Kubernetes - Service 与 Endpoint
1 概述
首先我们需要明确 Service 出现的背景:因为 Pod 设计上是无状态的,可以说没有固定的 IP,所以在其他组件访问某一个网络服务时,需要一个 “固定” 的地址。
这个固定的地址,就需要由 Service 来提供。同样,因为访问的地址固定了,Service 也可以提供负载均衡这样的功能。
最简单的例子,有一个 Web 后端服务,有着 3 个 Pod 运行。而前端想访问该后端服务,想要的只是一个固定的域名或者地址,而不关系后端服务的 Pod 会怎样被调度。
2 Service 基础
2.1 Spec
Service 基本的定义如下:
|
|
上述 Service 会将 Port 80 的请求转发到 Pod 的 Port 9376,通过 selector 来筛选作为后端的 Pod。
Pod 中定义的端口是有名字的,因此也可以在 Service 中引用这些名称:
|
|
2.2 Cluster IP
创建 Service 后,Kubernetes 为分配一个 Cluster IP 作为 Service 的地址。该 IP 是虚拟的,kube-proxy 处理数据包时才会使用该 IP。
当然,你也可以通过设置 spec.clusterIP 来手动指定 Service IP。不过该 IP 地址必须在 service-cluster-ip-range CIDR 范围内。
Kubernetes 根据配置的 service-cluster-ip-range 来选择 Cluster IP。会将该 CIDR 分为两段:
- Kubernetes 会优先从高段中选择 Cluster IP。
- 手动指定 Cluster IP 应该从底端中选择,以防止冲突。
2.3 LB Policy
k8s 默认提供两种负载均衡策略:
-
RoundRobin :轮询模式,将请求轮询到后端各个 Pod。默认模式
-
SessionAffinity :基于客户端 IP 地址进行会话保持的模式。即第一次将某个客户端发起请求到后端某个 Pod,之后相同客户端发起请求都会被转发到对应 Pod。
将
spec.sessionAffinity指定为 “ClientIP”,就表明了开启 SessionAffinity 策略。通过
spec.sessionAffinityConfig.clientIP.timeoutSeconds来设置会话最大的持续时间,默认为 3h。
2.4 Traffic Policy
2.4.1 Internal Traffic Policy
spec.internalTrafficPolicy 来配置 Kubernetes 集群内部的流量(Pod 之间的流量)如何被路由。支持:
-
Cluster
集群中的所有 Node 都可以将流量转发到任意 Ready Pod,即使要转发的 Pod 不在当前 Node 上。
例如,Node A B C 三个节点都运行了一个 Pod,那么 Node A 的
kube-proxy路由流量时,可能将流量路由到 Node A B C 的 Pod。这种方式提供了高可用性,如果某个 Pod 故障时,还是能将流量路由到其他 Node 上的 Pod。
-
Local
流量只能路由给当前 Node 上的 Pod。如果当前 Node 上没有 Pod,那么会丢弃该流量。
例如,Node A B C 三个节点都运行了一个 Pod,那么 Node A 的
