1 概述
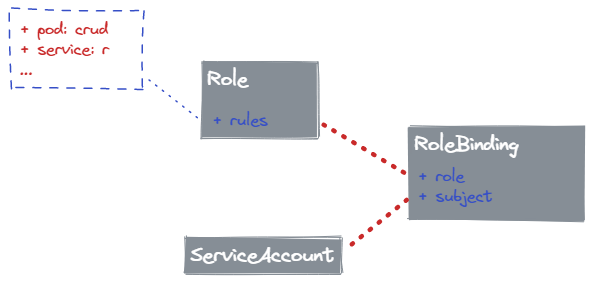
在 Kubernetes 认证与鉴权机制 中提到,Kubernetes 支持的授权机制有多种,其中 RBAC 是最常用的授权方式。RBAC 基于角色访问控制,全称 Role-Base Access Control。
对于理解 RBAC,首先需要知道三个关键的概念:
-
Role :角色,代表一组对 Kubernetes API 对象操作的权限。
-
Subject :被作用者,包括 User、Group、ServiceAccount。
-
RoleBinding :定义 Role 与 Subject 的映射关系。
因此,我们会预先创建一些 Role,然后创建 Subject 时,定义 RoleBinding 来表明对 Subject 的权限控制。

为什么这么设计?
通过 RoleBinding,实现了 Role Subject 之间的解耦。
2 Role 与 ClusterRole
2.1 Role
Role 就是一个 Kubernetes 资源对象,并且是一个 namespaced Resouce,因此其 Role 控制的权限范围也只能是所属的 namespace 下。
基本定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: default
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
|
metadata.namespace :指定 Role 所属的 namespacerules.apiGroups :表明针对哪些 API Group 生效,为空表示 core API Group;rules.resources :表明针对哪些 Resource 生效;rules.verbs :允许执行的操作;
示例中 rules 定义的规则就是:允许对 “mynamespace” 下的所有 Pod 对象,执行 GET、Watch、List 操作。
能够支持限制的操作为:“get”, “list”, “watch”, “create”, “update”, “patch”, “delete”,“deletecollection” 。
2.2 ClusterRole
ClusterRole 是一个 non-namespaced Resource,所以是针对所有 namespace 的资源生效,也可以实现控制 non-namespaced Resource 的权限。
基本定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
# "namespace" omitted since ClusterRoles are not namespaced
name: secret-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
|
rules.apiGroups :表明针对哪些 API Group 生效,为空表示 core API Group;rules.resources :表明针对哪些 Resource 生效;rules.verbs :允许执行的操作;
示例中 rules 定义的规则是:允许对所有 namespace 下的 所有 Secret 对象,执行 GET、Watch、List 操作。
2.2.1 聚合 ClusterRole
多个 ClusterRole 可以聚合为一个新的 ClusterRole,用于简化 ClusterRole 的管理工作。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: monitoring
aggregationRule:
clusterRoleSelectors:
- matchLabels:
rbac.example.com/aggregate-to-monitoring: "true"
rules: [] # rules 规则会自动被设置
|
aggregationRule 字段设置了匹配 ClusterRole 的规则,当一个 ClusterRole 被匹配到后,其 rules 自动会填充相关的规则。
2.3 对非资源对象限制
某些 Kubernetes API 包含下次子资源,例如 Pod 的日志。
1
2
3
4
5
|
# ...
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resource: ["pods", "pods/log"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
|
2.4 对指定资源对象限制
通过 rules.resourceName 字段可以限制对指定资源的权限:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
# ...
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resource: ["configmap"]
resourceName: ["mu-configmap"]
verbs: ["update", "get"]
|
当然,因为是对指定的资源,因此无法限制 list、watch、create 或 deletecollections 操作。
2.5 内置 Role 与 ClusterRole
默认下,Kubernetes 已经内置了许多个 Role 与 ClusterRole,它们都是以 system: 开头命名。
所有系统默认的 ClusterRole 和 RoleBinding 都会使用 label kubernetes.io/bootstrappiong=rbac-defaults 来标记。
每次集群启动时,APIServer 会更新默认的集群 Role 缺失的权限,也会更新默认 Role 绑定的 Subject。这样可以防止一些破坏性的更改,保证集群升级情况下相关内容能够及时更新。
使用内置 Role 与 ClusterRole 已经完全可以满足大部分的使用场景。
内置的 Role 的含义见 Default roles and role bindings。
3 RoleBinding 与 ClusterRoleBinding
3.1 RoleBinding
RoleBinding 用于绑定一个 Role 与多个 Subject,通过 RoleBinding 才能让某个 Subject 有 namespace 相关资源的访问权限。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
