Kubernetes 编程系列 主要记录一些开发 Controller 所相关的知识,大部分内容来自于《Programming Kubernetes》(推荐直接阅读)。
1 核心代码库
1.1 k8s.io/client-go
编写 Operator 代码时,最核心的库就是 k8s.io/client-go,其提供了访问 Kubernetes 最基本的 client 实现。
client-go 与 Kubernetes 同时发布,对应 Kubernetes 1.x.y 版本就会有着对应的 client-go 版本。不过 client-go 还会发布独立的版本号,例如 client-go 9.0.0。
1.2 k8s.io/api
k8s.io/api 库包含了所有 Kubernetes 基本对象的结构体,其按照 GroupVersion 进行组织。
例如 Pod 一类的最基本的对象,包含在 core Group 中,因此放在 k8s.io/api/core/v1 包中的 types.go 文件中。其他对象也是类似。

1.3 k8s.io/apimachinery
k8s.io/apimachinery 提供了 Kubernetes API 所需要的一些通用代码。
apimachinery 也包含了很多通用的 API 类型,例如 ObjectMeta、TypeMeta、GetOptions。
Tip
因为 API Machinery 的设计优秀,你可以在任何 API 相关的业务代码上尝试使用该库。
2 使用 client-go
2.1 创建并使用
下面是最基本在一个 Go 项目中使用 client-go 的方式(省略了异常处理):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import (
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes"
)
// 读取 config
kubeconfig = flag.String("kubeconfig", "~/.kube/config", "kubeconfig file")
flag.Parse()
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", *kubeconfig)
// 创建 client set
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
// 通过 client set 访问资源
pod, err := clientset.CoreV1().Pods("book").Get("example", metav1.GetOptions{})
|
在项目中,所有的资源(包括 CR)都是通过 ClientSet 类的对象来访问。ClientSet 包含了多个 Group 多个 Version 的 Client。
在集群内部 Pod 中,每个容器会挂载一个 ServiceAccount,路径为目录 /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount。通过该目录下提供的证书与 Token,可以替代 kubeconfig 文件来创建 ClientSet,用于访问 Kubernetes。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
// 读取 ServiceAccount 的目录创建 config
config, err := rest.InClusterConfig()
if err != nil {
// 回滚使用 kubeconfig 文件创建 config
kubeconfig := filepath.Join("~", ".kube", "config")
if envvar := os.Getenv("KUBECONFIG"); len(envvar) >0 {
kubeconfig = envvar
}
config, err = clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", kubeconfig)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("The kubeconfig cannot be loaded: %v\n", err
os.Exit(1)
}
}
// 创建 client set
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
|
默认下所有 Client 以 JSON 格式与 APIServer 进行通信,你可以通过以下方式使用 Protobuf 格式:
1
2
3
4
|
cfg, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", *kubeconfig)
cfg.AcceptContentTypes = "application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf,application/json" // 允许回复的格式
cfg.ContentType = "application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf" // 发送请求的格式
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(cfg)
|
2.2 版本与兼容性
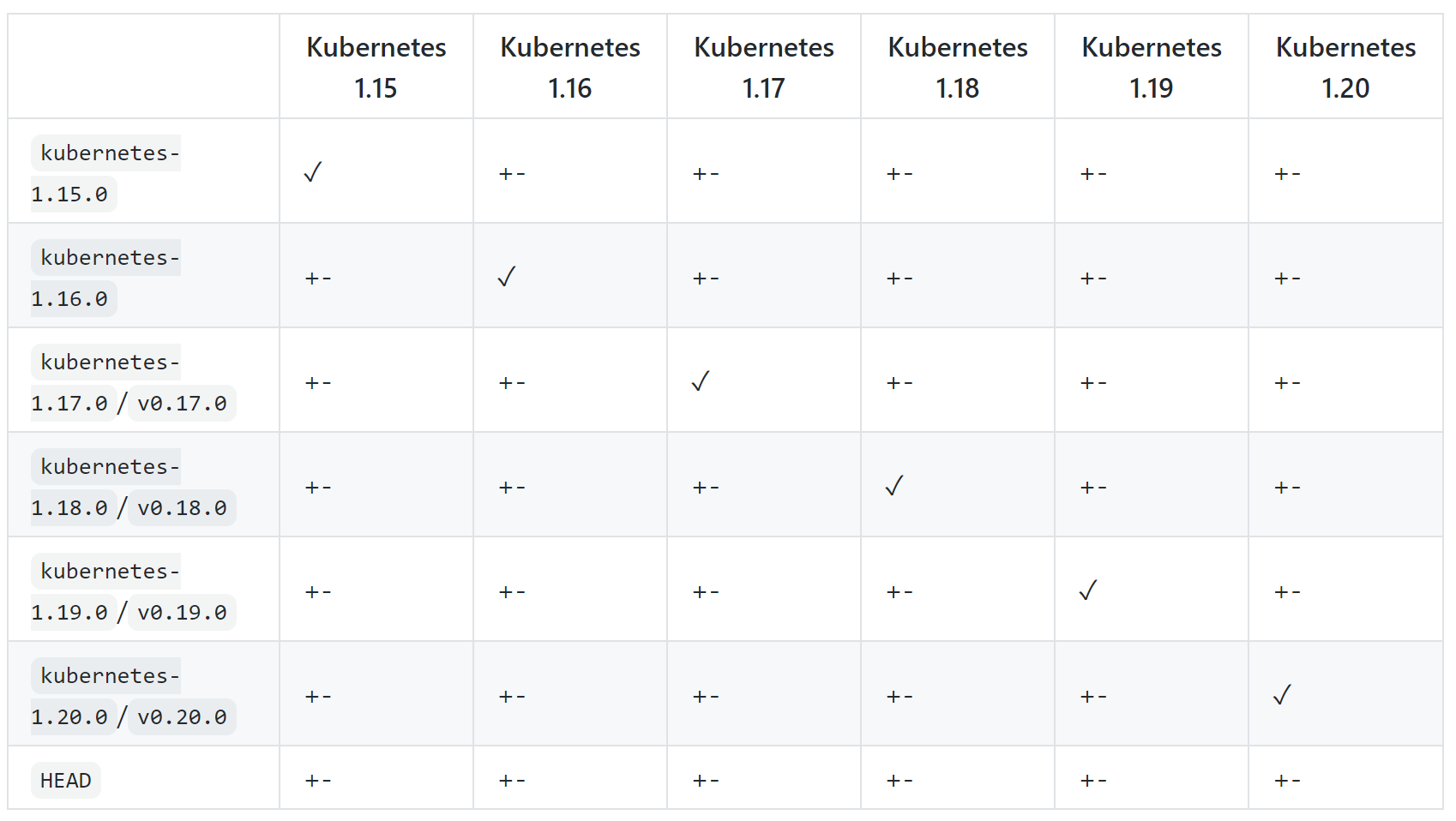
可以看到,ClientSet 使用的资源类型都是静态通过 api 库导入的,与 APIServer 使用的资源类型没有直接关系。也就是说,如果 client-go 库与 Kubernetes APIServer 对应的版本不同,那么就可能双方使用的资源定义不同。
为此,client-go 仓库的 README 中,会发布一个兼容性矩阵。

- √ 表示 client-go 与 Kubernetes 集群有着完全相同的 API 组版本。
- + 表示 client-go 包含一些功能或者 API 对象,Kubernetes 集群还不支持。不过公共的部分还是能够正常工作。
- - 表示 Kubernetes 的一些特性 client-go 不能使用。不过大部分公共的部分能够正常工作。
因此,当你使用的 client-go 库与 Kubernetes 版本不一致时,需要清楚某些特性是否能够兼容。
2.3 API 兼容性保证
在 Kubernetes 风格中,API 可能包含以下版本:
-
Alpha - v1alpha1、v1aplpha2 等称为 Alpha 版本,表示不稳定的版本。