kube-proxy只能将流量路由到 Node A 的 Pod。这种方式减少了跨 Node 间的流量,但是如果 Pod 故障时,请求可能无法被服务。
2.4.2 External Traffic Policy
spec.externalTrafficPolicy 控制从外部的流量(外部 -> Node -> Pod 的流量)如何被路由。支持:
-
Cluster
集群中的所有 Node 都可以提供外部服务,能够将流量转发到其他 Node 上的 Pod。
Node 之间的流量会经过一次 SNAT,所以会隐藏源 IP 地址。
-
Local
Node 只能路由流量给本地上运行的 Pod,也就是说不是所有 Node 都能提供外部服务。
2.5 支持的协议
目前 Service 支持如下网络协议:
- TCP: 默认网络协议,可用于所有类型 Service
- UDP: 可用于大多数类型 Service。LoadBalancer 类型取决于云服务是否支持
- HTTP: 取决于云服务是否支持
- PROXY: 取决于云服务是否支持
- SCTP
另外,可以为 Service 设置 spec.ports[_].appProtocol 字段,用于表示后端服务在某端口停的应用层协议类型。该字段会被映射到对应的 Endpoints 或者 EndpointSlices 对象。
|
|
3 服务发现
Kubernetes 提供了两种机制供客户端以固定的范式获取后端 Service 的访问地址:环境变量和 DNS。
3.1 环境变量方式
如果 Pod 在 Service 之后创建,那么集群中同 namespace Service 地址信息会通过 ENV 传递给容器(不包括 Headless Service)。相关的环境变量包括:
|
|
默认相关的环境变量使用的都是 spec.port[0] 信息。如果使用的多 port 代理,需要使用 xxx_PORT_xxx 相关环境变量。
环境变量默认还会提供 Kubernetes 的 APIServer Service 地址,用于 Pod 来访问 APIServer。
3.2 DNS 方式
所有 Service 都会自动对应一个 DNS 域名,其命令方式为 <service>.<namespace>.svc.cluster.<cluster_domain>。由 CoreDNS 作为集群的默认 DNS 服务器,提供域名解析服务。
如果 Service 定义中设置了 spec.ports[].name,那么该端口号也会有一个域名:<port_name>._<protocol>.<service>.<namespace>.svc.<cluster_domain>。
|
|
当执行 nslookup <service> 时,自动在当前的 namespace 下访问。通过 nslookup <service>.<namespace> 可以跨 namespace 进行 DNS 解析。
4 Service 类型
Service 核心的功能是:代理。代理涉及到两个点:访问代理的前端,被代理的后端。
针对这个前后端的不同,Service 分为了几种类型:
-
ClusterIP(默认):代理一组后端 Pod,提供一个固定的内部地址 ClusterIP + Port,也称为 VIP; -
NodePort:NodePort 在 ClusterIP 基础上,会将 ClusterIP + Port 映射到 Node 上的某个端口,使得集群外部可以访问内部服务 -
