Kubernetes 编程系列 主要记录一些开发 Controller 所相关的知识,大部分内容来自于《Programming Kubernetes》(推荐直接阅读)。
下面代码都来自于 agnhost/webhook,这是官方的 Admission Webhook 的示例
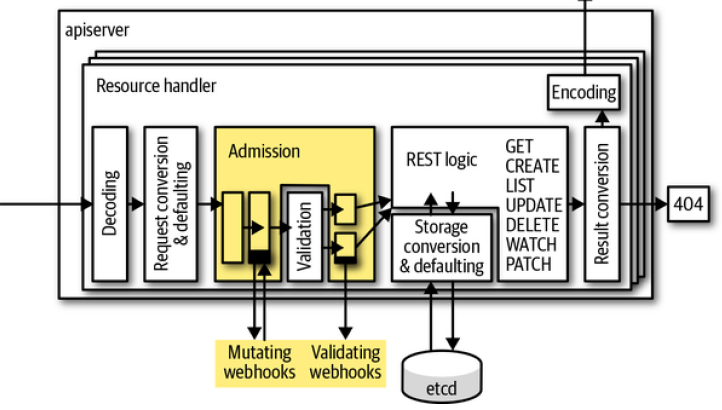
在 Custom APIServer/Admission 一节中看到,APISever 提供了 Admission Plugin 机制来进行 Mutating 与 Validating 的插件式扩展。不过 Admission Plugin 是要重新编译 APISever 来实现的,因此 APISever 提供了更加灵活的 Admission Webhook。
Admission Webhook 的调用时机在 Admission Plugin 的尾部,在 Quota Plugin 之前。

Admission Webhook 的使用包含:
-
部署 Webhook Server,用于 APISever 转发请求;
-
部署 ValidatingWebhookConfiguration/MutatingWebhookConfiguration 资源,向 APISever 注册 Webhook Server;
-
RBAC(如果 Webhook Server 需要)
1 WebhookConfiguration
通过部署 ValidatingWebhookConfiguration/MutatingWebhookConfiguration 来向 APIServer 注册 Validating/Mutating Webhook Server。
下面是一个 ValidatingWebhookConfiguration 示例,而 MutatingWebhookConfiguration 是类似的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
name: "pod-policy.example.com"
webhooks:
- name: "pod-policy.example.com"
# objectSelector:
# matchLabels:
# foo: bar
# namespaceSelector:
# matchExpressions:
# - key: runlevel
# operator: NotIn
# values: ["0","1"]
matchPolicy: Equivalent
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
apiVersions: ["v1"]
operations: ["CREATE"]
resources: ["pods"]
scope: "Namespaced"
clientConfig:
# url: " https://my-webhook.example.com:9443/my-webhook-path"
service:
namespace: "example-namespace"
name: "example-service"
caBundle: "Ci0tLS0tQk...<`caBundle` is a PEM encoded CA bundle which will be used to validate the webhook's server certificate.>...tLS0K"
admissionReviewVersions: ["v1", "v1beta1"]
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 5
reinvocationPolicy: IfNeeded
failurePolicy: Fail
|
- webhooks: 定义一个或者多个 webhook servers
- name - 定义多个 webhook 情况下,需要定义一个唯一的 name
- clientConfig - 定义 APIServer 转发的目标,可以为 URL 或者 Service
- admissionReviewVersions - 表明 webhook server 支持的 AdmissionReview 的版本
- sideEffects - 表明 Webhook 是否支持 Side effect
- timeoutSeconds(1-30) - 配置 APIServer 等待 webhook server 回复的超时时间,超时后根据 failure policy 处理
- rules - 定义转发的匹配规则
- objectSelector - 根据 object 的 label 来筛选 APIServer 需要转发的请求
- namespaceSelector - 根据 namespace 来筛选 APIServer 需要转发的请求
- matchPolicy - 定义 rule 如何匹配请求
- reinvocationPolicy - 定义是否需要重跑 webhook,在 object 修改后
- failurePolicy - 定义请求失败后的行为
1.1 请求匹配规则
1.1.1 rules
每个 webhook 必须指定一组 rules,用以让 APIServer 决定是否转发请求给 webhook server。
当一个请求能够匹配 operation、group、version、resource、scope,那么请求就会转发。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
apiVersions: ["v1"]
operations: ["CREATE"]
resources: ["pods"]
scope: "Namespaced"
|
- operations - 匹配请求的操作,支持 CREATE UPDATE DELETE CONNECT *
- apiGroups - 匹配请求的操作的 API Group,"" 表示 core API,"*" 匹配所有的 API Group
- apiVersions - 匹配 API Group 下的多个版本,"*" 匹配所有版本
- resources - 匹配 API Group 下多个 resource
- “*” 表示匹配所有 resource,但是不包含 subresource
- “*/” 表示匹配所有 resource 与 subresource
- “pods/” 表示匹配 Pod 下的所有 subresource
- “*/status” 表示匹配所有 resource 下的 status subresource
- scope - 定义需要匹配 resource 与 subresource 的范围,支持 Cluster Namespaced *
1.1.2 objectSelector
通过 objectSelector 根据请求操作的 object 的 label 来筛选请求,成功匹配的请求才会被转发。
下面示例中,经过 rules 匹配后的请求,还会经过 objectSelector 筛选(需要包含 label foo:bar)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
