:

- Initial - (不存在 cache 中)刚刚创建的新 Pod
- Assumed - 在 Scheduler 本地调度后分配了 Node 的 Pod
- Added - 完成实际 Node 绑定 Pod
- Deleted -(不存在 cache 中)被删除的 Pod
- Expired -(不存在 cache 中)Assumed Pod 超时后还未完成实际 Node 绑定的 Pod
可以看到,Cache 中保存的都是 Assumed Pod 与 Added Pod。因此,Cache 中只会保存即将绑定或者已经绑定 Node 的 Pod。
为什么需要 Assumed 状态
因为可能多个 Scheduler 的存在,绑定 Pod 与 Node 需要经过二次确认。Assume 相当于预绑定,占据了 Node 的资源。但是当 Bind 操作失败后,就会释放。
3.2 Cache 实现
Cache interface 如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
type Cache interface {
// AssumePod 假定 Pod 调度到某个 Node 上
AssumePod(pod *v1.Pod) error
// FinishBinding 表示 Assumed Pod 能够变为 Expired
// 表示 Bind 操作已经执行
FinishBinding(pod *v1.Pod) error
// ForgetPod 移除一个 Assumed Pod
ForgetPod(pod *v1.Pod) error
// AddPod 添加一个 Pod 到 Cache 中
AddPod(pod *v1.Pod) error
// UpdatePod 更新 Pod 信息
UpdatePod(oldPod, newPod *v1.Pod) error
// Remove 移除一个 Node
RemovePod(pod *v1.Pod) error
// GetPod
GetPod(pod *v1.Pod) (*v1.Pod, error)
// IsAssumedPod 判断 Assumed Pod
IsAssumedPod(pod *v1.Pod) (bool, error)
// AddNode 添加一个 Node 信息
AddNode(node *v1.Node) *framework.NodeInfo
// UpdateNode 更新 Node 信息
UpdateNode(oldNode, newNode *v1.Node) *framework.NodeInfo
// RemoveNode 移除一个 Node 信息
RemoveNode(node *v1.Node) error
// UpdateSnapshot 根据 Snapshot 更新 Cache
UpdateSnapshot(nodeSnapshot *Snapshot) error
}
|
对应的 Implement 如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
type cacheImpl struct {
// 存储 Assumed Pod 集合
assumedPods sets.String
// 所有 Pod 的状态
podStates map[string]*podState
// 所有 Node 的信息
nodes map[string]*nodeInfoListItem
// ...
}
|
可以看到主要的 Node 数据集合分为了(其他属性可能为改数据集合的不同数据形态):
- Assumed Pods - 单独记录 Assumed Pod,也包括完成 Node 调度的 Pod
- All Pods - 所有 Assumed Pod 以及 Added Pod 的具体信息
- All Nodes - 所有 Node 的信息
3.3 Pod State 流转
-
Initial -> Added
Scheduler 接收到 Pod Add Event 后,Pod 已经被调度了,因此加入 Cache 时就是 Added 状态。
-
Initial -> Assumed
Scheduler 经过调度算法将 Pod 调度到一个 Node,因此更新 Cache 中的 Pod 状态为 Assumed。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
func (sched *Scheduler) schedulingCycle(/*...*/) (ScheduleResult, *framework.QueuedPodInfo, error) {
pod := podInfo.Pod
scheduleResult, err := sched.SchedulePod(ctx, fwk, state, pod)
// ...
err = sched.assume(assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
// ...
return scheduleResult, assumedPodInfo, nil
}
func (sched *Scheduler) assume(assumed *v1.Pod, host string) error {
assumed.Spec.NodeName = host
if err := sched.Cache.AssumePod(assumed); err != nil {
return err
}
// ...