LoadBalancer:LoadBalancer 在 NodePort 上,将一部分 Node 的端口映射到一个 IP 上,使得外部网络可以访问 Node; -
ExternalName:代理集群外部服务的 DNS 域名,而不是通过 selector 来选择集群内部后端 Pod;
可以看到,ClusterIP NodePort LoadBalancer 是针对访问代理的前端做了区分,而 ExternalName 是在被代理后端的不同。
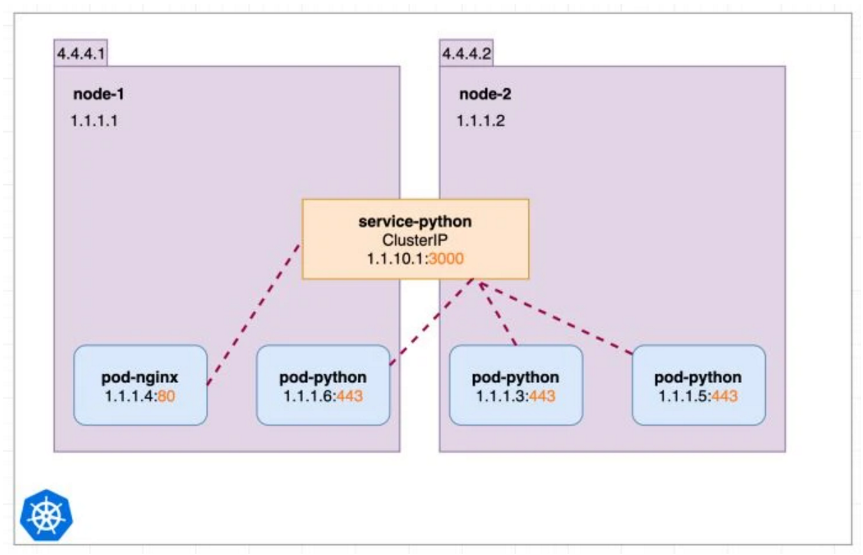
4.1 ClusterIP
ClusterIP 是最基本的 Service,通过一个 VIP + Port 来在集群内部代理了一组 Pod 的 Port。始终要记得,VIP 是在集群内部才能使用。
|
|
上述定义创建了一个随机选择 IP,代理 TCP 3000 -> 443 端口的 Service。
4.2 NodePort
NodePort 是对 ClusterIP 的增强,增加一个宿主机上端口到代理源端口的转发,使得集群外部通过访问 Node 来访问集群内部的服务。
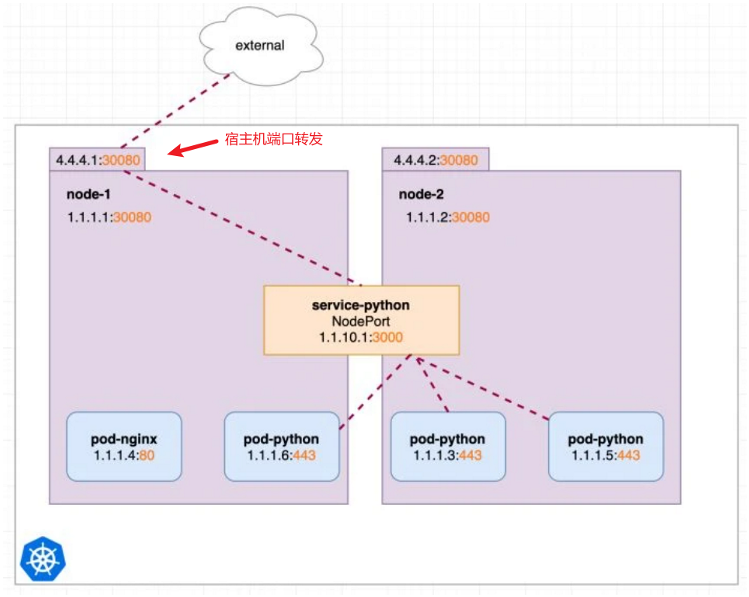
Kubernetes 会在 --service-node-port-range 参数指定的范围内分配端口(默认 30000-32767)。也可以通过 .spec.ports[*].nodePort 来指定端口号。
|
|
Node 上的 kube-proxy 负责监听 NodePort 并转发,通过 --nodeport-addresses 或者配置文件可以配置 kube-proxy 监听的 IP 地址或者 IP Range。
4.3 LoadBalancer
LoadBalancer Service 在 NodePort 基础上,提供了云厂商需要的负载均衡信息,而云厂商根据该信息配置好相应的 LB。进而外部通过访问 LB 就可以访问集群中的 Pod。
对于 LB 如何将流量转发给 Pod,各个云厂商的实现可能不同。
|
|
externalTrafficPolicy: Local,因为 LB 能够直接将流量转发到对应 Pod 的 Node 上,不需要 Node 间转发流量了。spec 中定义仅仅是约定的规范,不同厂商所需要的更加细节的 LoadBalancer 的参数,大多数是通过 service.metadata.annotations 来提供。以 AWS LB 为例:
|
|
对于 LoadBalancer,更多的信息见官方文档:LoadBalancer。
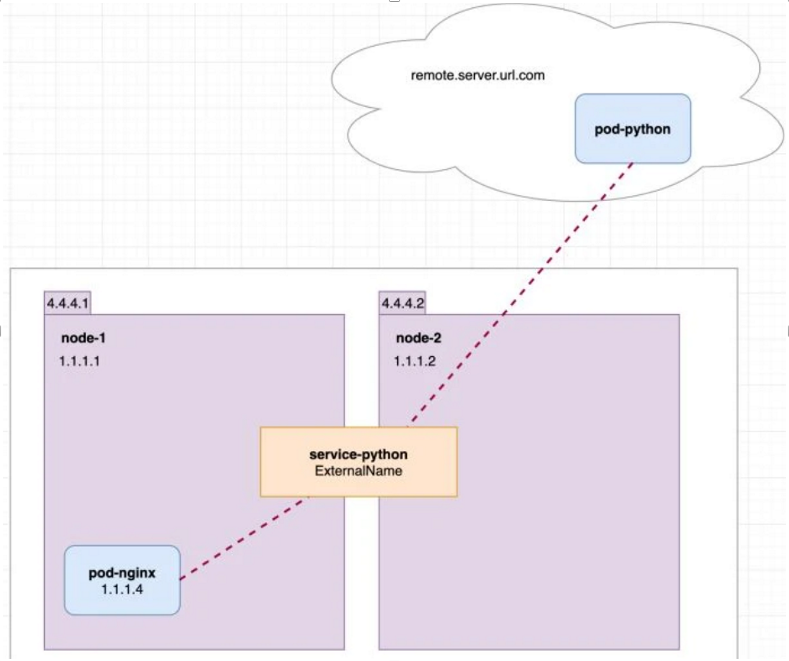
4.4 ExternalName
前面三种 Service 代理的后端都是集群内部的 Pod,而 ExternalName 不再是代理 Pod,而是将请求域名重定向另一个域名。
因此,ExternalName Service 不再提供代理的功能,而是提供了域名重定向的功能。
|
|
通过 serivce.spec.externalName 指定被代理的域名,而集群内部的 Pod 就可以通过该 Service 访问外部服务了。
4.5 External IP
External IP 不是一种 Service 类型,而是用于标识该 Service 的外部 IP 地址。Kubernetes 不会管理外部 IP。