# ...
webhooks:
- name: my-webhook.example.com
objectSelector:
matchLabels:
foo: bar
rules:
- operations: ["CREATE"]
apiGroups: ["*"]
apiVersions: ["*"]
resources: ["*"]
scope: "*"
# ...
|
1.1.3 namespaceSelector
通过 namespaceSelector 根据请求操作的 object 的 namespace 来筛选请求。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
# ...
webhooks:
- name: my-webhook.example.com
namespaceSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: runlevel
operator: NotIn
values: ["0","1"]
rules:
- operations: ["CREATE"]
apiGroups: ["*"]
apiVersions: ["*"]
resources: ["*"]
scope: "Namespaced"
# ...
|
1.1.4 matchPolicy
一个资源可能属于多个 API Group,这在升级资源版本时很常见。例如,Deployment 支持 extensions/v1beta1,apps/v1beta1 等。
matchPolicy 用于定义 rules 如何匹配请求,其值可以为:
- Exact - 表示请求需要完全匹配
- Equivalent(默认值) - 表示请求可以匹配不同 APIGroup 的相同资源
例如下面示例,通过 matchPolicy 也可以匹配 extensions/v1beta1 的 Deployment 了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
# ...
webhooks:
- name: my-webhook.example.com
matchPolicy: Equivalent
rules:
- operations: ["CREATE","UPDATE","DELETE"]
apiGroups: ["apps"]
apiVersions: ["v1"]
resources: ["deployments"]
scope: "Namespaced"
# ...
|
如何实现的?
这是根据资源版本转换的实现,因为 extensions/v1beta1 Deployment 在 APIServer 中会被转化为 v1 请求,从而可以匹配到 Webhook 转发。
1.2 与 Webhook 通信方式
1.2.1 URL
URL 为一个 webhook server 地址,以标准的 URL 格式。但是,不允许使用用户或者基本身份认证(例如 URL 中的 user:password@),也不允许 URL 中使用 # 和 ? 传参。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
# ...
webhooks:
- name: my-webhook.example.com
clientConfig:
url: "https://my-webhook.example.com:9443/my-webhook-path"
# ...
|
1.2.2 Service
如果 Webhook Server 运行在集群中,可以指定 Service 来转发请求。其 port 默认为 443,path 默认为 “/"。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
# ...
webhooks:
- name: my-webhook.example.com
clientConfig:
caBundle: "Ci0tLS0tQk...<base64-encoded PEM bundle containing the CA that signed the webhook's serving certificate>...tLS0K"
service:
namespace: my-service-namespace
name: my-service-name
path: /my-path
port: 1234
# ...
|
1.3 Side effects
有些情况下,Webhook Server 不仅仅是处理 AdmissionReview 对象,而要进行一些 “带外” 操作(指操作实际的资源),这也被称为 Side effect。
sideEffects 字段用于指定 Webhook Server 能否处理 dryRun 的 请求(dryRun:true)。值可以为:
- Unknown - 未知,对于 dryRun 请求要转发给 Webhook 的,直接视为请求失败。
- None - 表明 Webhook 没有 Side effect。
- Some - 表明 Webhook 有一些 side effect,对于 dryRun 请求要转发给 Webhook 的,将直接视为请求失败。
- NoneOnDryRun - 表明 Webhook 有一些 side effect,而 Webhook 能够处理 dryRun 请求。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