这些版本可能随时会消失或者进行不兼容的改变。默认是被禁用的,需要管理员手动启用它们。
-
Beta - v1beta1、v1beta2、v2beta1 等称为 Beta 版本,表示相对稳定的版本。
通常不会发生不兼容的改动,但是不是严格保证。Beta 版本功能默认会被启用。
-
GA - v1、v2 等不带后缀的都是稳定版本。
会一直存在,并且一直保持兼容性。
在进行项目开发时,要记住两点:
-
代码中一个资源定义的某些字段也可能准许上述版本定义(注释中说明)。
-
访问 APIServer 时,APIServer 会在相同的资源不同版本间自动进行转换。
例如,某个资源是由 v1beta1 版本的 API 创建的,但是你可以通过 v1 版本的 API 来访问该资源。
3 Kubernetes 对象
3.1 Object
Go 语言中的 Kubernetes 对象都实现了 runtime.Object interface,该接口位于 k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime 包:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
// Object interface must be supported by all API types registered with Scheme. Since objects in a scheme are
// expected to be serialized to the wire, the interface an Object must provide to the Scheme allows
// serializers to set the kind, version, and group the object is represented as. An Object may choose
// to return a no-op ObjectKindAccessor in cases where it is not expected to be serialized.
type Object interface {
GetObjectKind() schema.ObjectKind
DeepCopyObject() Object
}
|
GetObjectKind() - 得到 ObjectKind,用以返回或设置 GVKDeepCopyObject() - 深拷贝得到一个 Object
schema.ObjectKind 就是代表一个具有 Kind 的 Object:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
// All objects that are serialized from a Scheme encode their type information. This interface is used
// by serialization to set type information from the Scheme onto the serialized version of an object.
// For objects that cannot be serialized or have unique requirements, this interface may be a no-op.
type ObjectKind interface {
// SetGroupVersionKind sets or clears the intended serialized kind of an object. Passing kind nil
// should clear the current setting.
SetGroupVersionKind(kind GroupVersionKind)
// GroupVersionKind returns the stored group, version, and kind of an object, or an empty struct
// if the object does not expose or provide these fields.
GroupVersionKind() GroupVersionKind
}
|
SetGroupVersionKind() - 设置 Object 的 GVKGroupVersionKind() - 得到 Object 的 GVK
总结一下,Object 对象可以得到对应的 Kind,以及允许进行深拷贝。
Object 仅仅是一个 interface,所有实际的 Kubernetes 对象都是通过内嵌 metav1.TypeMeta 结构来包含 GroupVersionKind 方法的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
// TypeMeta describes an individual object in an API response or request
// with strings representing the type of the object and its API schema version.
// Structures that are versioned or persisted should inline TypeMeta.
//
// +k8s:deepcopy-gen=false
type TypeMeta struct {
// Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object represents.
// Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits requests to.
// Cannot be updated.
// In CamelCase.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds
// +optional
Kind string `json:"kind,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=kind"`
// APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object.
// Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal value, and
// may reject unrecognized values.
