Kubernetes - 认证与鉴权机制
1 概述
如下图所示,APIServer 在接受到一个 API 请求时,第一阶段就是对请求进行 认证 与 鉴权。
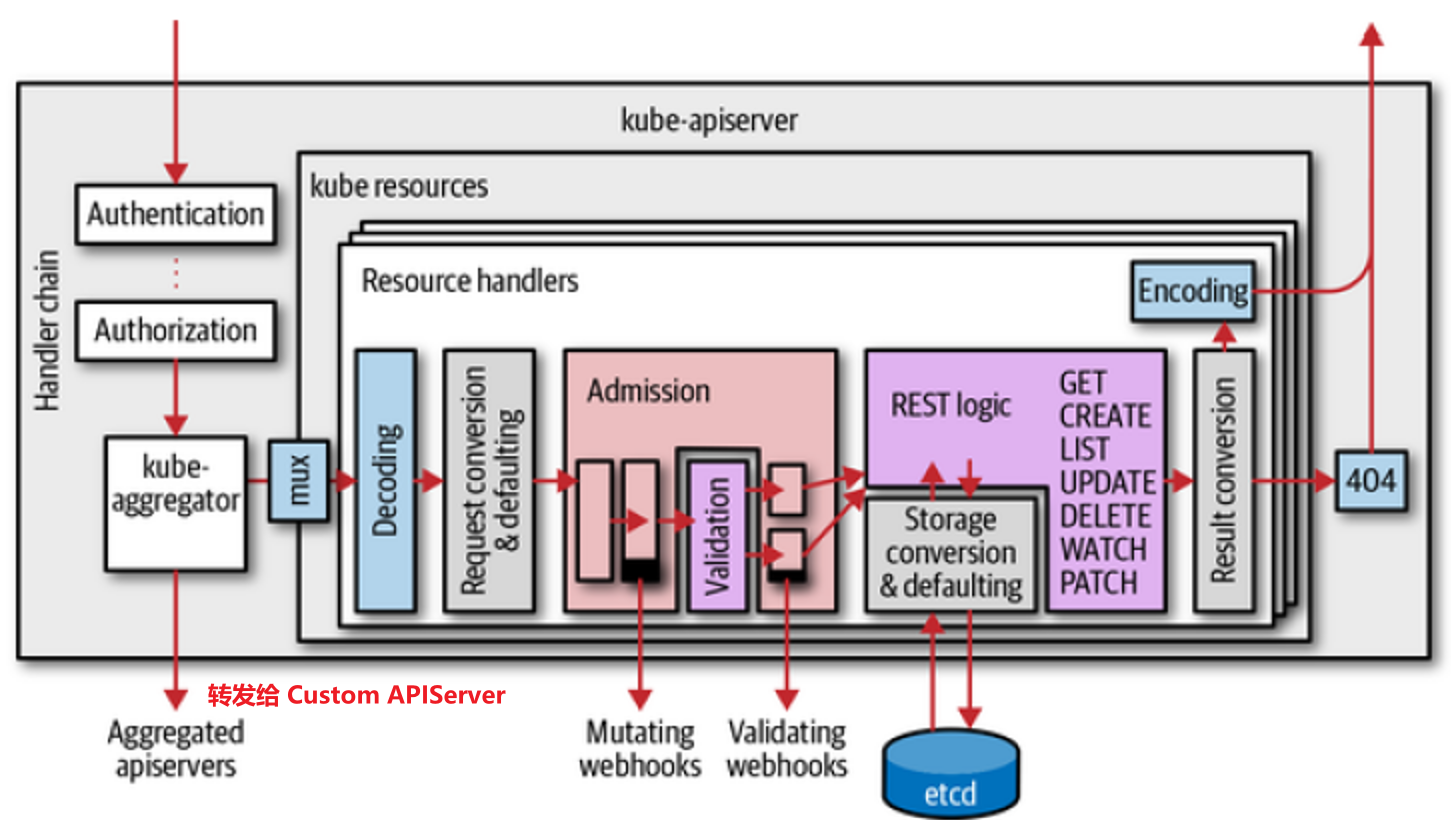
APIServer 支持多种认证与鉴权方式,不过无论经过哪种身份认证,APIServer 都会从中读取以下用户信息,用以后续对该用户进行权限判断。
- Username - 用户名,例如
kube-admin或者user@example.com; - UID - 用户 ID,比用户名有更好的唯一性;
- Group -(可选)用户组,用于集合管理一批用户的权限,例如
system:master或者devops-team; - Extra fields -(可选)一些鉴权使用的额外的信息;

2 身份认证
APIServer 支持多种的认证方式,不过从本质上大致分为三类:
- 证书认证 - Client 提供证书与私钥,APIServer 检查是否由 CA 颁发;
- Bearer Token 认证 - Client 发送的 HTTP 请求 Header 包含 Token 值,APIServer 检查 Token 是否合法;
- Proxy - 由 Proxy 进行认证,APIServer 仅仅从请求中读取信息而不认证;
同时开启多种认证方式的情况下,一个成功完成身份认证的模块(无论成功还是失败)会直接决定结果,各个认证方式之间不保证特定的运行顺序。
2.1 X509 Client Cert
在 SSL/TLS 总结 中提到过,TLS 使用证书来对服务器进行身份认证。X509 Client Cert 机制就是需要在 API 请求中提供客户端的证书,然后 APIServer 确认证书是否是由正确的 CA 签发的。
CertificateSigningRequests 消息给 APIServer 来申请颁发证书,具体过程参考文档:Certificate Signing Requests。2.1.1 认证原理
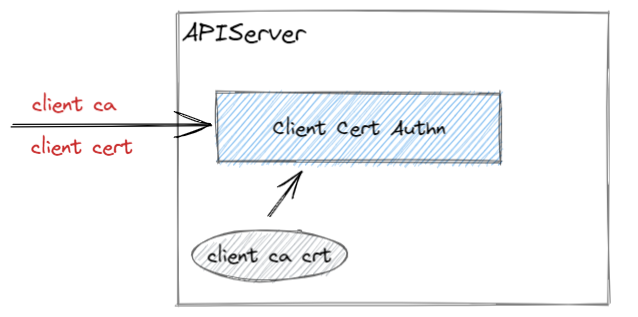
Client 在连接 APIServer 后,提供 Client 证书与私钥,APIServer 检查是否是由 CA 证书签发。
后续,APIServer 会以 Client 证书中的 Common Name 作为用户名,然后进行鉴权判断。
2.1.2 开启
在 APIServer 启动时,通过参数 --client-ca-file 开启 X509 Client Cert 认证方式,并指定了 CA 的证书。
--client-ca-file 提供的证书仅仅用于 APIServer 单向认证 Client 证书,Client 认证 APIServer 是由 --tls-cert-file 以及 --tls-private-key-file 设置的证书与私钥。2.1.3 示例
例如,我们可以直接使用 kube config 中的证书信息,通过 curl 来访问 APIServer。
|
|
--insecure 以跳过提供 CA 证书。2.2 Static Token File
APIServer 支持预置 Static Token,后续能够通过 Token 访问集群。但是,预置的 Token 长期有效(无法设置超时时间),并且只有在 APIServer 重启时才会重新读取 Token。
2.2.1 认证原理
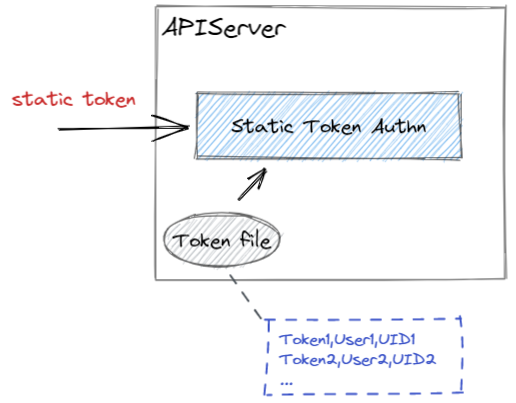
APIServer 支持启动时指定一个 Static Token 文件,APIServer 会读取该文件中的 Token 作为可访问 APIServer 的 Token。
Static Token 文件是一个 CSV 文件,包含至少三个列:Token Username 和 UID。
|
|
当发送 API 请求时,在 HTTP Header Authorization 设置值为 Bearer ${Token}。例如:
|
|
APIServer 会读取该 Token,然后查找对应的 Static Token 记录,以验证 Token 身份。