# ...
webhooks:
- name: my-webhook.example.com
sideEffects: NoneOnDryRun
# ...
|
1.4 Reinvocation policy
对于 Mutating Admission Plugin,顺序调用不适用于所有的情况。可能 Webhook 修改了对象的结构,但是其他 Mutating Plugin 对于其新结构是拒绝的(但是其已经被调用过了,因此不再被调用)。
而 1.15 后,如果 Mutating Webhook 更改对象,内置的 Mutating Admission Plugin 会重跑。
reinvocationPolicy 字段可以控制 Webhook Server 在这种情况下,是否需要重跑。值可以为:
- Never - 一次中 Admission Control 不能多次调用 Webhook。
- IfNeeded - Webhook 调用后的对象又被其他 Admission Plugin 修改了,那么 Webhook 会再次重跑。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
# ...
webhooks:
- name: my-webhook.example.com
reinvocationPolicy: IfNeeded
# ...
|
不过需要注意:
- 不保证额外调用次数是一次
- 如果额外调用,导致对象再一次被修改,那么不保证还会再次调用 Webhook
- 使用此选项的 Webhook 可能会被重新排序,以减少额外调用数。
- 要保证修改后验证对象,应该使用 Validate Admission Webhook
这也表明了,Mutating Webhook 必须是幂等的。
1.5 Failure policy
failurePolicy 字段定义了,当 APIServer 请求 Webhook 失败后,如何处理(包括超时错误)。
- Ignore - Webhook 返回的错误会被忽略,API 请求继续
- Fail(默认) - Webhook 返回错误,API 请求被拒绝
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
# ...
webhooks:
- name: my-webhook.example.com
failurePolicy: Fail
# ...
|
2 Request 与 Response
2.1 Request
APIServer 发送 POST HTTP 请求,其设置了 HTTP Header 中 Content-Type: application/json,body 内容为 AdmissionReview 对象的 JSON 格式,设置了其中的 “request” 字段。
下面示例展示了对于 apps/v1 Deployment scale 子资源的调用请求,对应的 AdmissionReview 对象内容。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
|
{
"apiVersion": "admission.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "AdmissionReview",
"request": {
// 随机 uid,用于标识这次 admission 调用
"uid": "705ab4f5-6393-11e8-b7cc-42010a800002",
// 请求中对象的 GVK
"kind": {"group":"autoscaling","version":"v1","kind":"Scale"},
// 请求中对象的 GVR
"resource": {"group":"apps","version":"v1","resource":"deployments"},
// 请求对象的 subresource
"subResource": "scale",
// 请求源对象的 GVK
// 因为 `matchPolicy: Equivalent` 可能会让请求转变,而这里保存转变前的 GVK
"requestKind": {"group":"autoscaling","version":"v1","kind":"Scale"},
// 请求源对象的 GVR
// 因为 `matchPolicy: Equivalent` 可能会让请求转变,而这里保存转变前的 GVR
// Fully-qualified group/version/kind of the resource being modified in the original request to the API server.
// This only differs from `resource` if the webhook specified `matchPolicy: Equivalent` and the
// original request to the API server was converted to a version the webhook registered for.
"requestResource": {"group":"apps","version":"v1","resource":"deployments"},
// 请求源对象的 subresource
// 因为 `matchPolicy: Equivalent` 可能会让请求转变,而这里保存转变前的 subresource
"requestSubResource": "scale",
// 请求对象的 name
"name": "my-deployment",
// 请求对象的 namespace
"namespace": "my-namespace",
// 请求的操作,CREATE UPDATE DELETE CONNECT
"operation": "UPDATE",
"userInfo": {
// APIServer 身份认证的 username
"username": "admin",
// APIServer 身份认证的 uid
"uid": "014fbff9a07c",
// APIServer 身份认证的 group
"groups": ["system:authenticated","my-admin-group"],
// Arbitrary extra info associated with the user making the request to the API server.
// This is populated by the API server authentication layer and should be included
// if any SubjectAccessReview checks are performed by the webhook.
"extra": {
"some-key":["some-value1", "some-value2"]
}
},
// 请求操作的对象,可以通过 scheme 解析为具体的结构
"object": {"apiVersion":"autoscaling/v1","kind":"Scale",...},
// 当前集群中的对象
// It is null for CREATE and CONNECT operations.