// More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources
// +optional
APIVersion string `json:"apiVersion,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=apiVersion"`
}
func (obj *TypeMeta) GetObjectKind() schema.ObjectKind { return obj }
|
Kind - 对象的类型;APIVersion - 对象的 API 版本;
这也就是你在资源定义 YAML 时看到的 apiVersion 与 kind 字段了:
1
2
3
|
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
# ...
|
Core Group Version
Pod 以及一些其他类型是 Kubernetes 很早就有的 Core Group,它们的 Group 为空,因此 apiVersion 就是 v1。
后来,Kubernetes 引入了 API Group 的概念,apiVersion 通过 <Group>/<version> 表示,例如 apps/v1。
而 Core Group 因为历史原因其 Group 为空,所以 apiVersion 的值看上去可能不太一样。
不要直接使用 Kind 与 Version 字段
在前面使用示例获取 Pod 后,你会发现返回的 Pod 对象并没有设置 Kind 与 Version 字段。这是 Kubernetes 在解码时故意抹去的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
// Decode does not do conversion. It removes the gvk during deserialization.
func (d WithoutVersionDecoder) Decode(data []byte, defaults *schema.GroupVersionKind, into Object) (Object, *schema.GroupVersionKind, error) {
obj, gvk, err := d.Decoder.Decode(data, defaults, into)
if obj != nil {
kind := obj.GetObjectKind()
// clearing the gvk is just a convention of a codec
kind.SetGroupVersionKind(schema.GroupVersionKind{})
}
return obj, gvk, err
}
|
不清楚为啥,目前可以通过这个 issue 跟进这个问题。
除了 TypeMeta,所有的对象都有一个 metav1.ObjectMeta 类型的字段:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
// ObjectMeta is metadata that all persisted resources must have, which includes all objects
// users must create.
type ObjectMeta struct {Clayton Coleman, 5 years ago: • iQEcBAABCAAGBQJYfoneAAoJED0WkGtPHFyzBGEH/ROj…
Name string `json:"name,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=name"`
GenerateName string `json:"generateName,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=generateName"`
Namespace string `json:"namespace,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=namespace"`
// DEPRECATED
SelfLink string `json:"selfLink,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=selfLink"`
UID types.UID `json:"uid,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,5,opt,name=uid,casttype=k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/types.UID"`
ResourceVersion string `json:"resourceVersion,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,6,opt,name=resourceVersion"`
Generation int64 `json:"generation,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,7,opt,name=generation"`
CreationTimestamp Time `json:"creationTimestamp,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,8,opt,name=creationTimestamp"`
DeletionTimestamp *Time `json:"deletionTimestamp,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,9,opt,name=deletionTimestamp"`
DeletionGracePeriodSeconds *int64 `json:"deletionGracePeriodSeconds,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,10,opt,name=deletionGracePeriodSeconds"`
Labels map[string]string `json:"labels,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,11,rep,name=labels"`
Annotations map[string]string `json:"annotations,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,12,rep,name=annotations"`
OwnerReferences []OwnerReference `json:"ownerReferences,omitempty" patchStrategy:"merge" patchMergeKey:"uid" protobuf:"bytes,13,rep,name=ownerReferences"`
Finalizers []string `json:"finalizers,omitempty" patchStrategy:"merge" protobuf:"bytes,14,rep,name=finalizers"`
ClusterName string `json:"clusterName,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,15,opt,name=clusterName"`
ManagedFields []ManagedFieldsEntry `json:"managedFields,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,17,rep,name=managedFields"`
}
|
-
Name - Object 的命名。
-
GenerateName - 生成基于 GenerateName 的随机名字,填充到 Name。
-
Namespace - 对象所属的 namespace,对于 namespace 下的对象,空代表着 “default”。
-
UID - 对象的的唯一 ID。
系统填充,只读不允许更改。
-
ResourceVersion - 对象的版本号,可用于 client 判断资源是否发生变更。
可以用于乐观并发,变更检测,watch 操作时使用,client 必须将其原封不动传递给 APIServer。
系统填充,只读不允许更改。
-
Generation - 资源期望状态的序列号。
系统填充,只读不允许更改。
-
CreationTimestamp - Server 创建对象的时间。
系统填充,只读不允许更改。
-
DeletionTimestamp - 对象将被删除的时间。
当用户优雅删除一个资源时,由系统设置。资源将预计在该时间后被删除。
如果存在着 finalizer,删除会阻塞等待 finalizer 去除。
一旦调用删除之后,无法取消删除。
-
DeletionGracePeriodSeconds - 优雅停止时间。当 DeletionTimestamp 设置时才会设置。
-
Labels - 对象的 label。
-
Annotations - 对象的 annotation。
-
OwnerReferences - 此对象依赖的对象的列表。
如果列表中所有的对象都被删除,该对象也会被垃圾回收。
如果该对象要由 Controller 来管理,将列表中其中一个对象指向 Controller,并设置 controler 字段。
-
Finalizers - 在对象被集群删除前,Finalizers 必须为空。
一旦 DeletionTimestamp 被设置后,表明组件可以开始进行清理操作,清理完成后删除对应的 Finalizer。
-
ClusterName - 对象所属的集群名字,用于区分不同集群内同名同 namespace 的资源。
目前该资源没有被 APIServer 使用到。
-
ManagedFields - Server Side Apply 使用的字段管理
3.4 Spec 与 Status
几乎所有顶级对象都包含 spec 与 status 字段,这体现了 Kubernetes 的声明式 API 设计。
spec 是用户期望的对象的状态,status 是对象的当前状态。
spec 通常由用户部署时配置,status 主要由系统中的 Controller 进行填充。
4 ClientSet
在前面的例子,通过 kubernetes.NewForConfig(config) 会返回一个 ClientSet。ClientSet 包含可以访问多个 APIGroup 的资源。
对于 client-go 返回的 ClientSet,几乎可以访问 Kubernetes APIServer 的所有资源(除了 APIService 与 CRD)。其主要的接口如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
type Interface interface {
Discovery() discovery.DiscoveryInterface
AdmissionregistrationV1() admissionregistrationv1.AdmissionregistrationV1Interface
AdmissionregistrationV1beta1() admissionregistrationv1beta1.AdmissionregistrationV1beta1Interface
InternalV1alpha1() internalv1alpha1.InternalV1alpha1Interface