集群管理员可以通过 Service 的 spec.externalIPs 表明 Service 的外部 IP。
|
|
5 Headless Service
Service 会自动发现一组 Pod,并提供代理服务与负载均衡。不过有时候,Pod 中程序并不想使用 Service 的代理功能,而是仅仅想让 Service 作为一个服务发现的作用,例如,peer2peer 程序想要知道有哪些对端的程序。
通过 Service 的定义看,这种情况也就是不需要 service.spec.clusterIP,但是需要 service.spec.selector。这种特殊的 Service 被称为 Headless Service。
|
|
spec.clusterIP: None 表明其为 Headless Servicesepc.publishNotReadyAddresses:为 true 时,即使 Pod 还不是 Ready 状态,也会提供 DNS 记录
service.spec.selector 让 Service 匹配到后端 Pod,并创建对应的 Endpoints。
当我们直接使用 Service DNS 进行解析时,会得到 DNS 系统返回的全部 Endpoint 地址。
|
|
通过 Headless Service,然后设置 Pod 的 spec.hostname 与 spec.subdomain,就可以实现通过固定 DNS 记录访问某个 Pod。也就是 StatefulSet 使用 Headless Service 的方式。
6 Endpoint 与 EndpointSlice
6.1 Endpoint
当创建一个 Service 后,会根据 service.spec.selector 自动来匹配作为后端的 Pod。实际上,会对应一个 Endpoints 对象来代表其匹配到的代理目标,而其每一个被代理的 Pod 称之为 Endpoint。
|
|
当然,你也可以不提供 service.spec.selector,也不使用 ExternalName Service,而指定创建一个 Endpoints 对象。这样可以实现,Service 只代理指定的地址。
|
|
同名的 Endpoints 与 Service 自动被认为是相绑定的。
6.2 EndpointSlice
因为 Endpoints 对象结构的局限性,EndpointSlice 是新版的替代方案。
EndpointSlice 在 Endpoints 的基础上,为每个 Endpoint 添加了额外的拓扑信息。并且每个 EndpointSlice 只能包含最大 100 个 Endpoint,如果超过后,Kubernetes 就会创建新的 EndpointSlice。
在多个 EndpointSlice 的情况下,通过 Label kubernetes.io/service-name 来判断 EndpointSlice 属于哪一个 Service。
|
|
默认情况下,创建一个 Service 后,就会存在对应的 EndpointSlice 对象,包含匹配到的 Endpoint。
|
|
6.3 Topology Aware Hints
大多数 Kubernetes 集群都是部署在 Mutli Zones 环境中。Topology Aware Hints 指的是:通过 EndpointSlice 将拓扑信息告知给 kube-proxy,并用这些来影响流量的路由(倾向于拓扑上相邻的 Endpoint)。