"oldObject": {"apiVersion":"autoscaling/v1","kind":"Scale",...},
// 操作的 Option,包含 CreateOptions、UpdateOptions、DeleteOptions
"options": {"apiVersion":"meta.k8s.io/v1","kind":"UpdateOptions",...},
// dryRun 表明请求是否是 dry run mode
// See http://k8s.io/docs/reference/using-api/api-concepts/#make-a-dry-run-request for more details.
"dryRun": false
}
}
|
2.2 Response
Webhook server 应该返回 200 HTTP code,并设置了 HTTP Header 中 Content-Type: application/json,body 内容为 AdmissionReview 对象的 JSON 格式,设置了其中的 “response” 字段。
不同的操作可能有着不同的 response,不过至少其必须包含以下字段:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
{
"apiVersion": "admission.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "AdmissionReview",
"response": {
"uid": "<value from request.uid>",
"allowed": true
}
}
|
uid - 复制 request.uidallowed - 设置为 true 或者 false,表明允许或者禁止
拒绝请求时,通过 status 字段可以提供需要 APIServer 返回给 client 的 HTTP code 与 message。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
{
"apiVersion": "admission.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "AdmissionReview",
"response": {
"uid": "<value from request.uid>",
"allowed": false,
"status": {
"code": 403,
"message": "You cannot do this because it is Tuesday and your name starts with A"
}
}
}
|
对于 MutatingWebhook 可以对对象进行修改,这是通过 JSON Patch 实现的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
{
"apiVersion": "admission.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "AdmissionReview",
"response": {
"uid": "<value from request.uid>",
"allowed": true,
"patchType": "JSONPatch",
"patch": "W3sib3AiOiAiYWRkIiwgInBhdGgiOiAiL3NwZWMvcmVwbGljYXMiLCAidmFsdWUiOiAzfV0="
}
}
|
patchType - 指定 patch 类型,目前仅仅支持 JSONPatchpatch - patch 操作的 base64 编码,示例中为 “[{“op”: “add”, “path”: “/spec/replicas”, “value”: 3}]”
1.19 后,也可以选择返回一个 WARN 信息,通过 warnings 字段。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
{
"apiVersion": "admission.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "AdmissionReview",
"response": {
"uid": "<value from request.uid>",
"allowed": true,
"warnings": [
"duplicate envvar entries specified with name MY_ENV",
"memory request less than 4MB specified for container mycontainer, which will not start successfully"
]
}
}
|
3 与 APIServer 的身份认证
3.1 APIServer 验证 Webhook 身份
APIServer 基于证书认证的方式来验证 Webhook 身份,通过使用 WebhookConfiguration 的clientConfig.caBundle 字段配置的 CA 证书来验证 Webhook 的证书。
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
# ...
clientConfig:
service:
namespace: "example-namespace"
name: "example-service"
caBundle: OMIT
|
3.2 Webhook 验证 APIServer 身份
如果 Webhook 需要认证 APIServer 身份,可以提供给 APIServer 一个 kubeconfig,APIServer 会使用 kubeconfig 文件中的配置作为访问凭证。
需要三个阶段来进行配置:
-
启动 APIServer 时,通过 --admission-control-config-file 参数指定 Admission Control 配置文件。
-
在 Admission Control 配置文件中,指定 MutatingAdmissionWebhook Controller 与 ValidatingAdmissionWebhook Controller 读取的证书。
在配置文件,通过 kubeConfigFile 字段指定对应的 kubeconfig 文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
apiVersion: apiserver.config.k8s.io/v1
kind: AdmissionConfiguration
plugins:
- name: ValidatingAdmissionWebhook
configuration:
apiVersion: apiserver.config.k8s.io/v1
kind: WebhookAdmissionConfiguration
kubeConfigFile: "<path-to-kubeconfig-file>"
- name: MutatingAdmissionWebhook
configuration:
apiVersion: apiserver.config.k8s.io/v1
kind: WebhookAdmissionConfiguration
kubeConfigFile: "<path-to-kubeconfig-file>"
|
-
在指定的 kubeConfig 文件中,提供需要的证书
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
apiVersion: v1
kind: Config
users:
# name should be set to the DNS name of the service or the host (including port) of the URL the webhook is configured to speak to.
