1 基本架构
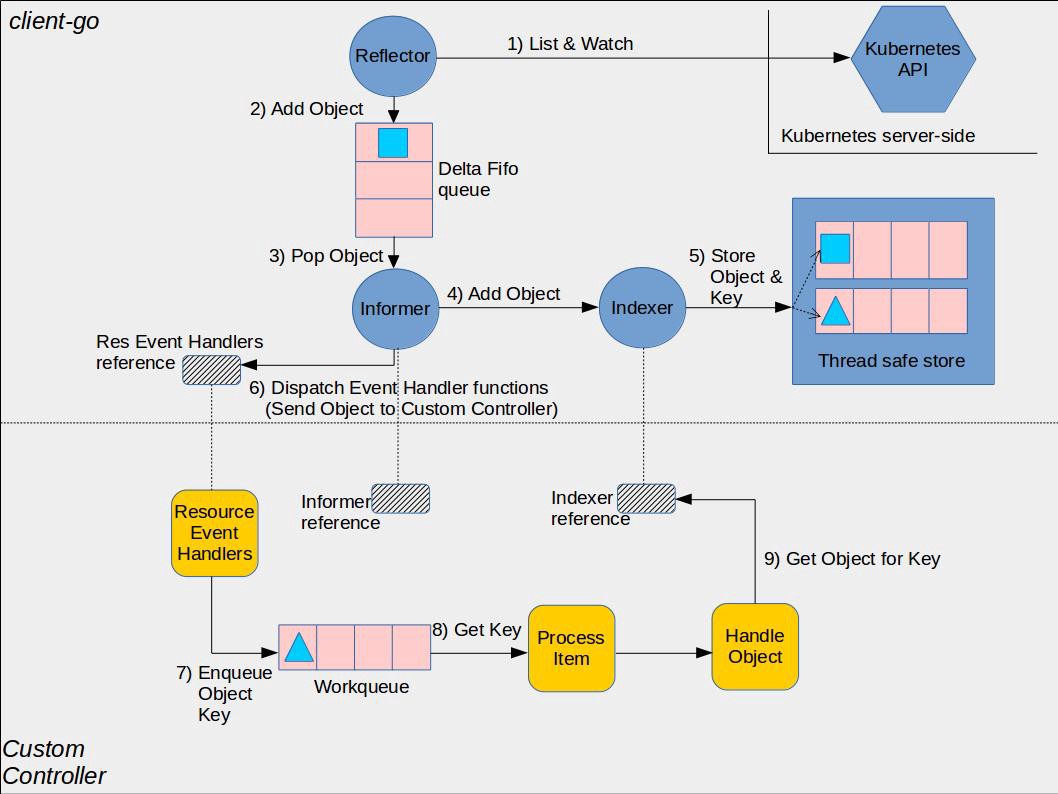
Kubernetes Client-go 库基于 ETCD 的实现了 Push + Pull 的基本模型,其实现的架构如下:

图中上半部分是 Client-go 的实现,包括核心组件:
Reflector - Watch 与 List Resource,当 Resource 出现变化时,会将其放入 Delta FIFO Queue 中。Delta FIFO Queue - 存储出现变化的 Resource。Informer - 从 Delta FIFO Queue 中读取 Resource,触发 Event Handler,并调用 Indexer 更新本地缓存。Indexer - 本地 Resource 缓存的索引,也可以认为是本地缓存。
对于 Controller 的编写者,往往是使用的封装好的 SharedInformer 注册 Event Handler:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
stopCh := make(chan struct{})
defer close(stopch)
sharedInformers := informers.NewSharedInformerFactory(clientset, time.Minute)
informer := sharedInformer.Core().V1().Pods().Informer()
informer.AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj interface{} {
// ...
},
UpdateFunc: func(obj interface{} {
// ...
},
DeleteFunc : func(obj interface{} {
// ...