return nil
}
|
-
Assumed -> Added
当调度过程中 Bind Plugin 执行 Bind 成功后,就表明 Pod 完成 Node 绑定,那么 Assumed 就变为了 Added。不过,这个状态并不会体现在 Cache 中。
-
Assumed -> Initial
当调度过程中 Bind Plugin 执行 Bind 失败后,Scheduler 会立即调用 Cache.ForgetPod() 将 Cache 中移除。也就表明 Pod 状态从 Assumed 变为了 Initial,等待后续重新调度。
-
Assumed -> Expire
当调度过程中 Bind Plugin 执行 Bind 后,Scheduler 就会调用 Cache.FinishBinding() 设置 Pod 的 Deadline,表明 Pod 开始计算超时。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
func (sched *Scheduler) bind(ctx context.Context, fwk framework.Framework, assumed *v1.Pod, targetNode string, state *framework.CycleState) (status *framework.Status) {
defer func() {
sched.finishBinding(fwk, assumed, targetNode, status)
}()
bound, err := sched.extendersBinding(assumed, targetNode)
if bound {
return framework.AsStatus(err)
}
return fwk.RunBindPlugins(ctx, state, assumed, targetNode)
}
|
当执行完 Bind 操作后,一直未收到 Pod 的 Update 事件,那么该 Pod 的 Deadline 就一直存在。
Scheduler 会周期性清理过期的 Pod,将其从 Cache 中移除。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
func (cache *cacheImpl) cleanupAssumedPods(now time.Time) {
for key := range cache.assumedPods {
ps, ok := cache.podStates[key]
// ...
if cache.ttl != 0 && now.After(*ps.deadline) {
cache.removePod(ps.pod)
}
}
}
|
-
Added -> Added
当调度过程中 Bind Plugin 执行 Bind 成功后,会修改 Pod.Spec.NodeName 字段,因此 Scheduler 会收到 Pod 的 Update 事件。
Scheduler 收到 Pod 的 Update 事件后,就会调用 Cache.UpdatePod() 更新 Pod 信息。也就是此时,会清空的 Pod Deadline,使其不被超时清理。
-
Expired -> Added
超时被清理的 Pod 又被重新加入 Cache。
-
Added -> Deleted
Scheduler 会 Watch Pod 的 Delete 事件,收到后就会调用 Cache.RemovePod() 将从 Cache 中删除,表示变为 Deleted 状态。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
func addAllEventHandlers(/*...*/) {
informerFactory.Core().V1().Pods().Informer().AddEventHandler(
cache.FilteringResourceEventHandler{
// ...
Handler: cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: sched.addPodToCache,
UpdateFunc: sched.updatePodInCache,
DeleteFunc: sched.deletePodFromCache,
},
},
)
// ...
}
func (sched *Scheduler) deletePodFromCache(obj interface{}) {
// ...
if err := sched.Cache.RemovePod(pod); err != nil {
klog.ErrorS(err, "Scheduler cache RemovePod failed", "pod", klog.KObj(pod))
}
}
|
4 ScheduleAlgorithm
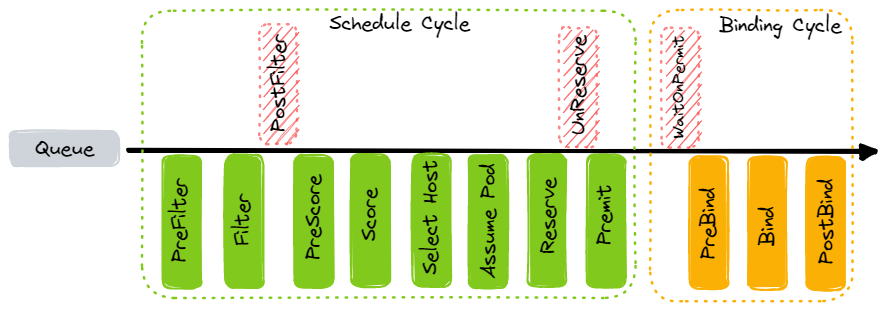
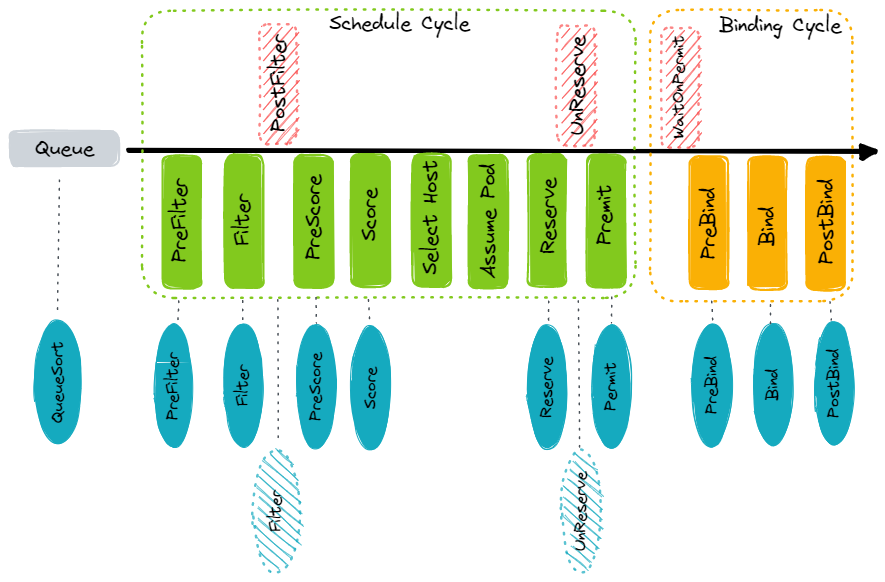
目前 Schedule 的大致流程如下:

大体上分为两个 Cycle:
- Schedule Cycle - 为 Pod 调度出一个最合适的 Node
- Binding Cycle - 将 Pod 绑定到调度的 Node
为了实现灵活的扩展性,每个 Cycle 会细分为多个子步骤,而这些步骤就是 Schedule Framework 的扩展点。
4.1 PreFilter
PreFilter 阶段为 Filter 阶段各个 Plugin 做检查与准备操作。例如,Plugin 可以在 PreFilter 阶段构建出 Filter 阶段需要使用的上下文。