# If a non-443 port is used for services, it must be included in the name when configuring 1.16+ API servers.
#
# For a webhook configured to speak to a service on the default port (443), specify the DNS name of the service:
# - name: webhook1.ns1.svc
# user: ...
#
# For a webhook configured to speak to a service on non-default port (e.g. 8443), specify the DNS name and port of the service in 1.16+:
# - name: webhook1.ns1.svc:8443
# user: ...
# and optionally create a second stanza using only the DNS name of the service for compatibility with 1.15 API servers:
# - name: webhook1.ns1.svc
# user: ...
#
# For webhooks configured to speak to a URL, match the host (and port) specified in the webhook's URL. Examples:
# A webhook with `url: https://www.example.com`:
# - name: www.example.com
# user: ...
#
# A webhook with `url: https://www.example.com:443`:
# - name: www.example.com:443
# user: ...
#
# A webhook with `url: https://www.example.com:8443`:
# - name: www.example.com:8443
# user: ...
#
- name: 'webhook1.ns1.svc'
user:
client-certificate-data: "<pem encoded certificate>"
client-key-data: "<pem encoded key>"
# The `name` supports using * to wildcard-match prefixing segments.
- name: '*.webhook-company.org'
user:
password: "<password>"
username: "<name>"
# '*' is the default match.
- name: '*'
user:
token: "<token>"
|
Note
配置中仅仅配置了 client 证书与私钥,而在 ValidatingWebhookConfiguration/MutatingWebhookConfiguration 定义中指定了 CA Bundle,即 CA 证书。
4 实现
接下来我们来看 Webhook Server 的实现,幸运的是,其比 Custom APIServer 要简单的多。
4.1 HTTP Server
Webhook Server 本质上就是一个 HTTP Server,因此其 main 函数中,主要就是启动了一个 HTTP Server。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
func main(cmd *cobra.Command, args []string) {
config := Config{
CertFile: certFile,
KeyFile: keyFile,
}
// 定义 HTTP handle
// 下面每个 Handle 都是一个 Admission Webhook
// ** 只要一个 HTTP Endpoint 能够处理 AdmissionReview 对象,那么就可以作为一个 Admission Webhook **
http.HandleFunc("/always-allow-delay-5s", serveAlwaysAllowDelayFiveSeconds)
http.HandleFunc("/always-deny", serveAlwaysDeny)
http.HandleFunc("/add-label", serveAddLabel)
http.HandleFunc("/pods", servePods)
http.HandleFunc("/pods/attach", serveAttachingPods)
http.HandleFunc("/mutating-pods", serveMutatePods)
http.HandleFunc("/mutating-pods-sidecar", serveMutatePodsSidecar)
http.HandleFunc("/configmaps", serveConfigmaps)
http.HandleFunc("/mutating-configmaps", serveMutateConfigmaps)
http.HandleFunc("/custom-resource", serveCustomResource)
http.HandleFunc("/mutating-custom-resource", serveMutateCustomResource)
http.HandleFunc("/crd", serveCRD)
http.HandleFunc("/readyz", func(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) { w.Write([]byte("ok")) })
// 创建被启动 APIServer
server := &http.Server{
Addr: fmt.Sprintf(":%d", port),
TLSConfig: configTLS(config),
}
err := server.ListenAndServeTLS("", "")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
|
上面的 HTTP Server 注册了许多的 HTTP API。因为每个 API 都可以处理 AdmissionReview 请求,所以就可以作为一个 Admission Webhook。当对应的 Webhook Configuration 定义部署后,就可以使用。
4.2 通用处理逻辑 serve
所有的 HTTP Endpoint HandleFunc 都是基于 serve 的调用,例如:
1
2
3
|
func serveAlwaysAllowDelayFiveSeconds(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
serve(w, r, newDelegateToV1AdmitHandler(alwaysAllowDelayFiveSeconds))
}
|
因为所有的 Webhook 有着最基本的编解码的逻辑,这一部分是相同的,而 server 就是处理这部分逻辑的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
|
// serve 处理 HTTP 请求,从 body 中解析得到 AdmissionReview,然后调用 admit 回调处理,最后将结果回复
func serve(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, admit admitHandler) {
// read http body
