Kubernetes 编程系列 主要记录一些开发 Controller 所相关的知识,大部分内容来自于《Programming Kubernetes》(推荐直接阅读)。
1 自定义资源定义
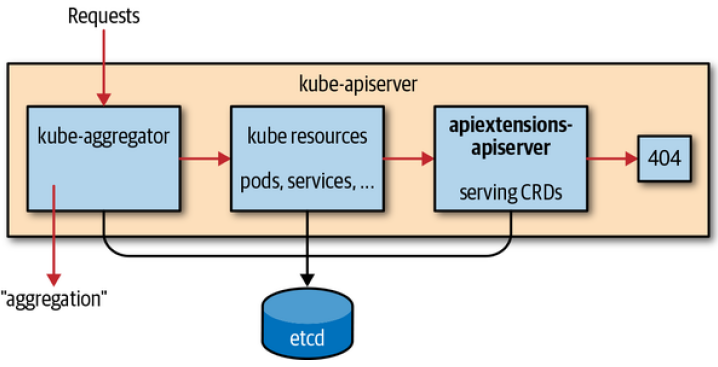
从 1.7 版本开始,Kubernetes 提供了 CR 的功能,CR 会与其他元素的 Kubernetes 资源存放在同一个 etcd 中,并由 APISever 为其提供 HTTP API 服务。
具体实现上,APIServer 中的 apiextensions-apiserver 会对 CR 相关的 HTTP 请求进行处理:

CR 由 CustomResourceDefinition(简称 CRD)来定义,其本身就是一种 Kubernetes 资源,用于描述可以在当前集群使用的 CR。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ats.cnat.programming-kubernetes.info
spec:
group: cnat.programming-kubernetes.info
names:
kind: At
listKind: AtList
plural: ats
singular: at
scope: Namespaced
subresources:
status: {}
version: v1alpha1
versions:
- name: v1alpha1
served: true
storage: true
|
关于 CR 与 CRD 更多的信息见 K8s 学习 - CRD。
2 服务发现信息
当部署 CRD 后,kubectl 就可以发现对应的 CR 了。一个关键的问题是:kubectl 如何发现一个新的 CR 的?
通过如下命令卡其 kubectl 执行日志,我们可以了解具体的细节:
1
|
$ kubectl get tidbcluster -v=7
|
-
kubectl 通过请求 APIServer 的 /apis 查询所有的 API Group。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
$ curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" --insecure $APISERVER/apis
{
"kind": "APIGroupList",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"groups": [
{
"name": "apiregistration.k8s.io",
"versions": [
{
"groupVersion": "apiregistration.k8s.io/v1",
"version": "v1"
},
{
"groupVersion": "apiregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1",
"version": "v1beta1"
}
],
"preferredVersion": {
"groupVersion": "apiregistration.k8s.io/v1",
"version": "v1"
}
},
// ...
|
-
对于所有的 API Group,请求一次 /apis/group/version 查询该 GroupVersion 下支持的所有 Resource。找到符合命名对应的 Resource。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
$ curl --insecure -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" $APISERVER/apis/pingcap.com/v1alpha1
{
"kind": "APIResourceList",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"groupVersion": "pingcap.com/v1alpha1",
"resources": [
{
"name": "tidbclusters",
"singularName": "tidbcluster",
"namespaced": true,
"kind": "TidbCluster",
"verbs": [
"delete",
"deletecollection",
"get",
"list",
"patch",
"create",
"update",
"watch"
],
"shortNames": [
"tc"
],
"storageVersionHash": "2dlERqlmc8s="
},
// ...