AppsV1() appsv1.AppsV1Interface
AppsV1beta1() appsv1beta1.AppsV1beta1Interface
AppsV1beta2() appsv1beta2.AppsV1beta2Interface
AuthenticationV1() authenticationv1.AuthenticationV1Interface
AuthenticationV1beta1() authenticationv1beta1.AuthenticationV1beta1Interface
AuthorizationV1() authorizationv1.AuthorizationV1Interface
AuthorizationV1beta1() authorizationv1beta1.AuthorizationV1beta1Interface
AutoscalingV1() autoscalingv1.AutoscalingV1Interface
AutoscalingV2beta1() autoscalingv2beta1.AutoscalingV2beta1Interface
AutoscalingV2beta2() autoscalingv2beta2.AutoscalingV2beta2Interface
BatchV1() batchv1.BatchV1Interface
BatchV1beta1() batchv1beta1.BatchV1beta1Interface
CertificatesV1() certificatesv1.CertificatesV1Interface
CertificatesV1beta1() certificatesv1beta1.CertificatesV1beta1Interface
CoordinationV1beta1() coordinationv1beta1.CoordinationV1beta1Interface
CoordinationV1() coordinationv1.CoordinationV1Interface
CoreV1() corev1.CoreV1Interface
DiscoveryV1() discoveryv1.DiscoveryV1Interface
DiscoveryV1beta1() discoveryv1beta1.DiscoveryV1beta1Interface
EventsV1() eventsv1.EventsV1Interface
EventsV1beta1() eventsv1beta1.EventsV1beta1Interface
ExtensionsV1beta1() extensionsv1beta1.ExtensionsV1beta1Interface
FlowcontrolV1alpha1() flowcontrolv1alpha1.FlowcontrolV1alpha1Interface
FlowcontrolV1beta1() flowcontrolv1beta1.FlowcontrolV1beta1Interface
NetworkingV1() networkingv1.NetworkingV1Interface
NetworkingV1beta1() networkingv1beta1.NetworkingV1beta1Interface
NodeV1() nodev1.NodeV1Interface
NodeV1alpha1() nodev1alpha1.NodeV1alpha1Interface
NodeV1beta1() nodev1beta1.NodeV1beta1Interface
PolicyV1() policyv1.PolicyV1Interface
PolicyV1beta1() policyv1beta1.PolicyV1beta1Interface
RbacV1() rbacv1.RbacV1Interface
RbacV1beta1() rbacv1beta1.RbacV1beta1Interface
RbacV1alpha1() rbacv1alpha1.RbacV1alpha1Interface
SchedulingV1alpha1() schedulingv1alpha1.SchedulingV1alpha1Interface
SchedulingV1beta1() schedulingv1beta1.SchedulingV1beta1Interface
SchedulingV1() schedulingv1.SchedulingV1Interface
StorageV1beta1() storagev1beta1.StorageV1beta1Interface
StorageV1() storagev1.StorageV1Interface
StorageV1alpha1() storagev1alpha1.StorageV1alpha1Interface
}
|
可以看到,包含了所有 Kubernetes 原生的 GroupVersion 接口,用于操作所有 GroupVersion 下的资源。
在每个 GroupVersion 方法内部(例如 AppsV1beta1),就是该 APIGroup 下的所有资源了:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
type AppsV1beta1Interface interface {
RESTClient() rest.Interface
ControllerRevisionsGetter
DeploymentsGetter
StatefulSetsGetter
}
|
RESTClient 是一个通用的 REST Client:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
// Interface captures the set of operations for generically interacting with Kubernetes REST apis.
type Interface interface {
GetRateLimiter() flowcontrol.RateLimiter
Verb(verb string) *Request
Post() *Request
Put() *Request
Patch(pt types.PatchType) *Request
Get() *Request
Delete() *Request
APIVersion() schema.GroupVersion
}
|
而其他资源接口就是可以操作对应的资源了:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
// DeploymentsGetter has a method to return a DeploymentInterface.
// A group's client should implement this interface.
type DeploymentsGetter interface {
Deployments(namespace string) DeploymentInterface
}
// DeploymentInterface has methods to work with Deployment resources.
type DeploymentInterface interface {
Create(ctx context.Context, deployment *v1beta1.Deployment, opts v1.CreateOptions) (*v1beta1.Deployment, error)
Update(ctx context.Context, deployment *v1beta1.Deployment, opts v1.UpdateOptions) (*v1beta1.Deployment, error)
UpdateStatus(ctx context.Context, deployment *v1beta1.Deployment, opts v1.UpdateOptions) (*v1beta1.Deployment, error)
Delete(ctx context.Context, name string, opts v1.DeleteOptions) error
DeleteCollection(ctx context.Context, opts v1.DeleteOptions, listOpts v1.ListOptions) error
Get(ctx context.Context, name string, opts v1.GetOptions) (*v1beta1.Deployment, error)
List(ctx context.Context, opts v1.ListOptions) (*v1beta1.DeploymentList, error)
Watch(ctx context.Context, opts v1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error)
Patch(ctx context.Context, name string, pt types.PatchType, data []byte, opts v1.PatchOptions, subresources ...string) (result *v1beta1.Deployment, err error)
Apply(ctx context.Context, deployment *appsv1beta1.DeploymentApplyConfiguration, opts v1.ApplyOptions) (result *v1beta1.Deployment, err error)
ApplyStatus(ctx context.Context, deployment *appsv1beta1.DeploymentApplyConfiguration, opts v1.ApplyOptions) (result *v1beta1.Deployment, err error)
DeploymentExpansion
}
|
大部分接口就是字面上的意思,下面是一些特殊的接口:
-
UpdateStatus
Deployment 包含一个子资源 /status,前面的 UpdateStatus 接口就是通过请求 /status 的 HTTP API 访问的。
举个例子,通过 /apis/apps/v1beta1/namespace/<ns>/depolyments/<name> HTTP Path 只能修改该对象的 spec,而通过 /apis/apps/v1beta1/namespace/<ns>/depolyments/<name>/status 可以修改该对象的 status。
默认情况下,生成 client 代码时会自动生成 UpdateStatus 方法的,但是不代表该资源可以支持修改 status。
-
DeleteCollection
DeleteCollection 用于一次性删除命名空间中的多个对象,在 ListOption 参数中使用 label selector 和 field selector 来筛选对象。
-
Watch
Watch 提供了发现该资源各种状态变化(增删改)的机制。返回的 interface 如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
// Interface can be implemented by anything that knows how to watch and report changes.
type Interface interface {
// Stops watching. Will close the channel returned by ResultChan(). Releases
// any resources used by the watch.