})
})
informer.Run(stopCh)
|
顾名思义,SharedInformer 是用于多个 Controller 共享的 Informer,使得多个 Controller 只需要一个 Informer 和 Reflector 来与 APIServer 建立连接,减少 APIServer 的负载。
2 Reflector
Reflector 用于 Watch 指定的 Resource,当 Resource 发生变化时,会将 Resource 放到 DeltaFIFOQueue。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
func NewReflector(
lw ListerWatcher, // 提供 List 与 Watch 接口
expectedType interface{}, // Watch 的 Resource 类型
store Store, // DeltaFIFOQueue
resyncPeriod time.Duration, // 触发 DeltaFIFOQueue Resync 的周期
) *Reflector {
return NewNamedReflector(naming.GetNameFromCallsite(internalPackages...), lw, expectedType, store, resyncPeriod)
}
|
2.1 Run
当调用某个 Resource 的 Informer 的 Run 接口启动时,Informer 底层会创建对应 Resource 的 Reflector 并启动。也就是说,一个 Informer 对应着一个 Reflector。
在 Reflector 启动过程主要包含三个步骤:
- 全量 List Resource,并填充
DeltaFIFOQueue。
- 启动 Goroutine 周期性执行 Resync。
- 启动 Goroutine 不断 Watch Resource 并更新
DeltaFIFOQueue。
2.2 List
Reflector 并不会周期性 List 全量 Resource 对象,仅仅是在启动时 List 一次所有 Resource 对象,然后填充到 DeltaFIFOQueue 中。
后续会说到,Informer 提供的周期性 Resync 功能,是由 Reflector 周期性遍历 DeltaFIFOQueue 来触发的。
2.3 Watch
在第一个 List 全量填充后,Reflector 就会与 APIServer 建立长连接,启动一个永久运行的 Goroutine 不断接收对应类型的 Resource Event。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
func (r *Reflector) ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
// ...
for {
// ...
// Watch 接口返回一个 channel
w, err := r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)
if err != nil {
if utilnet.IsConnectionRefused(err) {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
return err
}
if err := r.watchHandler(start, w, &resourceVersion, resyncerrc, stopCh); err != nil {
return nil
}
}
}
func (r *Reflector) watchHandler(/*...*/) error {
loop:
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
return errorStopRequested
case err := <-errc:
return err
case event, ok := <-w.ResultChan():
if !ok {
break loop
}
// 解析 Object
meta, err := meta.Accessor(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
continue
}
newResourceVersion := meta.GetResourceVersion()
// 更新 Resource Event 更新到 DeltaFIFOQueue
switch event.Type {
case watch.Added:
err := r.store.Add(event.Object)
case watch.Modified:
err := r.store.Update(event.Object)
case watch.Deleted:
err := r.store.Delete(event.Object)
case watch.Bookmark:
// A `Bookmark` means watch has synced here, just update the resourceVersion
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
}
}
}
return nil
}
|
在底层,Reflector 调用的 Watch 函数实际上就是 Informer 提供的 Watch 函数,其实现就是 ClientSet 提供的 Watch 函数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
func NewFilteredPodInformer(...) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
// ...
WatchFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
return client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).Watch(options)
},
},
// ...
)
}
|
2.4 Resync
在第一次全量填充后,Reflector 同样会启动一个 Goroutine 周期性调用 DeltaFIFOQueue 的 Resync 功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
func (r *Reflector) ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
// ...