从 Static Token 记录中可以得到对应的用户(Static Token 文件中设置的),进而对该用户进行鉴权判断。
2.2.2 开启
APIServer 启动参数设置 --token-auth-file=${token_file} 时,APIServer 会读取该文件作为可以访问 APIServer 的 Token。
2.2.3 示例
下面示例我们尝试使用 Static Token File 来访问 APIServer。
-
启动 APIServer 时指定
--token-auth-file参数。以 kind 创建集群为例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17kind: Cluster apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4 nodes: - role: control-plane # 将 static token 文件挂载到 control-plane 节点上 extraMounts: - hostPath: /root/static-token containerPath: /etc/kubernetes/pki/static-token kubeadmConfigPatches: - | kind: ClusterConfiguration apiServer: # 配置 APIServer 的启动参数(节点上的 /etc/kubernetes/pki 目录会挂载到 Pod 中) extraArgs: token-auth-file: /etc/kubernetes/pki/static-token - role: worker - role: workerToken 文件内容为
123123,kind-kind,123,token 值为 123123,对应用户名为 kind-kind。 -
创建 ClusterRoleBinding,设置对应的用户有权限执行操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12kind: ClusterRoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: for-user subjects: - kind: User name: kind-kind apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-admin apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io -
现在,我们可以直接通过 Static Token 访问集群了。不需要配置 Client 证书,为了简单使用
--insecure跳过验证 APIServer 的证书。1curl -H "Authorization: Bearer 123123" --insecure ${APIServer}/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/pods/
2.3 Bootstrap Tokens
为了支持平滑启动新的集群,Kubernetes 支持动态的 Token 访问集群,称为 Bootstrap Token。
2.3.1 认证原理
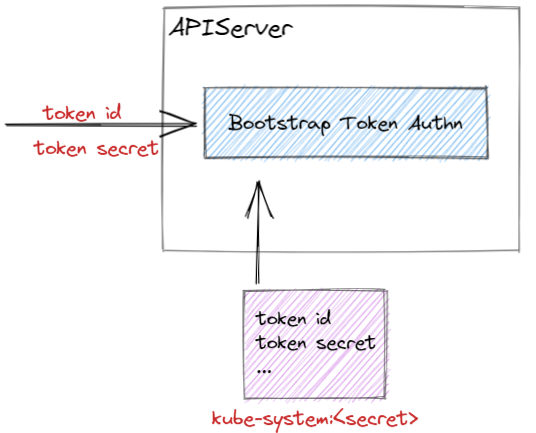
Bootstrap Token 信息以 Secret 资源存储在 kube-system namespace 下,支持动态的管理和创建。
|
|
auth-extra-groups- Bootstrap Token 都是属于system:bootstrappers:用户组下,可以使用该字段设置额外的子用户,以实现更加精细化的权限控制。token-id- 访问 APIServer 需要提供的 Token ID,格式为[a-z0-9]{6}。token-secret- 访问 APIServer 需要提供的 Token Secret,格式为[a-z0-9]{16}。expiration- Token 超时时间,超时的 Token 会由 controller-manager 中的 TokenCleaner 删除。