Stop()
// Returns a chan which will receive all the events. If an error occurs
// or Stop() is called, the implementation will close this channel and
// release any resources used by the watch.
ResultChan() <-chan Event
}
|
通过 ResultChan() 返回的 channel 就可以监听到资源的变更事件了。
不建议使用 Watch
实践中,不建议使用 Watch 监听对象,应该使用 Informer 提供的事件通知接口。因为 Informer 提供了缓存,并支持了 Resync 机制,也能正确处理各种出错的情况。
4.1 ClientSet Option
下面看下在生成 ClientSet 时可以配置的一些选项。
为了能够区分访问 APIServer 的不同 client,可以设置配置中的 User Agent 字段标识不同的 client。它的默认值为 binary/version (os/arch) kubernetes/commit,例如 kubectl 设置的 User Agent 为 kubectl/v1.14.0 (darwin/amd64) kubernetes/d654b49。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
cfg, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags("", *kubeconfig)
cfg.AcceptContentTypes = "application/vnd.kubernetes.protobuf,application/json"
cfg.UserAgent = fmt.Sprintf(
"book-example/v1.0 (%s/%s) kubernetes/v1.0",
runtime.GOOS, runtime.GOARCH
)
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(cfg)
|
配置中还可以设置 client 发送请求的速率限制和超时的配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
// Config holds the common attributes that can be passed to a Kubernetes
// client on initialization.
type Config struct {
// QPS indicates the maximum QPS to the master from this client.
// If it's zero, the created RESTClient will use DefaultQPS: 5
QPS float32
// Maximum burst for throttle.
// If it's zero, the created RESTClient will use DefaultBurst: 10.
Burst int
// The maximum length of time to wait before giving up on a server request.
// A value of zero means no timeout.
Timeout time.Duration
...
}
|
虽然 Client 默认没有设置请求的超时时间,但是 APIServer 会对非长时间运行请求有着 60s 的超时时间。
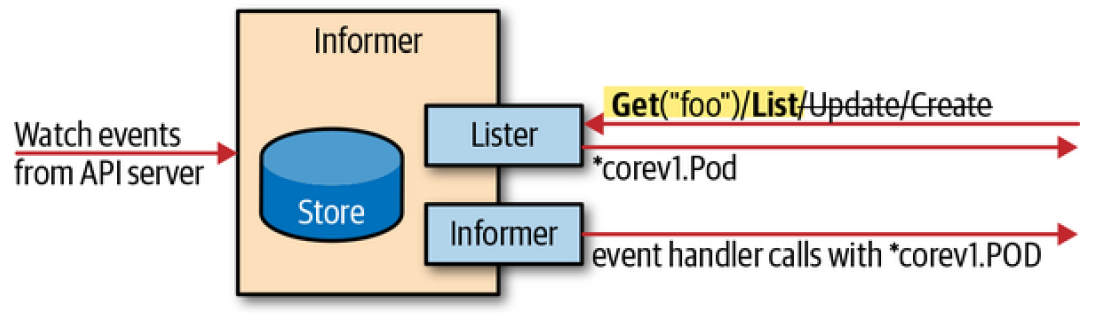
Controller 如果每次需要查询就去访问 APIServer,会造成比较大的压力。Informer 提供了对象的 内存缓存,而通过 Watch 机制来监听对象的即时变化。

Informer 内部实现了完善的错误处理能力:当与 APIServer Watch 的长连接发生断开时,它会通过一个新的 Watch 请求尝试恢复,从事件中找到正确的事件继续处理。也就是不会丢失事件。如果连接断开时间很长,Informer 会获取完整的对象列表重新构建缓存。
Informer 还提供了 resync 的机制:没经过一定的时间,它就会调用注册过的事件处理函数(Update 回调),提供完成的对象列表。
Note
resync 也是基于 Informer 内存缓存提供的对象列表,不会向 APIServer 发起请求。
为了减少程序中使用多个 Informer 带来的开销,可以通过 SharedInformerFactory 来方便地对 Informer 进行复用。SharedInformerFactory 允许在一个应用程序中复用 Informer,这样底层只有一个与 APIServer 构建的 Watch 连接。
通过 ClientSet 可以很方便的创建一个 SharedInformerFactory:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
import (
// ...