var body []byte
if r.Body != nil {
if data, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body); err == nil {
body = data
}
}
// 检查 Header Content-Type,Webhook 只支持 "application/json"
contentType := r.Header.Get("Content-Type")
if contentType != "application/json" {
klog.Errorf("contentType=%s, expect application/json", contentType)
return
}
klog.V(2).Info(fmt.Sprintf("handling request: %s", body))
// 解析 body -> runtime.Object
// 因为 AdmissionReview 也是一个 Kubernetes 资源,所以直接使用 Kubernetes 进行解析
deserializer := codecs.UniversalDeserializer()
obj, gvk, err := deserializer.Decode(body, nil, nil)
if err != nil {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Request could not be decoded: %v", err)
klog.Error(msg)
http.Error(w, msg, http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
// 进一步得到 Admission Request
var responseObj runtime.Object
switch *gvk {
case v1beta1.SchemeGroupVersion.WithKind("AdmissionReview"):
// v1beta1 版本 AdmissionReview 对象支持
requestedAdmissionReview, ok := obj.(*v1beta1.AdmissionReview)
if !ok {
klog.Errorf("Expected v1beta1.AdmissionReview but got: %T", obj)
return
}
// 得到真正的 v1beta1.AdmissionReview 对象
responseAdmissionReview := &v1beta1.AdmissionReview{}
responseAdmissionReview.SetGroupVersionKind(*gvk)
// 调用回调处理,返回值为 AdmissionReview.Response
responseAdmissionReview.Response = admit.v1beta1(*requestedAdmissionReview)
// 设置好 Response
responseAdmissionReview.Response.UID = requestedAdmissionReview.Request.UID
responseObj = responseAdmissionReview
case v1.SchemeGroupVersion.WithKind("AdmissionReview"):
// v1 版本 AdmissionReview 对象支持
requestedAdmissionReview, ok := obj.(*v1.AdmissionReview)
if !ok {
klog.Errorf("Expected v1.AdmissionReview but got: %T", obj)
return
}
// 得到真正的 v1.AdmissionReview 对象
responseAdmissionReview := &v1.AdmissionReview{}
responseAdmissionReview.SetGroupVersionKind(*gvk)
// 调用回调处理,返回值为 AdmissionReview.Response
responseAdmissionReview.Response = admit.v1(*requestedAdmissionReview)
// 设置好 Response
responseAdmissionReview.Response.UID = requestedAdmissionReview.Request.UID
responseObj = responseAdmissionReview
default:
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Unsupported group version kind: %v", gvk)
klog.Error(msg)
http.Error(w, msg, http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
// 编码 http response
klog.V(2).Info(fmt.Sprintf("sending response: %v", responseObj))
respBytes, err := json.Marshal(responseObj)
if err != nil {
klog.Error(err)
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
// 回复
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
if _, err := w.Write(respBytes); err != nil {
klog.Error(err)
}
}
|
从中我们也可以总结出基本的 Webhook 处理逻辑:
- 读取 HTTP 请求的 body。
- 检查 HTTP 请求的 Content-Type 是否为 application/json。
- 将 body 解析为 AdmissionReview 对象。
- 业务处理,得到 AdmissionReview Response。
- 将回复的 AdmissionReview 对象 JSON 编码。
- 设置好 Content-Type:application/json 后回复。
4.3 业务处理逻辑 admitHandler
在 serve 中看到,抽象了 admitHandler 来进行业务逻辑的处理。其包含处理 v1beta1 与 v1 版本的 AdmissionReview 对象的回调。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
// admitv1beta1Func handles a v1beta1 admission
type admitv1beta1Func func(v1beta1.AdmissionReview) *v1beta1.AdmissionResponse
// admitv1beta1Func handles a v1 admission
type admitv1Func func(v1.AdmissionReview) *v1.AdmissionResponse
// admitHandler 是 Webhook handler 的抽象,需要能够处理 v1beta1 v1 版本 AdmissionReview 对象
type admitHandler struct {
v1beta1 admitv1beta1Func
v1 admitv1Func
}
|
为了让大部分的处理函数仅仅只需要支持 v1 版本的 AdmissionReview 对象,内置了 newDelegateToV1AdmitHandler 函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