|
-
kubectl 将获取到的信息转换为三元组:
- Group(如 pingcap.com)
- Version(如 v1alpha1)
- Resource(如 tidbclusters)
可以想到,这些映射关系在代码中都是靠着 RESTMapper 实现的。
kubectl 的缓存
kubectl 还会在 `~/.kube/cache" 目录中缓存一份 Resource 的列表,有效期为 10min。
所以如何 CRD 发生变化,最多需要 10min 才会在 CLI 中体现出来。
3 CustomResourceDefinition
3.1 基本定义
3.2 高级功能
3.2.1 CRD 合法性验证
创建和更新 CR 时,会由 APIServer 进行合法性验证。该验证基于 CRD 定义中的 validation 字段所指定的 OpenAPI v3 Schema 进行。
更复杂的验证
CRD 中的验证只能做到类型与值的合法性验证,如果需要更复杂的验证,可以通过 Admission Webhook 做到。Webhook 会在基于 OpenAPI 的验证逻辑完成后立即被调用。
在 1.14 之前,OpenAPI v3 Schema 是可选的,也就是可以不用在 Schema 中指定所有的字段。
从 1.15 开始,CRD Schema 会作为 Kubernetes APIServer 的 OpenAPI 一部分发布,当使用 kubectl 时,它将用于客户端验证,可以及时发现未定义的字段。例如,用于在对象中使用了 foo:bar 类型,但是 OpenAPI Schema 中却没有定义 foo 类型,那么 kubectl 就会拒绝该对象。
未来,未在 Schema 中指定过的字段也将不会被持久化,因此必须为 CRD 指定 OpenAPI Schema 来保证其合法性。
3.2.2 ShortName 与 Category
CRD 也可以使用 ShortName,也称为别名。一种资源可以由多个别名。
kubectl api-resource 命令可以列出所有短名字:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
$ kubectl api-resource
NAME SHORTNAMES APIVERSION NAMESPACED KIND
bindings v1 true Binding
componentstatuses cs v1 false ComponentStatus
configmaps cm v1 true ConfigMap
endpoints ep v1 true Endpoints
events ev v1 true Event
limitranges limits v1 true LimitRange
namespaces ns v1 false Namespace
|
CRD 中也可以指定 categories 字段,加入一个类别。这样 kubectl get <category> 就可以列出一个类别下的所有资源了。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
metadata:
name: ats.cnat.programming-kubernetes.info
spec:
# ...
categories:
- all
|
3.2.3 打印列
3.2.4 SubResource
SubResource 是一个特殊的 HTTP Endpoint,在普通资源的 HTTP API Path 后加上一个后缀得到的,例如 /logs、/portforward、/exec 等。
目前 CRD 支持两种 SubResource:/scale 与 /status。
(1) Status
/status 用于用户将 CR 实例的 spec 与 status 字段权限隔离。因为:
- 用户一般不会更新 status 字段。
- Controller 不应该更新 spec 字段。
RBAC 无法做到控制这两个字段的权限,而引入 /status SubResource 用于解决这个问题。启用 status SubResource 后,status 的更新与读取就会基于 /status API,而 RBAC 可以做到控制 HTTP endpoint 的权限。
也就是说,RBAC + status SubResource 实现了 spec 与 status 字段的权限隔离。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata: # ...
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["ats/status"]
verbs: ["update", "patch"]
|
当你开启 status Resource 时,你需要注意的一些变化:
- 主 HTTP Endpoint 上创建或更新资源时,会自动忽略 status 字段的值。
- 对应的, /status HTTP Endpoint 的任何操作都会忽略 status 字段以外的值。
- 当 metadata 和 status 以外的字段值发生变化时,才会递增 metadata.generation 字段的值(这表明了 spec 发生变化)。
你可以通过如下方式为 CRD 开启 status SubResource:
1
2
3
4
5
|
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
spec:
subresources:
status: {}
|
WARN
可以看到,启动 status 子资源会导致更新 status 字段的 HTTP API 发生变化。这就表明了,你不能开启 /status SubResource 后热更新 CRD,因为正在运行中的 Controller 还是会请求主 HTTP Endpoint 来更新 status 字段,而更新后这将失败。
对此,你可能需要升级 CRD 的版本。例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
spec:
# ...
versions:
- name: v1alpha1
served: true
storage: true
- name: v1beta1
served: true
subresources:
status: {}
|
(2) Scale
scale 子资源用于查看或修改资源中定义的副本数量。这个子资源主要是用于类似 Deployment 和 ReplicaSet 这样有副本数的资源,通过它可以对资源进行扩容和缩容。
kubectl scale 就是通过 /scale 子资源来实现的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
$ kubectl scale --replicas=3 your-custom-resource -v=7
I0429 21:17:53.138353 66743 round_trippers.go:383] PUT https://host/apis/group/v1/your-custom-resource/scale
apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: CustomResourceDefinition
spec:
subresources:
scale:
specReplicasPath: .spec.replicas
statusReplicasPath: .status.replicas
labelSelectorPath: .status.labelSelector
...