发送的 API 请求的 HTTP Header Authorization 设置值为 Bearer ${Token}。
|
|
APIServer 会读取 Token ID 与 Token Secret,从而查找对应的 Bootstrap Token Secret 是否存在。
从 Bootstrap Token Secret 中可以得到用户(或者使用默认的 system:bootstrappers 用户组),然后基于该用户进行鉴权判断。
2.3.2 开启
为了使用 Bootstrap Token,需要确保(默认都已经开启):
- APIServer 启动时指定
--enable-bootstrap-token-auth参数,表明开启 Bootstrap Token 验证功能; - controller-manager 启动时指定
--controllers=*,tokencleaner参数,表明开启 TokenCleaner 控制器;
2.3.3 示例
-
找到启动时使用的 Bootstrap Token 的 Secret:
1 2$ kubectl get secrets -n kube-system | grep bootstrap-token bootstrap-token-abcdef bootstrap.kubernetes.io/token 6 11h得到其中的 Token ID 与 Token Secret,访问 APIServer 时需要使用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7# Token ID $ kubectl get secrets -n kube-system bootstrap-token-abcdef -o jsonpath='{.data.token-id}' | base64 -d abcdef # Token Secret $ kubectl get secrets -n kube-system bootstrap-token-abcdef -o jsonpath='{.data.token-secret}' | base64 -d 0123456789abcdef -
确认 Token 的权限,找到对应的 ClusterRole 与 ClusterRoleBinding,可以知晓其只有 CertificateSigningRequests 的权限。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: kubeadm:kubelet-bootstrap roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: system:node-bootstrapper subjects: - apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: Group name: system:bootstrappers:kubeadm:default-node-token # 对应 Token User --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: annotations: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true" creationTimestamp: "2022-03-26T16:01:24Z" labels: kubernetes.io/bootstrapping: rbac-defaults name: system:node-bootstrapper rules: - apiGroups: - certificates.k8s.io resources: - certificatesigningrequests verbs: - create - get - list - watch
|
|
2.4 ServiceAccount Token