"k8s.io/client-go/informers"
)
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
// 创建 SharedInformerFactory:
informerFactory := informers.NewSharedInformerFactory(clientset, time.Second*30)
// 注册事件回调
podInformer := informerFactory.Core().V1().Pods()
podInformer.Informer().AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(new interface{}) {...},
UpdateFunc: func(old, new interface{}) {...},
DeleteFunc: func(obj interface{}) {...},
})
// 启动
informerFactory.Start(wait.NeverStop)
// Cache 同步
informerFactory.WaitForCacheSync(wait.NeverStop)
// 使用(纯内存的查询)
pod, err := podInformer.Lister().Pods("programming-kubernetes").Get("client-go")
|
AddEventHandler - 添加事件回调,这也是 Controller 的基础。Start - 启动 InformerFactory,内部会启动一些 groutine 去访问 APIServer。WaitForCacheSync - 让代码停下来,等待 InformerFactory 第一次同步所有的缓存。
例子中设置了 30s 的 resync 周期,也就是每隔 30s Informer 针对所有的对象会,触发一次 UpdateFunc 函数回调。因此,UpdateFunc 可能需要通过 ObjectMeta.resourceVersion 字段来判断是否是真正的更新事件。
ReadOnly
程序只能从 Informer 中读取、查询对象,不能通过 Informer 修改对象(需通过 ClientSet),而且也不能修改 Informer 返回的对象,因为这些对象是由 Informer 管理的。
6 WorkQueue
client-go 库中在 k8s.io/client-go/util/workqueue 中提供了一种强大的优先队列,可以实现让控制变得更加方便。
所有的 WorkQueue 都实现了下面的 interface:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
type Interface interface {
Add(item interface{})
Len() int
Get() (item interface{}, shutdown bool)
Done(item interface{})
ShutDown()
ShuttingDown() bool
}
|
Add(item) - 用于添加一个元素,反复添加同一个未出队的 item 只会对该元素打上标记。Len() - 返回队列的当前长度。Get() - 返回一个最高优先级的元素,Get() 并不代表元素从队列中取出。Done(item) - 表明元素处理完成,从队列中移出。
DelayingInterface 是基于基础 interface 的扩展,用于延迟添加元素。这适用于很方便地把处理失败的元素延时重新加入队列。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
// DelayingInterface is an Interface that can Add an item at a later time. This makes it easier to
// requeue items after failures without ending up in a hot-loop.
type DelayingInterface interface {
Interface
// AddAfter adds an item to the workqueue after the indicated duration has passed
AddAfter(item interface{}, duration time.Duration)
}
|
- AddAfter() - 在指定时间后将元素重新加入队列。
RateLimitingInterface 是更加常用的 interface 的扩展,对元素加入队列进行频率限流:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
// RateLimitingInterface is an interface that rate limits items being added to the queue.
type RateLimitingInterface interface {
DelayingInterface
// AddRateLimited adds an item to the workqueue after the rate limiter says it's ok
AddRateLimited(item interface{})
// Forget indicates that an item is finished being retried. Doesn't matter whether it's for perm failing
// or for success, we'll stop the rate limiter from tracking it. This only clears the `rateLimiter`, you
// still have to call `Done` on the queue.
Forget(item interface{})
// NumRequeues returns back how many times the item was requeued
NumRequeues(item interface{}) int
}
|
- AddRateLimited() - 添加元素到队列,收到频率限制。
- Forget() - 表明一个元素处理结束,重置该元素的限频值(仅仅针对频率限制,还是依旧要调用 Done())。
- NumRequeues() - 返回一个元素入队的次数。
client-go 提供了多种方式的限频算法,包括:
- BucketRateLimiter
- ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter
- ItemFastSlowRateLimiter
- MaxOfRateLimiter
不过大部分情况下,我们都只需要使用
1
|
func DefaultControllerRateLimiter() *RateLimiter
|
- 指数级的退避策略,从 5ms 考试,最大 1000s,每次退避时间翻倍。
- 允许每秒向队列中添加 10 个元素,允许突发添加 100 个元素。
7 基本类型系统
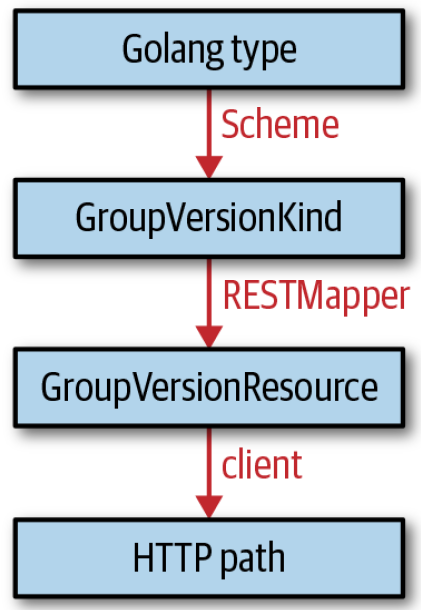
首先,我们看着下图,有着在对代码中类型系统的转化路径的整体概念:

-
代码中,我们得到一个对象,可以通过 Scheme 得到对应的 GroupVersionKind
-
从 GroupVersionKind,通过 RESTMapper 可以映射到对应的 GroupVersionResource
-
client 基于 GroupVersionResource 就可以请求对应的 HTTP API Path
7.1 GroupVersionKind
在 API 基本概念 - Kind 中说过,Kind 表示一个对象的类型。因为对象都是基于 GroupVersion 来说的,所以在代码中,Kind 的代表就是核心概念:GroupVersionKind,简写为 GVK。
看下具体的结构:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
// GroupVersionKind unambiguously identifies a kind. It doesn't anonymously include GroupVersion
// to avoid automatic coercion. It doesn't use a GroupVersion to avoid custom marshalling
type GroupVersionKind struct {
Group string
Version string
Kind string
}
|
7.2 GroupVersionResource
在 API 基本概念 - Resource 中说明了 Resource 的概念,Resource 也是基于 GroupVersion 来说的,所以代码中也有着对应的 GroupVersionResource 的概念,简写为 GVR。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
// GroupVersionResource unambiguously identifies a resource. It doesn't anonymously include GroupVersion
// to avoid automatic coercion. It doesn't use a GroupVersion to avoid custom marshalling
type GroupVersionResource struct {
Group string
Version string
Resource string
}
// GroupKind specifies a Group and a Kind, but does not force a version. This is useful for identifying
// concepts during lookup stages without having partially valid types
type GroupKind struct {
Group string
Kind string
}
|
每个 GVR 都对应了一个 HTTP API Path。例如 apps/v1.deployments 这个 GVR 对应于 HTTP APi /apis/apps/v1/$namespace/deployments。
7.3 REST Map
大多数 Kind 与 Resource 存在着一一对应的关系,用于记录 GVK 与 GVR 之间的映射关系被称为 REST Map。
代码中 RestMapper 为记录 RESTMap 的抽象 interface,其提供多个用于 GVK 与 GVR 之间转换的方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
// RESTMapper allows clients to map resources to kind, and map kind and version
// to interfaces for manipulating those objects. It is primarily intended for
// consumers of Kubernetes compatible REST APIs as defined in docs/devel/api-conventions.md.