resyncerrc := make(chan error, 1)
cancelCh := make(chan struct{})
defer close(cancelCh)
go func() {
resyncCh, cleanup := r.resyncChan()
defer func() {
cleanup() // Call the last one written into cleanup
}()
for {
select {
case <-resyncCh:
case <-stopCh:
return
case <-cancelCh:
return
}
if r.ShouldResync == nil || r.ShouldResync() {
if err := r.store.Resync(); err != nil {
resyncerrc <- err
return
}
}
cleanup()
resyncCh, cleanup = r.resyncChan()
}
}()
}
|
这也是 Controller 周期性收到 Update 事件的原理。
3 DeltaFIFOQueue
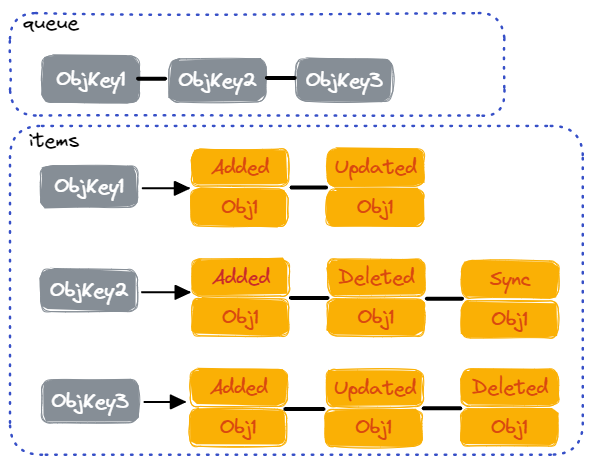
DeltaFIFOQueue 用于保存 Resource 的变更事件。其存储方式是 FIFO Queue,存储的元素称为 Delta。之所以会称为 Delta,因为对应存储的是 Resource 的变更事件。
对应的数据结构如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
const (
Added DeltaType = "Added"
Updated DeltaType = "Updated"
Deleted DeltaType = "Deleted"
// Replaced is emitted when we encountered watch errors and had to do a
// relist. We don't know if the replaced object has changed.
Replaced DeltaType = "Replaced"
// Sync is for synthetic events during a periodic resync.
Sync DeltaType = "Sync"
)
type Delta struct {
Type DeltaType // Event Type
Object interface{} // 对应 Resource Object
}
type Deltas []Delta
type DeltaFIFO struct {
// `items` maps keys to Deltas.
// `queue` maintains FIFO order of keys for consumption in Pop().
items map[string]Deltas
queue []string
// ...
}
|
其中 items 用于索引某一个 Object 对应的所有 Delta,queue 用于排序各个 Object。

3.1 Add / Update / Delete
DeltaFIFOQueue 提供的 Add / Update / Delete 接口用于添加 Added / Updated / Deleted 类型的 Delta。
其底层实现都是调用的 queueActionLocked() 接口向将 Delta 保存到 Queue 中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
func (f *DeltaFIFO) queueActionLocked(actionType DeltaType, obj interface{}) error {
// get key of the object
id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)
// append to items and queue
newDeltas := append(f.items[id], Delta{actionType, obj})
newDeltas = dedupDeltas(newDeltas)
if len(newDeltas) > 0 {
if _, exists := f.items[id]; !exists {
f.queue = append(f.queue, id)
}
f.items[id] = newDeltas
f.cond.Broadcast() // notify
} else {
delete(f.items, id)
}
return nil
}
|
3.2 Resync
前面看到 Reflector 会定期调用 DeltaFIFOQueue 的 Resync() 接口,来让 Informer 定期收到所有 Object 的 Sync Delta。后续会看到 Informer 是如何处理 Sync Delta 的。
Resync() 会遍历所有 Indexer 中的 Object Key,然后插入一个 Sync Delta。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Resync() error {
// ...
// knownObjects 实际上就是 Indexer,也就是缓存的所有 Object
keys := f.knownObjects.ListKeys()
for _, k := range keys {
if err := f.syncKeyLocked(k); err != nil {
return err
}
}
return nil
}
func (f *DeltaFIFO) syncKeyLocked(key string) error {
// 从 Indexer 获取 Object
obj, exists, err := f.knownObjects.GetByKey(key)
// 如果 Object 已经存在 Queue,那么不需要 Resync
id, err := f.KeyOf(obj)
if err != nil {
return KeyError{obj, err}
}
if len(f.items[id]) > 0 {
return nil
}
// 插入一个 Sync Delta
if err := f.queueActionLocked(Sync, obj); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("couldn't queue object: %v", err)
}
return nil
}
|
也就是说,Reflector 定期调用 Queue 的 Resync(),会为 Indexer 中的所有 Object 插入一个 Sync Delta。
3.3 Pop
DeltaFIFOQueue 的 Pop() 接口就是用于消费一个 Delta 了,就是正常的 Queue 实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
func (f *DeltaFIFO) Pop(process PopProcessFunc) (interface{}, error) {
for {
// Queue 为空时,阻塞等待
for len(f.queue) == 0 {
if f.closed {
return nil, ErrFIFOClosed
}
f.cond.Wait()
}
// 从 queue 与 items 读取 Delta
id := f.queue[0]
f.queue = f.queue[1:]
item, ok := f.items[id]
if !ok {
// Item may have been deleted subsequently.