|
当然,/scale 只能修改 replica 的值,而其具体的操作还是需要自定义 Controller 实现的。
/scale HTTP Endpoint 读取或写入的对象 Kind 为 Scale,属于 autoscaling/v1 APIGroup。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
// Scale represents a scaling request for a resource.
type Scale struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
// Standard object metadata; More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata.
// +optional
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
// defines the behavior of the scale. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status.
// +optional
Spec ScaleSpec `json:"spec,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=spec"`
// current status of the scale. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status. Read-only.
// +optional
Status ScaleStatus `json:"status,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=status"`
}
// ScaleSpec describes the attributes of a scale subresource
type ScaleSpec struct {
// desired number of instances for the scaled object.
// +optional
Replicas int32 `json:"replicas,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=replicas"`
}
// ScaleStatus represents the current status of a scale subresource.
type ScaleStatus struct {
// actual number of observed instances of the scaled object.
Replicas int32 `json:"replicas" protobuf:"varint,1,opt,name=replicas"`
// label query over pods that should match the replicas count. More info: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/labels#label-selectors
// +optional
Selector map[string]string `json:"selector,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,rep,name=selector"`
// label selector for pods that should match the replicas count. This is a serializated
// version of both map-based and more expressive set-based selectors. This is done to
// avoid introspection in the clients. The string will be in the same format as the
// query-param syntax. If the target type only supports map-based selectors, both this
// field and map-based selector field are populated.
// More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/labels/#label-selectors
// +optional
TargetSelector string `json:"targetSelector,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=targetSelector"`
}
|
同样,/scale 子资源的更新也是乐观并发语义。
4 代码中使用 CR
在 Golang 中有着以下方式可以访问 CR:
- 使用
client-go 的 dynamic client(无强类型)。
kubernetes/controller-runtime 提供的 client,在 Operator SDK 与 Kubebuilder 中使用。- client-gen 生成的 client,与 client-go 包中使用的一样。
4.1 dynamic client
k8s.io/client-go/dynamic 中提供了 Client 可以对 GVK 完全无感知。它只会使用 unstructured.Unstructured 结构。
dynamic client 不使用 Scheme 与 RESTMapper,需要手动进行 GVR 的注册。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
gvr := schema.GroupVersionResource{
Group: "apps",
Version: "v1",
Resource: "deployments",
}
client, err := NewForConfig(cfg)
client.Resource(gvr).