//
// The Kubernetes API provides versioned resources and object kinds which are scoped
// to API groups. In other words, kinds and resources should not be assumed to be
// unique across groups.
//
// TODO: split into sub-interfaces
type RESTMapper interface {
// KindFor takes a partial resource and returns the single match. Returns an error if there are multiple matches
KindFor(resource schema.GroupVersionResource) (schema.GroupVersionKind, error)
// KindsFor takes a partial resource and returns the list of potential kinds in priority order
KindsFor(resource schema.GroupVersionResource) ([]schema.GroupVersionKind, error)
// ResourceFor takes a partial resource and returns the single match. Returns an error if there are multiple matches
ResourceFor(input schema.GroupVersionResource) (schema.GroupVersionResource, error)
// ResourcesFor takes a partial resource and returns the list of potential resource in priority order
ResourcesFor(input schema.GroupVersionResource) ([]schema.GroupVersionResource, error)
// RESTMapping identifies a preferred resource mapping for the provided group kind.
RESTMapping(gk schema.GroupKind, versions ...string) (*RESTMapping, error)
// RESTMappings returns all resource mappings for the provided group kind if no
// version search is provided. Otherwise identifies a preferred resource mapping for
// the provided version(s).
RESTMappings(gk schema.GroupKind, versions ...string) ([]*RESTMapping, error)
ResourceSingularizer(resource string) (singular string, err error)
}
|
KindFor() - 部分 GVR 转换为单个 GVKKindsFor() - 部分 GVR 转换为所有 GVKResourceFor() - 部分 GVR 转换为单个 GVRResourcesFor() - 部分 GVR 转换为所有 GVRRESTMapping() - 从一个 Kind 得到对应最优先的 RestMappingRESTMappings() - 从一个 Kind 得到所有对应的 RestMapping
部分 GVR
部分 GVR 指的是仅仅设置了部分字段的 GVR。例如 kubectl get pods 时,没有指定 Group 与 Version,但是能够映射到 v1 Pod 这样的 Kind。
RESTMapping 就代表了一个 GVK 与 GVR 的一对一映射:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
// RESTMapping contains the information needed to deal with objects of a specific
// resource and kind in a RESTful manner.
type RESTMapping struct {
// Resource is the GroupVersionResource (location) for this endpoint
Resource schema.GroupVersionResource
// GroupVersionKind is the GroupVersionKind (data format) to submit to this endpoint
GroupVersionKind schema.GroupVersionKind
// Scope contains the information needed to deal with REST Resources that are in a resource hierarchy
Scope RESTScope
}
|
RESTMapper interface 有着许多的 implement,不过在编写 Operator 时,通常我们使用基于发现机制的 DeferredDiscoveryRESTMapper 实现。它通过调用 APIServer 的接口动态解析 REST Mapping。
7.4 Scheme
Scheme 应该是编写代码时最重要的结构了。其包含了多个 Golang 类型与 GVK 的映射,并且特定的 Kind,可以注册不同版本的转换函数,以及设置默认值的函数。
总结一下其主要作用:
- GVK 与 Golang 类型的转换;
- 注册 Convert 函数,用于 Kind 不同版本对象之间的转换;
- 注册 Default 函数,用于设置对象的默认值;
Note
当我们需要实现 Custom APIServer 时,就会要了解到 Convert 与 Default。
7.4.1 类型转换
Scheme 提供 GVK 与特定类型转换功能。
首先,我们需要通过 Scheme.AddKnownTypes 接口来注册 Golang 类型与 GroupVersion。通常,代码生成器会在 register.go 文件中生成该代码。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
// SchemeGroupVersion is group version used to register these objects
var SchemeGroupVersion = schema.GroupVersion{Group: groupName, Version: "v1alpha1"}
func init() {
// We only register manually written functions here. The registration of the
// generated functions takes place in the generated files. The separation
// makes the code compile even when the generated files are missing.