Scheduler 会调用 Framework.RunPreFilterPlugins() 执行 PreFilter,Framework 会运行所有注册的 PreFilterPlugin。如果遇到任意 Plugin 返回错误,那么整个调度流程会终止
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
func (sched *Scheduler) findNodesThatFitPod(/*...*/) ([]*v1.Node, framework.Diagnosis, error) {
preRes, s := fwk.RunPreFilterPlugins(ctx, state, pod)
if !s.IsSuccess() {
if !s.IsUnschedulable() {
return nil, diagnosis, s.AsError()
}
return nil, diagnosis, nil
}
// ...
}
|
4.2 Filter
Filter 阶段过滤不符合 Pod 调度要求的 Node,保留合适的 Node。
Scheduler 先会并发对每个 Node 调用 Framework.RunFilterPluginsWithNominatedPods(),每个 Node 会经过所有 FilterPlugin 来检查是否符合调度要求。如果任意 Plugin 返回错误,那么整个调度流程会终止。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
func (sched *Scheduler) findNodesThatPassFilters(/*...*/) ([]*v1.Node, error) {
// ...
checkNode := func(i int) {
// We check the nodes starting from where we left off in the previous scheduling cycle,
// this is to make sure all nodes have the same chance of being examined across pods.
nodeInfo := nodes[(sched.nextStartNodeIndex+i)%numAllNodes]
status := fwk.RunFilterPluginsWithNominatedPods(ctx, state, pod, nodeInfo)
// ...
}
fwk.Parallelizer().Until(ctx, numAllNodes, checkNode, frameworkruntime.Filter)
// ...
return feasibleNodes, nil
}
|
经过 FilterPlugin 筛选后,Scheduler 会调用所有 Scheduler Extender 过滤所有的 Node。所有的 Extender 会顺序执行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
func findNodesThatPassExtenders(/*...*/) ([]*v1.Node, error) {
for _, extender := range extenders {
if !extender.IsInterested(pod) {
continue
}
feasibleList, failedMap, failedAndUnresolvableMap, err := extender.Filter(pod, feasibleNodes)
// ...
feasibleNodes = feasibleList
}
return feasibleNodes, nil
}
|
Filter 阶段完成后,如果没有任何可用的 Node,那么直接返回错误。如果只有一个可用的 Node,那么直接返回调度结果,不需要经过 Score 阶段。
4.3 PostFilter
PostFilter 阶段比较特殊,正常调度流程不会执行 PostFilter,只有在 Filter 阶段后没有任何可用的 Node 时才会执行。
Scheduler 会调用 Framework.RunPostFilterPlugins(),Framework 会运行所有注册的 PostFilterPlugin。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
func (sched *Scheduler) schedulingCycle(/*...*/) (ScheduleResult, *framework.QueuedPodInfo, error) {
scheduleResult, err := sched.SchedulePod(ctx, fwk, state, pod)
if err != nil {
if fitError, ok := err.(*framework.FitError); ok {
if !fwk.HasPostFilterPlugins() {
klog.V(3).InfoS("No PostFilter plugins are registered, so no preemption will be performed")
} else {
// Run PostFilter plugins to try to make the pod schedulable in a future scheduling cycle.
result, status := fwk.RunPostFilterPlugins(ctx, state, pod, fitError.Diagnosis.NodeToStatusMap)
}
}
}
// ...