Namespace(namespace).Get("foo", metav1.GetOptions{})
|
其输入与输出都是 *unstructured.Unstructured 对象,数据结构与 json.Unmarshal 反序列化后输出一样:
- 对象通过
map[string]interface{} 表示。
- 数组通过
[]interface{} 表示。
- 基础数据类型为:string、bool、float64、int64。
UnstructuredContent() 提供了访问 unstructed 对象内部数据的功能:
1
|
name, found, err := unstructured.NestedString(u.Object, "metadata", "name")
|
可以看到,dynamic client 提供了一种抽象访问资源的方法,因此主要在通用类型的控制器中使用。例如垃圾回收控制器,可以删除任何资源进行操作,所以需要 dynamic client。
4.2 强类型 client
强类型 client 为每种 GVK 都采用了具体的 Golang 类。它们使用起来更方便,也能更加安全。不过因为其类都需要在编译期都确定,所以需要通过工具去生成对应的类。
4.2.1 类型风格
对应资源的结构体通常与 Kind 相同名字命名,并且放在所属 GVK 的 Group + Version 对应包中。例如,group/verion.Kind 会放在包 pkg/apis/group/version。
通常,对应的结构体会放在 types.go" 文件。如之前提到的,CR 的定义也要包含 TypeMeta 与 ObjectMeta 结构体,通常也会包含 Spec 与 Status 字段。
例如 Deployment 对象放在 k8s.io/kubernetes/apps/v1/types.go 文件里:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
type Deployment struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty"`
Spec DeploymentSpec `json:"spec,omitempty"`
Status DeploymentStatus `json:"status,omitempty"`
}
|
4.2.2 包结构
除了 types.go 文件,还需要了解一些其他文件。
doc.go 文件描述 API 的功能,并包含了一系列全局的代码生成标签:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
// Package v1alpha1 contains the cnat v1alpha1 API group
//
// +k8s:deepcopy-gen=package
// +groupName=cnat.programming-kubernetes.info
package v1alpha1
|
register.go 文件包含一些用于把 CRD 注册到 Scheme 中的辅助函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
package version
import (
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime/schema"
group "repo/pkg/apis/group"
)
// SchemeGroupVersion is group version used to register these objects var SchemeGroupVersion = schema.GroupVersion{
Group: group.GroupName,
Version: "version",
}
// Kind takes an unqualified kind and returns back a Group qualified GroupKind
func Kind(kind string) schema.GroupKind {
return SchemeGroupVersion.WithKind(kind).GroupKind()
}
// Resource takes an unqualified resource and returns a Group
// qualified GroupResource
func Resource(resource string) schema.GroupResource {
return SchemeGroupVersion.WithResource(resource).GroupResource()
}
var (
SchemeBuilder = runtime.NewSchemeBuilder(addKnownTypes)
AddToScheme = SchemeBuilder.AddToScheme
)
// Adds the list of known types to Scheme.
func addKnownTypes(scheme *runtime.Scheme) error {
scheme.AddKnownTypes(SchemeGroupVersion,
&SomeKind{},
&SomeKindList{},
)
metav1.AddToGroupVersion(scheme, SchemeGroupVersion)
return nil
}
|
zz_generated.deepcopy.go 为自定义资源对应的类定义了 DeepCopy() 方法,包括其所有的子结构体(例如 spec 与 status)。
4.3 controller-runtime client
controller-runtime 提供的 client 用于处理任何在 Scheme 中注册的 Kind,也就是说,它也是动态的。
它使用 APIServer 提供的发现信息,将不同的 Kind 映射到不同的 HTTP API Path 上。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
import (
"flag"
corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes/scheme"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
runtimeclient "sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/client"
)
// 读取 config
kubeconfig = flag.String("kubeconfig", "~/.kube/config", "kubeconfig file
path")
flag.Parse()
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", *kubeconfig)
// 创建 client
cl, _ := runtimeclient.New(config, client.Options{
Scheme: scheme.Scheme,
})
// 查找 Pods
podList := &corev1.PodList{}
err := cl.List(context.TODO(), client.InNamespace("default"), podList)
|
- 可以看到,List() 方法可以作用于任意指定 Scheme 中注册过的,将结果解析到传递的类型中。
对于 CR,通过自定义的 Scheme 创建 client 即可:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
import (
"flag"
corev1 "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes/scheme"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
runtimeclient "sigs.k8s.io/controller-runtime/pkg/client"
cnatv1alpha1 "github.com/.../cnat/cnat-kubebuilder/pkg/apis/cnat/v1alpha1"
)
kubeconfig = flag.String("kubeconfig", "~/.kube/config", "kubeconfig file")
flag.Parse()
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", *kubeconfig)
// 注册 CR Scheme
crScheme := runtime.NewScheme()
cnatv1alpha1.AddToScheme(crScheme)
// 创建 client
cl, _ := runtimeclient.New(config, client.Options{
Scheme: crScheme,
})
// 操作 CR
list := &cnatv1alpha1.AtList{}
err := cl.List(context.TODO(), client.InNamespace("default"), list)
|
参考