# This role binding allows "jane" to read pods in the "default" namespace.
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: User
name: jane
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: pod-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
|
Tip
RoleBinding 也可以引用 ClusterRole,将其权限限制在了 RoleBinding 所属的 namespace 下。
3.2 ClusterRoleBinding
ClusterRoleBinding 让 Subject 有着整个集群相关资源的访问权限。
3.2.1 ClusterRole 聚合
在 ClusterRole 中可以通过 aggregationRule 来与其他 ClusterRole,也就是可以自动组合多个 ClusterRole 为一个。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: monitoring
aggregationRule: # 通过 label selector 方式自动组合
clusterRoleSelectors:
- matchLabels:
rbac.example.com/aggregate-to-monitoring: "true"
rules: [] # Rules 由组合起来的 ClusterRole 自动填充
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: monitoring-endpoints
labels:
rbac.example.com/aggregate-to-monitoring: "true"
# These rules will be added to the "monitoring" role.
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services", "endpoints", "pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
|
4 Subject
Subject 表明请求者的身份,包括:User、User Group 和 ServiceAccount。
不过,Kubernetes 并不包含一个用户系统,我们并不可以创建或删除用户或者用户组。User 仅仅会在权限检查时使用:请求提供 User 信息,鉴权模块根据 User 判断是否有对应操作的权限。
4.1 User 与 User Group
前面提到,User 只是一个逻辑上的标识。不需要任何的注册与登陆,我们就可以基于一个 User 来设置相关的权限。
下面以设置 User 的权限为示例,为 shiori 用户仅提供 Pod 相关的权限:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: pod-admin
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["*"]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: shiori-pod-admin
subjects:
- kind: User
name: shiori
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: pod-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
|
创建后,我们会发现已经可以以 shiori 用户来执行了,并且限制了他的权限:
1
2
3
4
5
|
$ kubectl get nodes --as=shiori
Error from server (Forbidden): nodes is forbidden: User "shiori" cannot list resource "nodes" in API group "" at the cluster scope
$ kubectl get pods --as=shiori
No resources found in default namespace.
|
User Group 是 User 的集合,以 group:group 的格式配置,User Group 用于更加方便的管理多个 User 的权限。
Kubernetes 默认创建的 RoleBinding/ClusterRoleBinding 一般会设置几个 User Group 的权限。例如,system:unauthenticated 表示 匿名用户。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
annotations:
rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true"
labels:
kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults
name: system:public-info-viewer
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:public-info-viewer
subjects:
- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Group
name: system:authenticated
- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Group
name: system:unauthenticated
|
ServiceAccount
下面会说到,ServiceAccount 也是一种特殊的用户。
4.2 ServiceAccount
ServiceAccount 本质上也是一种特殊的 User,对应的 User 命为 system:serviceaccount:${NAMESPACE}:${SERVICE_ACCOUNT}。可以看到,所有的 ServiceAccount 是属于 system:serviceaccount User Group 的。
Kubernetes 为 ServiceAccount 提供了专门的认证方式 ServiceAccount Token,并且设置权限起来非常方便。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
# 创建 ServiceAccount
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: crossplane-provider
namespace: infra
---
# ClusterRoleBinding 绑定 ServiceAccount 与 Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: crossplane-provider
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: crossplane-provider
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: crossplane-provider
namespace: infra
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: crossplane-provider
rules:
- apiGroups:
- "*"
resources:
- "*"
verbs:
- "*"
|
ServiceAccount 本质上还是基于 Token 的方式来进行身份认证,创建一个 ServiceAccount 会对应自动创建相关 Secret。Secret 中记录了对应的 JWT Token。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
annotations:
kubernetes.io/service-account.name: crossplane-provider
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: b8d7500c-66cd-491c-bba3-ff00ef5e1ccf
name: crossplane-provider-token-x6x7j
namespace: infra
type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
data:
ca.crt: <OMIT>
namespace: aW5mcmE=
# JWT base64 encode
token: <OMIT>
|
使用 JWT 记录了相关的用户信息,从而使得 Kubernetes 能够知道该 Token 对应于哪个 ServiceAccount,进一步通过 RBAC 进行权限判断。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
// JWT Header
{
"alg": "RS256",
"kid": "hdxo5HvF6FihotWJ9Mf1uu8bgLAwa37nOLseffIvg6w"
}
// JWT PAYLOAD
{
"iss": "kubernetes/serviceaccount",
"kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/namespace": "infra",
"kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/secret.name": "crossplane-provider-token-x6x7j",
"kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/service-account.name": "crossplane-provider",
"kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/service-account.uid": "b8d7500c-66cd-491c-bba3-ff00ef5e1ccf",
"sub": "system:serviceaccount:infra:crossplane-provider"
}
|
参考