}
|
4.4 PreScore
PreScore 阶段为为 Score 阶段各个 Plugin 做检查和准备操作。例如,Plugin 可以在 PreScore 阶段构建出 Score 阶段需要使用的上下文。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
func prioritizeNodes(/*...*/) (framework.NodeScoreList, error) {
preScoreStatus := fwk.RunPreScorePlugins(ctx, state, pod, nodes)
if !preScoreStatus.IsSuccess() {
return nil, preScoreStatus.AsError()
}
// ...
}
|
4.5 Score
Score 阶段为各个 Node 进行打分,Scheduler 会调用 Framework.RunScorePlugins() 接口。Framework 会调用所有 Plugin 的 Score 与 NormalizeScore 接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
func prioritizeNodes(/*...*/) (framework.NodeScoreList, error) {
// ...
nodesScores, scoreStatus := fwk.RunScorePlugins(ctx, state, pod, nodes)
if !scoreStatus.IsSuccess() {
return nil, scoreStatus.AsError()
}
// ...
}
|
所有 ScorePlugin 打分后,会调用并行调用 Scheduler Extender 对 Node 进行打分。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
func prioritizeNodes(/*...*/) (framework.NodeScoreList, error) {
// ...
if len(extenders) != 0 && nodes != nil {
for i := range extenders {
if !extenders[i].IsInterested(pod) {
continue
}
wg.Add(1)
go func(extIndex int) {
prioritizedList, weight, err := extenders[extIndex].Prioritize(pod, nodes)
if err != nil {
return
}
// record resule
}(i)
}
wg.Wait()
}
// ...
}
|
Plugin 和 Extender 打的分会按照设置的权重累加,得到最后每个 Node 的分数。
4.6 Select Host
对所有可用的 Node 完成打分后,Select Host 挑选出分数最高的 Node。如果有多个同分的 Node,则随机选择一个 Node。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
func selectHost(nodeScoreList framework.NodeScoreList) (string, error) {
maxScore := nodeScoreList[0].Score
selected := nodeScoreList[0].Name
cntOfMaxScore := 1
for _, ns := range nodeScoreList[1:] {
if ns.Score > maxScore {
maxScore = ns.Score
selected = ns.Name
cntOfMaxScore = 1
} else if ns.Score == maxScore {
cntOfMaxScore++
if rand.Intn(cntOfMaxScore) == 0 {
// Replace the candidate with probability of 1/cntOfMaxScore
selected = ns.Name
}
}
}
return selected, nil
}
|
4.7 Assume Pod
Assume 将 Pod 与最终的 Node 预绑定,也就是调用 Cache.AssumePod() 接口。
最终绑定操作将会在 Bind 阶段执行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
func (sched *Scheduler) assume(assumed *v1.Pod, host string) error {
// Optimistically assume that the binding will succeed and send it to apiserver
// in the background.
// If the binding fails, scheduler will release resources allocated to assumed pod
// immediately.
assumed.Spec.NodeName = host
if err := sched.Cache.AssumePod(assumed); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
|
4.8 Reserve
在 Scheduler 本地通过 Assume 预绑定 Pod 和 Node 后,Reserve 阶段让对应的 Node 为 Pod 预留资源。
Reserve 调用的时机为 Assume 之后与 Bind 之前。目的是避免在等待 Bind 操作前,有新的 Pod 调度到该 Node 上,导致 Assumed Pod 无法成功地被调度。
Scheduler 会调用 Framework.RunReservePluginsReserve() 接口,顺序运行所有 ReservePlugin。如果操作失败,会调用 Framework.RunReservePluginsUnreserve() 接口释放预占用的资源。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
func (sched *Scheduler) schedulingCycle(/*...*/) (ScheduleResult, *framework.QueuedPodInfo, error) {
// ...
if sts := fwk.RunReservePluginsReserve(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost); !sts.IsSuccess() {
// trigger un-reserve to clean up state associated with the reserved Pod
fwk.RunReservePluginsUnreserve(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
}
// ...