localSchemeBuilder.Register(addKnownTypes)
}
func addKnownTypes(scheme *runtime.Scheme) error {
Scheme = scheme // Scheme 是全局的 Scheme 对象
scheme.AddKnownTypes(SchemeGroupVersion,
&TidbCluster{}, // 自定义的类型
)
metav1.AddToGroupVersion(scheme, SchemeGroupVersion)
return nil
}
|
通常,我们会有一个全局的 Scheme 对象,然后通过向其中注册 Golang 类型。这样,我们就可以通过 Scheme.New 方法从一个 GVK 得到一个 Golang 对象,然后通过类型断言转换为特定的类型。
1
2
3
|
robj, err := t.scheme.New(gvk) // 得到 GVK 对应的空的对象
cobj, ok := robj.(*TidbCluster) // 类型断言得到具体的对象
|
总结一下,Scheme 提供的相关接口:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
// AddKnownTypeWithName 注册 GVK 与类型(obj 的类型)
func (s *Scheme) AddKnownTypeWithName(gvk schema.GroupVersionKind, obj Object)
// AddKnownTypes 注册 GV 与其下的多个类型,Kind 就是类型的名字
func (s *Scheme) AddKnownTypes(gv schema.GroupVersion, types ...Object)
// KnownTypes 从 GV 中取出包含的类型
func (s *Scheme) KnownTypes(gv schema.GroupVersion) map[string]reflect.Type
// New 根据 GVK 创建一个对应类型的对象
func (s *Scheme) New(kind schema.GroupVersionKind) (Object, error)
// ObjectKinds 返回对象对应的可能的 GVK,如果是 unversioned object 返回 true,如果类型未注册返回错误
func (s *Scheme) ObjectKinds(obj Object) ([]schema.GroupVersionKind, bool, error)
// PreferredVersionAllGroups 返回每个 Group 的优先级最高 Version
func (s *Scheme) PreferredVersionAllGroups() []schema.GroupVersion
// PrioritizedVersionsForGroup 按照优先级顺序返回所有的 GroupVersion
func (s *Scheme) PrioritizedVersionsForGroup(group string) []schema.GroupVersion
// PrioritizedVersionsForGroup 按照优先级返回一个 group 所有的 version
func (s *Scheme) PrioritizedVersionsForGroup(group string) []schema.GroupVersion
// Recognizes GVK 是否是注册过的
func (s *Scheme) Recognizes(gvk schema.GroupVersionKind) bool
// SetVersionPriority 设置一个 Group 下的 Version 的优先级
// NOTE: versions 必须是同一个 Group 下的不同 Version
func (s *Scheme) SetVersionPriority(versions ...schema.GroupVersion) error
|
可以看到,这样就实现了 Kind 与对象类型的互转。这也就是 Client 与 APIServer 通信时,进行数据序列化与反序列化的核心。
7.4.2 不同版本类型间转换
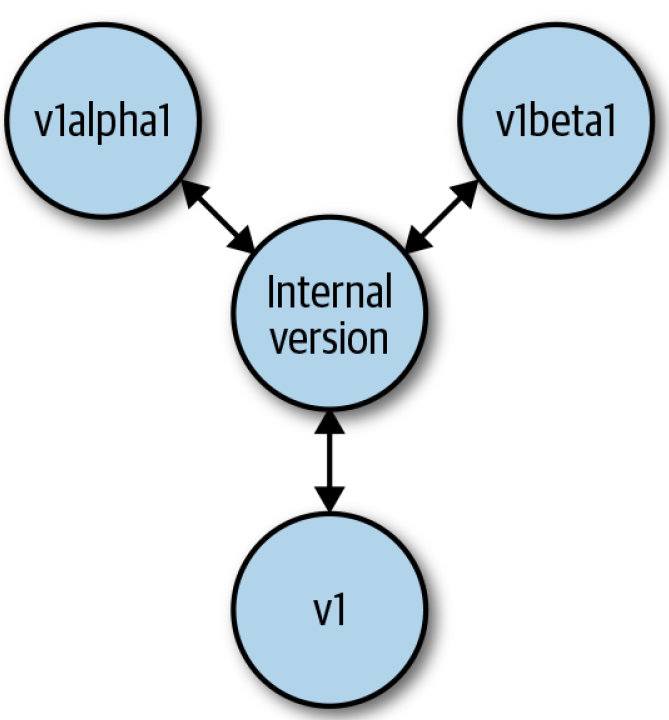
前面可以看到,Scheme 存储着许多 Group,其 Group 下可以有着不同 Version 的类型。在 APIServer 中,为了能够处理多个 Version 共存的情况,又有着一个 Internal Version。作为不同 Version 间转换中转。

而 Scheme 也是保存着各个版本之间转换的地方(因为其知道所有版本的类型),通过以下函数提供功能:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
// AddConversionFunc 注册一个转换路径,对应 a 类型到 b 类型的转换,使用 fn 进行转换
func (s *Scheme) AddConversionFunc(a, b interface{}, fn conversion.ConversionFunc) error
func (s *Scheme) AddFieldLabelConversionFunc(gvk schema.GroupVersionKind, conversionFunc FieldLabelConversionFunc) error
func (s *Scheme) AddGeneratedConversionFunc(a, b interface{}, fn conversion.ConversionFunc) error
func (s *Scheme) AddIgnoredConversionType(from, to interface{}) error
// Convert 将 in 类型对象转换为 out 类型对象
func (s *Scheme) Convert(in, out interface{}, context interface{}) error
func (s *Scheme) ConvertFieldLabel(gvk schema.GroupVersionKind, label, value string) (string, string, error)
// ConvertToVersion 将 in 类型对象转化为 taget 指定的版本对象
func (s *Scheme) ConvertToVersion(in Object, target GroupVersioner) (Object, error)
|
我们将在后面的 Custom APIServer 编写中看到何时使用这些函数。
7.4.3 设置默认值
Scheme 在处理数据类型序列化,和处理数据类型转换时,会通过默认值相关函数设置对象的默认值。通过以下函数:
1
2
3
4
5
|
// AddTypeDefaultingFunc 注册一个对象的默认值处理函数
func (s *Scheme) AddTypeDefaultingFunc(srcType Object, fn func(interface{}))
// Default 设置一个对象的默认值,就是使用注册的默认值处理函数
func (s *Scheme) Default(src Object)
|
Note
注意,默认值设置在 APIServer 转换时是自动进行的,而 Scheme 中仅仅是用于 Default() 接口,不会自动进行。
因此,在编写 Custom APIServer 时要正确设置好设置默认值的函数。
我们将在后面的 Custom APIServer 编写中看到何时使用这些函数。
7.4.4 原生的 Scheme
client-go 中有着一些预定义的 Scheme,位于 k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes/scheme 包中。其包含了 Kubernetes 所有的核心类型,也就是原生类型都已经注册到了该 Scheme 中(包括 Convert 与 Default 相关)。
参考