此特性启用分为两个组件:EndpointSlice Controller 和 kube-proxy。
-
在 Service 中添加 Annotation
service.kubernetes.io/topology-aware-hints: auto,表明开启功能。 -
EndpointSlice Controller 会在 EndpointSlice 上设置提示信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11# ... endpoints: - addresses: - "10.1.2.3" conditions: ready: true hostname: pod-1 zone: zone-a hints: forZones: - name: "zone-a" -
kube-proxy 根据 EndpointSlice 来路由流量。大多数场合下,kube-proxy 将流量路由到同 Zone 的 Endpoint。
7 Ingress
Service 提供了基于 4 层的代理,也就是基于 IP + Port 的代理。而 Ingress 出现就是为了支持 7 层的代理,典型的就是支持 HTTP/HTTPS 协议的代理。
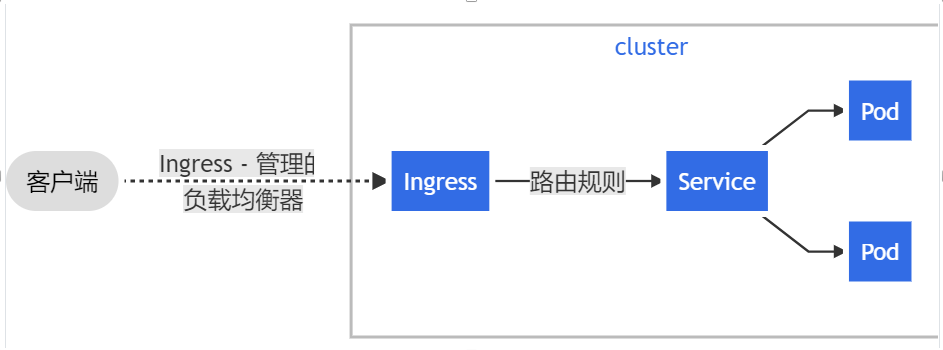
Ingress 类似于 nginx 的配置,提供应用层的路由,将流量路由给基于传输层的 Service,而由 Service 将流量路由给底层的 Pod。
不过 Ingress 类似于 Service,仅仅是一个规则的定义,其代理的实现依赖于 Ingress Controller。
7.1 Ingress Controller
Ingress Controller 基于定义好的 Ingress 来实现实际的路由,可以理解为就是实际上的 nginx。
Ingress Controller 是不包含在 controller manager 默认启动的 controller 的,需要手动进行 controller。
当然,目前有着许多种的 Ingress Controller 的实现,具体见 Ingress Controller。
7.2 Ingress 定义
Ingress 的配置和配置 nginx 类似,基于 HTTP path 路径进行路由的配置。
看一个示例定义:
|
|
spec.ingressClassName- 指定使用的 Ingress Controller 的名字,为保持兼容 annotationkubernetes.io/ingress.class依旧可以使用spec.tls- 证书对应的 secret 与允许的 hostsspec.defaultBackend- 用于配置默认的后端,当 rules 中所有都不满足时,就会使用 default 路由service- 转发到一个 Kubernetes Servicename- service 的名字port- 转发给 service 的 port,可以是名字或者端口号
resource- 转发给 Ingress 对象同 Namespace 下的一个 Resource(与 service 选项互斥)
spec.rules- 定义路由策略host- 匹配请求的 host,可以是精确匹配或者通配符匹配http- http 层的多个匹配路径