continue
}
delete(f.items, id)
// 调用回调处理
err := process(item)
if e, ok := err.(ErrRequeue); ok {
f.addIfNotPresent(id, item)
err = e.Err
}
// 返回 Object
return item, err
}
}
|
4 Indexer
在整体的架构中,Indexer 是作为一个本地 Cache。当 Informer 收到 Object 事件后,就会更新 Indexer,以保证 Indexer 与 ETCD 中数据是一致的。用户实现的 Controller 会从 Indexer 中读取 Resource 对象。
4.1 数据结构
对于使用者,Indexer 提供的 Interface 是一个带有索引功能的 Store:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
type Indexer interface {
Store
// Index returns the stored objects whose set of indexed values
// intersects the set of indexed values of the given object, for
// the named index
Index(indexName string, obj interface{}) ([]interface{}, error)
// IndexKeys returns the storage keys of the stored objects whose
// set of indexed values for the named index includes the given
// indexed value
IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error)
// ListIndexFuncValues returns all the indexed values of the given index
ListIndexFuncValues(indexName string) []string
// ByIndex returns the stored objects whose set of indexed values
// for the named index includes the given indexed value
ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error)
// GetIndexer return the indexers
GetIndexers() Indexers
// AddIndexers adds more indexers to this store. If you call this after you already have data
// in the store, the results are undefined.
AddIndexers(newIndexers Indexers) error
}
type Store interface {
Add(obj interface{}) error
Update(obj interface{}) error
Delete(obj interface{}) error
List() []interface{}
ListKeys() []string
Get(obj interface{}) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)
GetByKey(key string) (item interface{}, exists bool, err error)
Replace([]interface{}, string) error
Resync() error
}
|
底层 threadSafeMap 实现了 Indexer:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
type threadSafeMap struct {
lock sync.RWMutex
items map[string]interface{}
// indexers maps a name to an IndexFunc
indexers Indexers // 索引函数
// indices maps a name to an Index
indices Indices // 索引结果
}
|
threadSafeMap 通过一个 Map 记录所有的 Object,其 Key 默认为 <namespace>/<name>。另外,通过 indexers 与 indices 实现了索引的功能。

4.2 Store 实现
threadSafeMap 实现 Store 相关功能很简单,就是在加锁的基础上更新 items 这个 Map。区别在于,更新的同时还需要更新索引。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
func (c *threadSafeMap) Add(key string, obj interface{}) {
oldObject := c.items[key]
c.items[key] = obj // 添加到 map
c.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key) // 更新索引结果
}
func (c *threadSafeMap) Update(key string, obj interface{}) {
oldObject := c.items[key]
c.items[key] = obj // 更新 map
c.updateIndices(oldObject, obj, key) // 更新索引结果
}
func (c *threadSafeMap) Delete(key string) {