}
|
4.9 Permit
Permit 阶段是在调度最后阻止或延迟绑定 Node。
Scheduler 会调用 Framework.RunPermitPlugins() 接口,顺序运行所有 PermitPlugin。如果操作失败,会调用 Framework.RunReservePluginsUnreserve() 接口释放预占用的资源。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
func (sched *Scheduler) schedulingCycle(/*...*/) (ScheduleResult, *framework.QueuedPodInfo, error) {
// ...
runPermitStatus := fwk.RunPermitPlugins(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
if !runPermitStatus.IsWait() && !runPermitStatus.IsSuccess() {
// trigger un-reserve to clean up state associated with the reserved Pod
fwk.RunReservePluginsUnreserve(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
}
// ...
}
|
4.10 WaitOnPermit
WaitOnPermit 在 Bind 操作开始前执行,如果 Permit 阶段结果为 Pod 绑定需要 Wait,那么 WaitOnPermit 会阻塞等待,直到 PermitPlugin 改变结果为 Allowed 或 Reject。
Scheduler 会调用 Framework.WaitOnPermit() 接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
func (sched *Scheduler) bindingCycle(/*...*/) *framework.Status {
if status := fwk.WaitOnPermit(ctx, assumedPod); !status.IsSuccess() {
return status
}
// ...
}
|
4.11 PreBind
PreBind 阶段在执行 Bind 操作前做一些准备工作。例如,PreBindPlugin 可以创建网络存储,并将其 Attach 到 Node 上。
Scheduler 会调用 Framework.RunPreBindPlugins() 接口,顺序运行所有的 PreBindPlugin。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
func (sched *Scheduler) bindingCycle(/*...*/) *framework.Status {
if status := fwk.RunPreBindPlugins(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost); !status.IsSuccess() {
return status
}
// ...
}
|
4.12 Bind
Bind 阶段完成实际的 Pod 与 Node 绑定操作。
Scheduler 会先调用 Scheduler Extender 进行 Bind。
接着,Scheduler 会调用 Framework.RunBindPlugins() 接口,顺序运行所有的 BindPlugin。默认下只有一个 BindPlugin,做的操作就是更新 APIServer 中的 Pod。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
func (sched *Scheduler) bind(/*...*/) (status *framework.Status) {
bound, err := sched.extendersBinding(assumed, targetNode)
if bound {
return framework.AsStatus(err)
}
return fwk.RunBindPlugins(ctx, state, assumed, targetNode)
}
|
4.13 PostBind
PostBind 阶段在 Bind 成功后调用,常常用于清理一些资源。
Scheduler 会调用 Framework.RunPostBindPlugins() 接口,顺序运行所有的 PostBindPlugin。
1
2
3
4
|
func (sched *Scheduler) bindingCycle(/*...*/) *framework.Status {
// ...