ServiceAccount 是最常用的认证方式,使用经过签名的 Token 来访问 APIServer。
当然,ServiceAccount 不仅仅只用于集群中 Pod 访问,集群外也可以通过 ServiceAccount Token 访问 APIServer。
2.4.1 认证原理
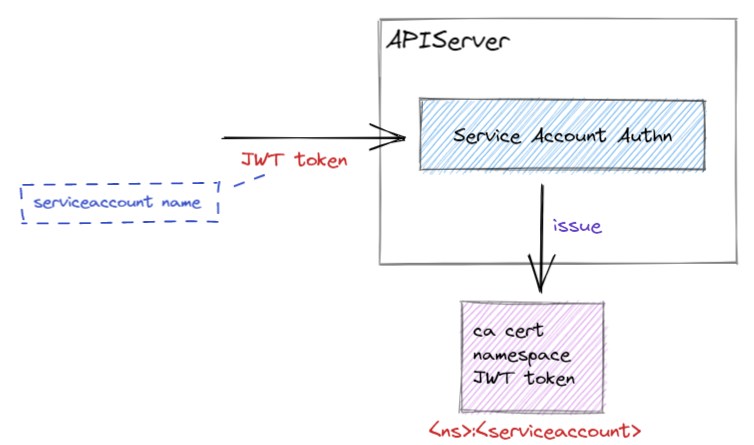
创建一个 ServiceAccount 资源时,Kubernetes 会在同 namespace 下创建对应的 Secret,其中包含了访问集群所需要的 Token。
|
|
ca.crt- APIServer 签发 Token 使用的 CA 证书,用于 Client 认证 APIServer 的证书;token- Client 访问 APIServer 使用的 ServiceAccount Token;
ServiceAccount Token 是 JWT 格式的,解析后可以看到其包含的信息:
|
|
APIServer 认证 JWT 的正确性后,通过其中的信息来对应的用户 system:serviceaccount:${NAMESPACE}:${SERVICE_ACCOUNT},从而使用该用户进行鉴权判断。
system:serviceaccounts 和 system:serviceaccounts:${NAMESPACE} 用户组,因此可以使用用户组批量管理 ServiceAccount 的权限。2.4.2 开启
Service Account 认证在 APIServer 启动时默认开启,有两个可选的控制参数:
--service-account-key-file- 为 ServiceAccount Token 签名的 PEM 编码私钥。不指定默认使用 APIServer 的 TLS 私钥;--service-account-lookup- 设置后,从 API 删除的 Token 会被回收;
2.4.3 示例
-
创建一个 ServiceAccount 资源,并查看对应的 Token。
1 2 3$ kubectl create serviceaccount custom $ SATOKEN=$(k get secrets custom-token-gsg7z -o jsonpath='{.data.token}' | base64 -d) -
为该 ServiceAccount 创建 ClusterRoleBinding 来鉴权。
1 2$ kubectl create clusterrolebinding cluster-admin-for-custom --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=default:custom clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-admin-for-custom created -
使用 ServiceAccount Token 访问 APIServer。
1curl --insecure -H "Authorization: Bearer ${SATOKEN}" https://127.0.0.1:46689/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods/
2.5 OpenID Connect Token
OpenID Connect(OIDC)是一种 OAuth2 认证方式,由额外的 OIDC Provider 来负责认证。
OIDC 本质上还是基于 Token 来访问 APIServer,区别在于 Token 是由 OIDC Provider 来颁发的。
参考文档:OpenID Connect Token。
2.6 Webhook Token
APIServer 提供了一种基于 Webhook 的回调认证机制,APIServer 调用 Webhook 服务来进行身份认证。
2.6.1 认证原理
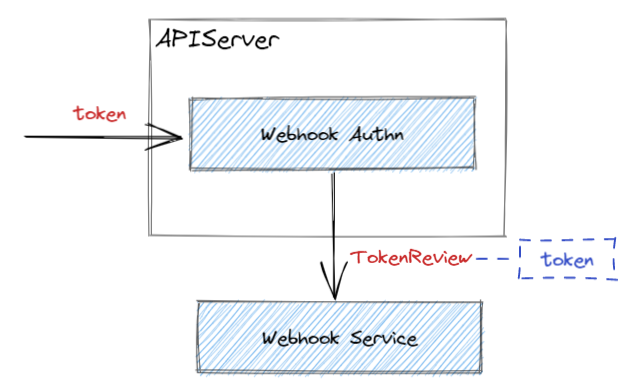
需要提供一个 kubeconfig 格式的配置文件给 APIServer,以描述 APIServer 如何访问 Webhook 服务:
|
|
-
clusters字段表明了如何访问 Webhook 服务:certificate-authority- 验证 Webhook 服务证书使用的 CA 证书;server- 发送认证请求的地址;
-
users字段表明 APIServer 使用的证书相关配置:client-certificate- Client 证书;client-key- Client 私钥;
-
contexts相关用于支持在多个 Webhook 验证中切换使用。
当使用基于 Bearer Token 方式访问 APIServer 时,APIServer 会发送一个 HTTP Post 请求(JSON 格式)给 Webhook 服务,来验证该 Token 的合法性。
发送的请求的内容为 JSON 格式的 TokenReview 消息。
|
|
Webhook 服务会回复相同的 TokenReview 消息,其中填充了 status 字段来表明 Token 的认证结果。
|
|
认证成功后,APIServer 读取请求中的 user 字段,然后基于该用户信息进行鉴权判断。
2.6.2 开启
使用 Webhook 方式需要设置 APIServer 启动参数:
--authentication-token-webhook-config-file- 指向一个配置文件,其中内容描述了如何访问 Webhook 服务;--authentication-token-webhook-cache-ttl- 身份认证的结果缓存时间,默认为 2min;
2.7 Authentication Proxy
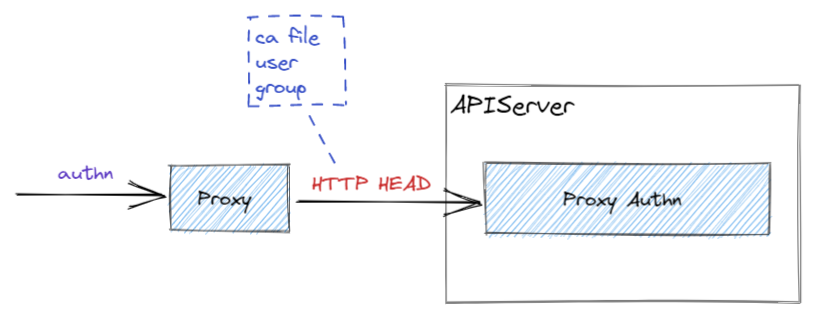
APIServer 支持从 HTTP Header 中读取用户名(例如 X-Remote-User)。这一设计用于支持 Authentication Proxy:Proxy 在前面负责身份认证,认证成功后设置用户名的 HTTP Header,发送给 APIServer 进行权限判断。
2.7.1 开启
APIServer 启动参数与 Proxy 相关的配置:
--requestheader-client-ca-file- 验证请求证书使用的 CA 证书;--requestheader-allowed-names-(可选)请求允许的 CN;--requestheader-username-headers- 设置 APIServer 读取用户名所使用的 HTTP Header,数组情况下第一个有值的 Header 会作为用户名;--requestheader-group-headers-(可选)指定用户所属的用户组,建议使用X-Remote-Group;--requestheader-extra-headers-prefi-(可选)设置 Header 的前缀,建议设置X-Remote-Extra-;
2.8 匿名请求 Anonymous requests
开启匿名请求功能后,如果请求没有被任何身份认证显式的拒绝,则请求被视为 匿名请求。这类请求会以用户 system:anonymous 和用户组 system:unauthenticated 进行鉴权。
Kubernetes 1.6 之后,如果鉴权模式不是 AlwaysAllow,那么匿名访问默认是启动的。
不过,为 * 用户或 * 用户组赋予的访问权限的规则都不包含匿名用户,所以默认匿名用户是没有任何操作权限的,你必须显式的为用户 system:anonymous 和用户组 system:unauthenticated 赋予访问权限,才能让匿名请求执行操作。
2.9 用户伪装 User impersonation
一个用户可以伪装为另一个用户来执行操作。使用该功能,可以让你模拟另一个用户来发送请求,从而调试用户的权限策略。
用户伪装的流程如下:
-
发起的用户在 API 请求中提供自身的凭证(Token 或者证书),以及伪装相关的 HTTP Header。
伪装相关的 HTTP Header:
Impersonate-User- 要伪装的用户名Impersonate-Uid- 要伪装的用户 IDImpersonate-Group-(可选)要伪装的用户组Impersonate-Extra-<附加名称>-(可选)附加的信息