if obj, exists := c.items[key]; exists {
c.deleteFromIndices(obj, key) // 从索引结果中删除
delete(c.items, key) // 从 map 中删除
}
}
|
4.3 Index 实现
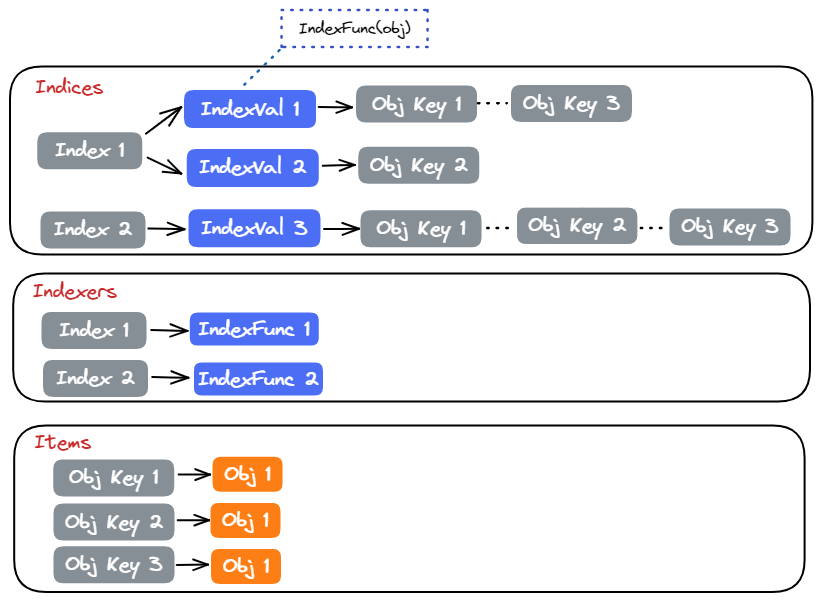
Indexer 提供了自定义索引的功能,对应地 threadSafeMap 使用两个 Map 来记录索引相关信息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
// IndexFunc 表示一个 IndexFunc,即从 Object 得到对应的 IndexVal
type IndexFunc func(obj interface{}) ([]string, error)
// Indexers 保存着所有的索引函数
// Key: IndexName Value: IndexFunc
type Indexers map[string]IndexFunc
// Index 保存 IndexVal 与对应 Object Key 的映射
// Key: IndexVal Value: Object Key Set
type Index map[string]sets.String
// Indices 存储索引结果
// Key: IndexName Value: Index
type Indices map[string]Index
|
Indexers 记录了所有自定义的索引函数Indices 记录了所有 Object 的索引结果
4.3.1 更新 Object 时更新索引
当调用 threadSafeMap 来更新 Object 时,会对 Object 计算索引,并更新结果到 Indices。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
func (c *threadSafeMap) updateIndices(oldObj interface{}, newObj interface{}, key string) {
if oldObj != nil {
c.deleteFromIndices(oldObj, key) // 表明删除 Object,同时删除索引
}
// 遍历所有索引函数
for name, indexFunc := range c.indexers {
// 计算 Object 索引
indexValues, err := indexFunc(newObj)
// 更新到对应的 Indices
index := c.indices[name]
if index == nil {
index = Index{}
c.indices[name] = index
}
for _, indexValue := range indexValues {
set := index[indexValue]
if set == nil {
set = sets.String{}
index[indexValue] = set
}
set.Insert(key)
}
}
}
|
4.3.2 通过索引查询 Object
threadSafeMap 支持通过索引值查询 Object 或者 Key。其实现就是从 Indices 查询索引对应的索引值,以及对应的 Object Key。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
func (c *threadSafeMap) ByIndex(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]interface{}, error) {
indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]
if indexFunc == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)
}
index := c.indices[indexName]
set := index[indexedValue]
list := make([]interface{}, 0, set.Len())
for key := range set {
list = append(list, c.items[key])
}
return list, nil
}
func (c *threadSafeMap) IndexKeys(indexName, indexedValue string) ([]string, error) {
indexFunc := c.indexers[indexName]
if indexFunc == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("Index with name %s does not exist", indexName)
}
index := c.indices[indexName]
set := index[indexedValue]
return set.List(), nil
}
|
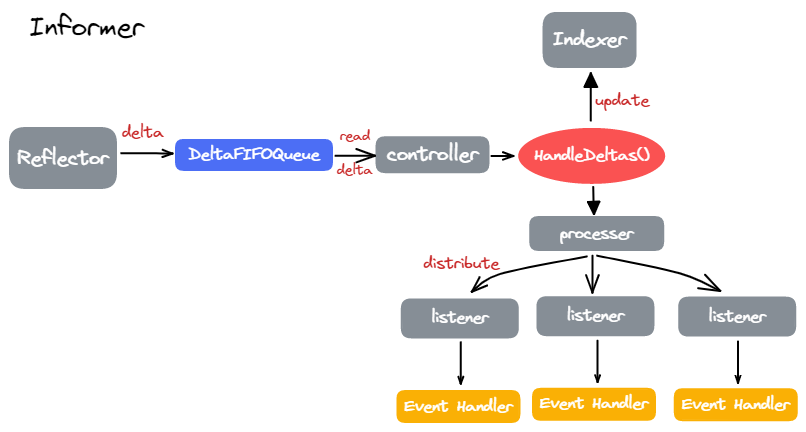
Informer 是整个架构中的 Router:接收着 Queue 中的 Delta,然后触发 Event Handler 以及更新 Indexer。
5.1 数据结构
代码中使用的 SharedInformer 由 sharedIndexInformer 实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
type sharedIndexInformer struct {
indexer Indexer
controller Controller
processor *sharedProcessor
cacheMutationDetector MutationDetector
listerWatcher ListerWatcher
// ...