// newDelegateToV1AdmitHandler 返回能够自动支持 v1beta1 版本 AdmissionReview 的 Handler
func newDelegateToV1AdmitHandler(f admitv1Func) admitHandler {
return admitHandler{
v1beta1: delegateV1beta1AdmitToV1(f),
v1: f,
}
}
func delegateV1beta1AdmitToV1(f admitv1Func) admitv1beta1Func {
return func(review v1beta1.AdmissionReview) *v1beta1.AdmissionResponse {
in := v1.AdmissionReview{Request: convertAdmissionRequestToV1(review.Request)} // 将 v1beta1 AdmissionReview Request 转换为 v1 版本
out := f(in)
return convertAdmissionResponseToV1beta1(out) // 将 v1 AdmissionReview Response 转换为 v1beta1 版本
}
}
func convertAdmissionRequestToV1(r *v1beta1.AdmissionRequest) *v1.AdmissionRequest {
return &v1.AdmissionRequest{
Kind: r.Kind,
Namespace: r.Namespace,
Name: r.Name,
Object: r.Object,
Resource: r.Resource,
Operation: v1.Operation(r.Operation),
UID: r.UID,
DryRun: r.DryRun,
OldObject: r.OldObject,
Options: r.Options,
RequestKind: r.RequestKind,
RequestResource: r.RequestResource,
RequestSubResource: r.RequestSubResource,
SubResource: r.SubResource,
UserInfo: r.UserInfo,
}
}
func convertAdmissionResponseToV1beta1(r *v1.AdmissionResponse) *v1beta1.AdmissionResponse {
var pt *v1beta1.PatchType
if r.PatchType != nil {
t := v1beta1.PatchType(*r.PatchType)
pt = &t
}
return &v1beta1.AdmissionResponse{
UID: r.UID,
Allowed: r.Allowed,
AuditAnnotations: r.AuditAnnotations,
Patch: r.Patch,
PatchType: pt,
Result: r.Result,
Warnings: r.Warnings,
}
}
|
通过提供的 convert 相关函数,我们所有的 Webhook 业务逻辑仅仅只需要支持 v1 AdmissionReview 即可。
4.4 业务逻辑
4.4.1 Validate
对请求进行 Validate,并允许请求。核心就是设置 Reponse.Allowed 字段:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
// alwaysAllowDelayFiveSeconds 是一个 v1 AdmissionReview Handler,sleep 5s 后返回 allowed response
func alwaysAllowDelayFiveSeconds(ar v1.AdmissionReview) *v1.AdmissionResponse {
klog.V(2).Info("always-allow-with-delay sleeping for 5 seconds")
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
klog.V(2).Info("calling always-allow")
reviewResponse := v1.AdmissionResponse{}
reviewResponse.Allowed = true // 设置 Response.Allowed 为 true,表明请求允许
reviewResponse.Result = &metav1.Status{Message: "this webhook allows all requests"}
return &reviewResponse
}
|
拒绝请求也是类似:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
// alwaysDeny 拒绝所有请求
func alwaysDeny(ar v1.AdmissionReview) *v1.AdmissionResponse {
klog.V(2).Info("calling always-deny")
reviewResponse := v1.AdmissionResponse{}
reviewResponse.Allowed = false // 返回 allowed 为 false 表明拒绝请求
reviewResponse.Result = &metav1.Status{Message: "this webhook denies all requests"}
return &reviewResponse
}
|
复杂一点,就需要通过编码器对 Request.Object.Raw 进行解析,得到一个具体的 Resource 对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
// admitPods 检查 Pod 的 image
func admitPods(ar v1.AdmissionReview) *v1.AdmissionResponse {
// 判断资源是否是 Pod
klog.V(2).Info("admitting pods")
podResource := metav1.GroupVersionResource{Group: "", Version: "v1", Resource: "pods"}
if ar.Request.Resource != podResource {
err := fmt.Errorf("expect resource to be %s", podResource)
klog.Error(err)
return toV1AdmissionResponse(err)
}
// 解码,解析为 Pod
raw := ar.Request.Object.Raw
pod := corev1.Pod{}
deserializer := codecs.UniversalDeserializer()
if _, _, err := deserializer.Decode(raw, nil, &pod); err != nil {
klog.Error(err)
return toV1AdmissionResponse(err)
}
reviewResponse := v1.AdmissionResponse{}
reviewResponse.Allowed = true
var msg string
if v, ok := pod.Labels["webhook-e2e-test"]; ok {
if v == "webhook-disallow" {
reviewResponse.Allowed = false