fwk.RunPostBindPlugins(ctx, state, assumedPod, scheduleResult.SuggestedHost)
}
|
5 Framework
Framework 是 Scheduler 提供的调度框架,在调度过程中的各个阶段中提供了一系列的扩展点,支持用户以 Plugin 的方式进行扩展。
在 ScheduleAlgorithm 可以看到,调度过程中调用了一系列的 Framework 的接口,而 Framework 会调用各个 Plugin 的接口。

可以看到,基本调度的各个阶段都有着对应的扩展点。
5.1 Framework 实现
如 ScheduleAlgorithm 中各个步骤看到,Framework 提供了 Scheduler 各个步骤的操作实现。
对于每个具体的操作,实际上 Framework 就是并行或者串行调用各个注册的 Plugin。举个例子,RunFilterPlugins 会串行运行所有的 FilterPlugin:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
func (f *frameworkImpl) RunFilterPlugins(/*...*/) framework.PluginToStatus {
statuses := make(framework.PluginToStatus)
for _, pl := range f.filterPlugins {
pluginStatus := f.runFilterPlugin(ctx, pl, state, pod, nodeInfo)
if !pluginStatus.IsSuccess() {
if !pluginStatus.IsUnschedulable() {
return map[string]*framework.Status{pl.Name(): errStatus}
}
pluginStatus.SetFailedPlugin(pl.Name())
statuses[pl.Name()] = pluginStatus
}
}
return statuses
}
func (f *frameworkImpl) runFilterPlugin(ctx context.Context, pl framework.FilterPlugin, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo) *framework.Status {
status := pl.Filter(ctx, state, pod, nodeInfo)
return status
}
|
5.2 Registry
Framework 中 Plugin 的注册使用的 Registry 模式,Registry 中的每个 PluginFactory 是每个 Plugin 的构造函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
type Registry map[string]PluginFactory
type PluginFactory = func(configuration runtime.Object, f framework.Handle) (framework.Plugin, error)
func NewInTreeRegistry() runtime.Registry {
fts := plfeature.Features{/**/}
return runtime.Registry{
selectorspread.Name: selectorspread.New,
imagelocality.Name: imagelocality.New,
tainttoleration.Name: tainttoleration.New,
nodename.Name: nodename.New,
nodeports.Name: nodeports.New,
nodeaffinity.Name: nodeaffinity.New,
podtopologyspread.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, podtopologyspread.New),
nodeunschedulable.Name: nodeunschedulable.New,
noderesources.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, noderesources.NewFit),
noderesources.BalancedAllocationName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, noderesources.NewBalancedAllocation),
volumebinding.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, volumebinding.New),
volumerestrictions.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, volumerestrictions.New),
volumezone.Name: volumezone.New,
nodevolumelimits.CSIName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, nodevolumelimits.NewCSI),
nodevolumelimits.EBSName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, nodevolumelimits.NewEBS),
nodevolumelimits.GCEPDName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, nodevolumelimits.NewGCEPD),
nodevolumelimits.AzureDiskName: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, nodevolumelimits.NewAzureDisk),
interpodaffinity.Name: interpodaffinity.New,
queuesort.Name: queuesort.New,
defaultbinder.Name: defaultbinder.New,
defaultpreemption.Name: runtime.FactoryAdapter(fts, defaultpreemption.New),
}
}
|
各个 Plugin 可以通过构造函数中的参数 framework.Handle 来共享 Informer。
5.3 Plugin 实现
各个 Plugin 的接口实现参考 Scheduler Framework 扩展点。
下面给出一些 Plugin 的一个实现作为示例。
5.3.1 QueueSortPlugin
QueueSortPlugin 用于影响 ScheduleQueue 的排序。Scheduler 中只能存在一个 QueueSortPlugin。
Scheduler 默认使用的是内置基于 Pod Priority 实现的 Plugin。也就是说,Priority 高的 Pod 会优先被调度。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
type PrioritySort struct{}
func (pl *PrioritySort) Less(pInfo1, pInfo2 *framework.QueuedPodInfo) bool {
p1 := corev1helpers.PodPriority(pInfo1.Pod)
p2 := corev1helpers.PodPriority(pInfo2.Pod)
return (p1 > p2) || (p1 == p2 && pInfo1.Timestamp.Before(pInfo2.Timestamp))
}
|
5.3.2 PreFilterPlugin
PreFilterPlugin 常用于为 FilterPlugin 做一些准备。例如,InterPodAffinity 会在 PreFilter 阶段统计好各个 Pod 的拓扑,从而在 Filter 步骤时使用拓扑来计算 Pod Affinity。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
type InterPodAffinity struct {}
func (pl *InterPodAffinity) PreFilter(ctx context.Context, cycleState *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod) (*framework.PreFilterResult, *framework.Status) {
var allNodes []*framework.NodeInfo
var nodesWithRequiredAntiAffinityPods []*framework.NodeInfo
var err error
if allNodes, err = pl.sharedLister.NodeInfos().List(); err != nil {
return nil, framework.AsStatus(fmt.Errorf("failed to list NodeInfos: %w", err))
}
if nodesWithRequiredAntiAffinityPods, err = pl.sharedLister.NodeInfos().HavePodsWithRequiredAntiAffinityList(); err != nil {
return nil, framework.AsStatus(fmt.Errorf("failed to list NodeInfos with pods with affinity: %w", err))
}
s := &preFilterState{}
// ...
cycleState.Write(preFilterStateKey, s)
return nil, nil
}
|
5.3.3 FilterPlugin
FilterPlugin 就是判断一个 Node 是否合适一个 Pod 了。例如,Fit 基于 Node Resource 判断是否满足 Pod 需求。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
type Fit struct {
// ...