}
|
indexer 就是 Indexer 对象,本地 Object 的缓存;controller 创建 Relfector 与 DeltaFIFOQueue;processor 为所有注册的 Event Handler 的路由器;

5.2 Run
各个组件都会在 Informer 的 Run() 函数中创建或运行:
- 创建
DeltaFIFOQueue;
- 运行
processor 开始分发 Event;
- 运行
controller 创建 Relector 并不断读取 Queue 处理 Delta;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
|
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
// 创建 DeltaFIFOQueue
fifo := NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(DeltaFIFOOptions{
KnownObjects: s.indexer,
EmitDeltaTypeReplaced: true,
})
cfg := &Config{
Queue: fifo,
ListerWatcher: s.listerWatcher,
ObjectType: s.objectType,
FullResyncPeriod: s.resyncCheckPeriod,
RetryOnError: false,
ShouldResync: s.processor.shouldResync,
Process: s.HandleDeltas, // Queue 处理函数
WatchErrorHandler: s.watchErrorHandler,
}
// ...
// 运行 processer
wg.StartWithChannel(processorStopCh, s.cacheMutationDetector.Run)
wg.StartWithChannel(processorStopCh, s.processor.run)
// 运行 controller
s.controller.Run(stopCh)
}
func (c *controller) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
// 创建 Relector
r := NewReflector(
c.config.ListerWatcher,
c.config.ObjectType,
c.config.Queue,
c.config.FullResyncPeriod,
)
c.reflectorMutex.Lock()
c.reflector = r
c.reflectorMutex.Unlock()
var wg wait.Group
wg.StartWithChannel(stopCh, r.Run)
wait.Until(c.processLoop, time.Second, stopCh)
wg.Wait()
}
|
5.3 处理 Delta
controller 运行后,会不断从 Queue 中读取 Delta 并执行处理函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
func (c *controller) processLoop() {
for {
obj, err := c.config.Queue.Pop(PopProcessFunc(c.config.Process))
if err != nil {
if err == ErrFIFOClosed {
return
}
if c.config.RetryOnError {
// This is the safe way to re-enqueue.
c.config.Queue.AddIfNotPresent(obj)
}
}
}
}
|
其处理函数就是 Informer.HandleDeltas(),负责了两个工作:
- 更新
Indexer;
- 调用
processor 触发所有的 Event Handler;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) HandleDeltas(obj interface{}) error {
for _, d := range obj.(Deltas) {
switch d.Type {
case Sync, Replaced, Added, Updated:
if old, exists, err := s.indexer.Get(d.Object); err == nil && exists {
// 更新 Indexer 中已有的 Object
if err := s.indexer.Update(d.Object); err != nil {
return err
}
isSync := false
switch {
case d.Type == Sync:
isSync = true
case d.Type == Replaced:
// ...