msg = msg + "the pod contains unwanted label; "
}
if v == "wait-forever" {
reviewResponse.Allowed = false
msg = msg + "the pod response should not be sent; "
<-make(chan int) // Sleep forever - no one sends to this channel
}
}
for _, container := range pod.Spec.Containers {
if strings.Contains(container.Name, "webhook-disallow") {
reviewResponse.Allowed = false
msg = msg + "the pod contains unwanted container name; "
}
}
if !reviewResponse.Allowed {
reviewResponse.Result = &metav1.Status{Message: strings.TrimSpace(msg)}
}
return &reviewResponse
}
|
对于 Subresource 的请求,就需要用到 Request.SubResource,以及明确 HTTP body 的内容:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
// denySpecificAttachment 检查 Pod attch 参数
func denySpecificAttachment(ar v1.AdmissionReview) *v1.AdmissionResponse {
klog.V(2).Info("handling attaching pods")
if ar.Request.Name != "to-be-attached-pod" {
return &v1.AdmissionResponse{Allowed: true}
}
// 检查 Resource 为 Pod
podResource := metav1.GroupVersionResource{Group: "", Version: "v1", Resource: "pods"}
if e, a := podResource, ar.Request.Resource; e != a {
err := fmt.Errorf("expect resource to be %s, got %s", e, a)
klog.Error(err)
return toV1AdmissionResponse(err)
}
// 检查请求的 SubResource 为 attach
if e, a := "attach", ar.Request.SubResource; e != a {
err := fmt.Errorf("expect subresource to be %s, got %s", e, a)
klog.Error(err)
return toV1AdmissionResponse(err)
}
// 解码,转变为 PodAttachOptions
raw := ar.Request.Object.Raw
podAttachOptions := corev1.PodAttachOptions{}
deserializer := codecs.UniversalDeserializer()
if _, _, err := deserializer.Decode(raw, nil, &podAttachOptions); err != nil {
klog.Error(err)
return toV1AdmissionResponse(err)
}
// validate
klog.V(2).Info(fmt.Sprintf("podAttachOptions=%#v\n", podAttachOptions))
if !podAttachOptions.Stdin || podAttachOptions.Container != "container1" {
return &v1.AdmissionResponse{Allowed: true}
}
return &v1.AdmissionResponse{
Allowed: false,
Result: &metav1.Status{
Message: "attaching to pod 'to-be-attached-pod' is not allowed",
},
}
}
|
4.4.2 Mutate
Mutate 可以在 Validate 基础上可以对对象进行修改,核心是设置好 Response.Patch 与 Response.PatchType 字段。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
const (
podsInitContainerPatch string = `[
{"op":"add","path":"/spec/initContainers","value":[{"image":"webhook-added-image","name":"webhook-added-init-container","resources":{}}]}
]`
)
// mutatePods 对请求进行修改,添加一个 container
func mutatePods(ar v1.AdmissionReview) *v1.AdmissionResponse {
shouldPatchPod := func(pod *corev1.Pod) bool {
if pod.Name != "webhook-to-be-mutated" {
return false
}
return !hasContainer(pod.Spec.InitContainers, "webhook-added-init-container")
}
return applyPodPatch(ar, shouldPatchPod, podsInitContainerPatch)
}
func applyPodPatch(ar v1.AdmissionReview, shouldPatchPod func(*corev1.Pod) bool, patch string) *v1.AdmissionResponse {
klog.V(2).Info("mutating pods")
podResource := metav1.GroupVersionResource{Group: "", Version: "v1", Resource: "pods"}
if ar.Request.Resource != podResource {
klog.Errorf("expect resource to be %s", podResource)
return nil
}
raw := ar.Request.Object.Raw
pod := corev1.Pod{}
deserializer := codecs.UniversalDeserializer()
if _, _, err := deserializer.Decode(raw, nil, &pod); err != nil {
klog.Error(err)
return toV1AdmissionResponse(err)
}
reviewResponse := v1.AdmissionResponse{}
reviewResponse.Allowed = true
if shouldPatchPod(&pod) {
reviewResponse.Patch = []byte(patch) // 添加 Patch(json 对 []byte 会自动 base64)
pt := v1.PatchTypeJSONPatch
reviewResponse.PatchType = &pt // 添加 PatchType
}
return &reviewResponse
}
|
参考