}
func (f *Fit) Filter(ctx context.Context, cycleState *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeInfo *framework.NodeInfo) *framework.Status {
s, err := getPreFilterState(cycleState)
if err != nil {
return framework.AsStatus(err)
}
insufficientResources := fitsRequest(s, nodeInfo, f.ignoredResources, f.ignoredResourceGroups)
if len(insufficientResources) != 0 {
// We will keep all failure reasons.
failureReasons := make([]string, 0, len(insufficientResources))
for i := range insufficientResources {
failureReasons = append(failureReasons, insufficientResources[i].Reason)
}
return framework.NewStatus(framework.Unschedulable, failureReasons...)
}
return nil
}
|
5.3.4 PostFilterPlugin
PostFilter 只在没有为 Pod 找到合适的 Node 才会运行。典型的例子是 DefaultPreemption 使用 PostFilter 实现抢占流程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
type DefaultPreemption struct {
// ...
}
func (pl *DefaultPreemption) PostFilter(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, m framework.NodeToStatusMap) (*framework.PostFilterResult, *framework.Status) {
pe := preemption.Evaluator{
PluginName: names.DefaultPreemption,
Handler: pl.fh,
PodLister: pl.podLister,
PdbLister: pl.pdbLister,
State: state,
Interface: pl,
}
result, status := pe.Preempt(ctx, pod, m)
if status.Message() != "" {
return result, framework.NewStatus(status.Code(), "preemption: "+status.Message())
}
return result, status
}
|
5.3.5 ScorePlugin
ScorePlugin 为一个 Node 打分,需要实现 Score() 与 NormalizeScore() 两个接口。Score() 是仅仅对一个 Node 进行打分,不会考虑所有 Node 的打分情况。NormalizeScore() 就是提供了所有 Node 的打分情况,来进一步规范每个 Node 的分数。
NormalizeScore() 通常是按照 Score() 得出的分数按比例分配各个 Node 的分数。例如,Score() 得出三个 Node 分数为 2:1:1,Plugin 允许的最大分数是 100,那么三个 Node 经过 NormalizeScore() 会按照 2:1:1 的比例分配 100 分,所以最终分数为 50:25:25。
TaintToleration 会在 Score() 阶段基于无法容忍的 Taint 给 Node 打分,有多少个无法容忍的 Taint 就几分。在 NormalizeScore() 时就会按比例规范所有 Node 的分数,越少 Taint 的 Node 会得到越高的分数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
func (pl *TaintToleration) Score(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, nodeName string) (int64, *framework.Status) {
s, err := getPreScoreState(state)
if err != nil {
return 0, framework.AsStatus(err)
}
score := int64(countIntolerableTaintsPreferNoSchedule(node.Spec.Taints, s.tolerationsPreferNoSchedule))
return score, nil
}
func (pl *TaintToleration) NormalizeScore(ctx context.Context, _ *framework.CycleState, pod *v1.Pod, scores framework.NodeScoreList) *framework.Status {
return helper.DefaultNormalizeScore(framework.MaxNodeScore, true, scores)
}
|
5.3.6 BindPlugin
BindPlugin 提供 Bind() 接口用于绑定 Node 与 Pod。存在多个 BindPlugin 时,任一一个 BindPlugin 处理后其他 Plugin 就不会执行。
默认下 Pod 与 Node 的绑定就是通过 DefaultBinder 调用 APIServer 中的 Bind API。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
func (b DefaultBinder) Bind(ctx context.Context, state *framework.CycleState, p *v1.Pod, nodeName string) *framework.Status {
binding := &v1.Binding{
ObjectMeta: metav1.ObjectMeta{Namespace: p.Namespace, Name: p.Name, UID: p.UID},
Target: v1.ObjectReference{Kind: "Node", Name: nodeName},
}
err := b.handle.ClientSet().CoreV1().Pods(binding.Namespace).Bind(ctx, binding, metav1.CreateOptions{})
if err != nil {
return framework.AsStatus(err)
}
return nil
}
|