}
// 通过 processor 分发 Event
s.processor.distribute(updateNotification{oldObj: old, newObj: d.Object}, isSync)
} else {
// 向 Indexer 添加新的 Obejct
err := s.indexer.Add(d.Object)
// 通过 processor 分发 Event
s.processor.distribute(addNotification{newObj: d.Object}, false)
}
case Deleted:
// 从 Indexer 删除 Object
err := s.indexer.Delete(d.Object)
// 通过 processor 分发 Event
s.processor.distribute(deleteNotification{oldObj: d.Object}, false)
}
}
return nil
}
|
5.4 Event Handler
5.4.1 添加 Event Handler
在使用 Client-go 时,往往会通过 Informer.AddEventHandler() 来添加 Event Handler。例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
factory := kubeinformers.NewSharedInformerFactoryWithOptions(clientSet, cliCfg.ResyncDuration)
podsInformer := deps.KubeInformerFactory.Core().V1().Pods()
podsInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: c.enqueuePod,
UpdateFunc: func(old, cur interface{}) {
c.enqueuePod(cur)
},
})
|
其调用的就是 Pod 对应的 sharedIndexInformer 的 AddEventHandler() 函数。实际上就是将 Event Handler 注册到 processor 中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) AddEventHandlerWithResyncPeriod(handler ResourceEventHandler, resyncPeriod time.Duration) {
// ...
// 创建一个 listener
listener := newProcessListener(handler, resyncPeriod, determineResyncPeriod(resyncPeriod, s.resyncCheckPeriod), s.clock.Now(), initialBufferSize)
// 注册到 processor 中
if !s.started {
s.processor.addListener(listener)
return
}
// 如果已经运行了,还会遍历一遍 Indexer 中 Object 触发一次
s.processor.addListener(listener)
for _, item := range s.indexer.List() {
listener.add(addNotification{newObj: item})
}
}
|
5.4.2 触发 Event Handler
在 HandleDeltas() 中看到,每个 Delta 会通过 processor.distribute() 分发给所有注册的 Event Handler:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
func (p *sharedProcessor) distribute(obj interface{}, sync bool) {
if sync {
for _, listener := range p.syncingListeners { // sync delta
listener.add(obj)
}
} else {
for _, listener := range p.listeners { // add update deleted delta
listener.add(obj)
}
}
}
func (p *processorListener) add(notification interface{}) {
p.addCh <- notification
}
func (p *processorListener) run() {
stopCh := make(chan struct{})
wait.Until(func() {
for next := range p.nextCh {
switch notification := next.(type) {
case updateNotification:
p.handler.OnUpdate(notification.oldObj, notification.newObj) // 触发 OnUpdate 回调
case addNotification:
p.handler.OnAdd(notification.newObj) // 触发 OnAdd 回调
case deleteNotification:
p.handler.OnDelete(notification.oldObj) // 触发 OnDelete 回调
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unrecognized notification: %T", next))
}
}
// the only way to get here is if the p.nextCh is empty and closed
close(stopCh)
}, 1*time.Second, stopCh)
}
|
可以看到,最终调用了不同类型的回调函数:
OnUpdate() - Object 在 Indexer 中存在时调用OnAdd() - Object 在 Indexer 中不存在时调用OnDelete() - 处理 Deleted Delta 时调用
前面看到,一个 Informer 对应着一个 Reflector 与 Indexer。也就是说,每个 Informer 会建立一个与 Kubernetes APIServer 的长连接,以及一个本地所有 Object 的缓存。
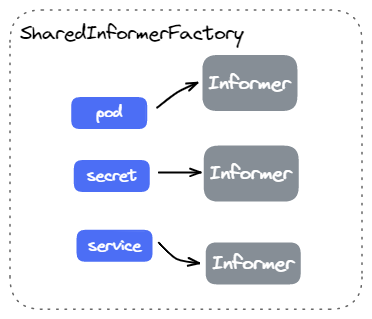
通常每个 Resource 只需要创建一个对应的 Informer 即可,程序中各个地方都需要复用唯一的 Informer 使用。
为此,Client-go 实现了 SharedInformerFactory 来方便的复用 Informer。在 SharedInformerFactory 中,每个 Resource 只会创建一个对应的 Informer。
一个典型的 SharedInformerFactory 使用方式如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
func main() {
// 创建 Factory
factory := kubeinformers.NewSharedInformerFactoryWithOptions(kubeCli, 30*time.Second)
// 创建或复用 `Informer` 和 `Lister`
lister := kubeInformerFactory.Core().V1().Pods().Lister()
informer := kubeInformerFactory.Core().V1().Pods().Informer()
// 启动 Factory 并等待第一次填充完毕
factory.Start(ctx.Done())
f.WaitForCacheSync(wait.NeverStop)
// 使用 informer 和 lister ...
}
|
6.1 数据结构
对于使用者,SharedInformerFactory 提供了创建各个 Resource Informer 的方法,例如内置资源的 SharedInformerFactory:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
type SharedInformerFactory interface {
internalinterfaces.SharedInformerFactory
ForResource(resource schema.GroupVersionResource) (GenericInformer, error)
WaitForCacheSync(stopCh <-chan struct{}) map[reflect.Type]bool
Admissionregistration() admissionregistration.Interface
Apps() apps.Interface
Autoscaling() autoscaling.Interface
Batch() batch.Interface
Certificates() certificates.Interface
Coordination() coordination.Interface
Core() core.Interface
Discovery() discovery.Interface
// ...
}
|
底层实现如下,其中最关键的就是通过 informers 属性记录了不同的 Informer,用以复用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
type sharedInformerFactory struct {
client kubernetes.Interface
namespace string
defaultResync time.Duration
customResync map[reflect.Type]time.Duration
informers map[reflect.Type]cache.SharedIndexInformer
startedInformers map[reflect.Type]bool
}
|

以 Pod 为例,看下 Informer 是如何注册到 Factory 中的。当我们调用 Lister() 或 Informer() 时,其底层实现会调用 Factory 接口注册。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
func (f *podInformer) Informer() cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return f.factory.InformerFor(&corev1.Pod{}, f.defaultInformer)
}
func (f *podInformer) Lister() v1.PodLister {
return v1.NewPodLister(f.Informer().GetIndexer())
}
|
factory.InformerFor() 就是返回已创建的 Informer,或者创建 Informer 并注册到 Factory 中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
func (f *sharedInformerFactory) InformerFor(obj runtime.Object, newFunc internalinterfaces.NewInformerFunc) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
// 复用 Informer
informerType := reflect.TypeOf(obj)
informer, exists := f.informers[informerType]
if exists {
return informer
}
// 新建 Informer
resyncPeriod, exists := f.customResync[informerType]
if !exists {
resyncPeriod = f.defaultResync
}
informer = newFunc(f.client, resyncPeriod)
f.informers[informerType] = informer
return informer
}
|
6.3 Start
当通过 Informer() 或者 Lister() 来注册各个 Informer 后,通过 Factory 的 Start() 接口来启动各个 Informer,也就是执行 Informer.Run():
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
func (f *sharedInformerFactory) Start(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
f.lock.Lock()
defer f.lock.Unlock()
for informerType, informer := range f.informers {
if !f.startedInformers[informerType] {
go informer.Run(stopCh)
f.startedInformers[informerType] = true
}
}
}
|
6.4 WaitForCacheSync
当我们执行完 Start() 后,就执行 Reflector.Run() 中的第一次全量 List Resource,从而进行 Indexer 的第一次填充。
WaitForCacheSync() 方法就是来等待所有 Informer 对应的 Indexer 第一次填充完毕。填充完毕的标志为 Informer.HasSynced() 方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
func (f *sharedInformerFactory) WaitForCacheSync(stopCh <-chan struct{}) map[reflect.Type]bool {
// ...
res := map[reflect.Type]bool{}
for informType, informer := range informers {
res[informType] = cache.WaitForCacheSync(stopCh, informer.HasSynced)
}
return res
}
|