-
APIServer 对发起的用户进行身份认证,并确认发起的用户具有伪装用户的权限。
例如,伪装相关权限的 Role 如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: impersonator rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["users", "groups", "serviceaccounts"] verbs: ["impersonate"]UID 与附加字段都属于 “authorization.k8s.io” API 组下,因此如果需要伪装 UID 与附加字段,需要赋予额外的权限。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: scopes-and-uid-impersonator rules: # 可以设置 "Impersonate-Extra-scopes" 和 "Impersonate-Uid" 头部 - apiGroups: ["authentication.k8s.io"] resources: ["userextras/scopes", "uids"] verbs: ["impersonate"] -
APIServer 将该 API 请求中的用户信息,替换为伪装字段的值,请求变为了伪装的用户发起的。
-
APIServer 确认伪装后的 API 请求的权限。
kubectl 也支持发起伪装请求,可以使用 --as 来配置请求的 Impersonate-User 字段,使用 --as-group 配置请求的 Impersonate-Group 字段。
|
|
3 鉴权模块
身份认证成功后,APIServer 的鉴权模块就会根据请求的用户信息,检查用户是否有权限执行请求。
开启多个鉴权模块时,APIServer 会按照顺序调用每个模块。如果任何模块 Allow 或 Deny 了请求,那么结果会立即返回,并且不会再调用其他模块。如果没有任何鉴权模块对请求做出决策,那么默认会 Deny 请求。
当请求被鉴权模块 Deny 时,会返回 HTTP Code 403。
鉴权模块可以从请求中读取以下的信息:
-
用户信息 - 请求者的信息- User - 提供的用户名
- Group - 用户所属的用户组
- Extra fields - 传递鉴权使用的额外的信息
-
资源信息 - 表示请求是对某个具体的资源的操作- API - 请求是否是针对 API 资源的
- Resource - 访问的资源 ID 或者名字
- Subresource - 资源的子操作,例如 /scale
- Namespace - 资源的 namespace
- API Group - 访问的 API 所属的 Group
- API request verb - 对于资源请求将要执行的操作,例如 get、list、update 等
-
非资源信息 - 表示请求是对 APIServer 一个 HTTP Path 的访问- Request Path - API 请求的非资源路径,例如 /healthz
- HTTP request verb - 对于非请求资源执行的 HTTP 动词,即 get、post、put 和 delete
3.1 鉴权模块 Node
Node 鉴权模块专门为 kubelet 发出的 API 请求进行鉴权。可以认为是 Kubernetes 自身的安全增强,用户不需要也没必要使用 Node 鉴权。
Node 鉴权模块会限制每个 Node 只能访问与修改它自身运行的 Pod 以及 Service 等资源。
更多的信息见官方文档:Using Node Authorization。
3.1.1 使用
配置 APIServer 启动参数 --authorization-mode=Node 表明使用 Node 鉴权模块。
3.2 鉴权模块 ABAC
ABAC 基于一个 Policy 文件来传入授权策略,APIServer 启动时读取该文件来预置鉴权策略。
3.2.1 鉴权原理
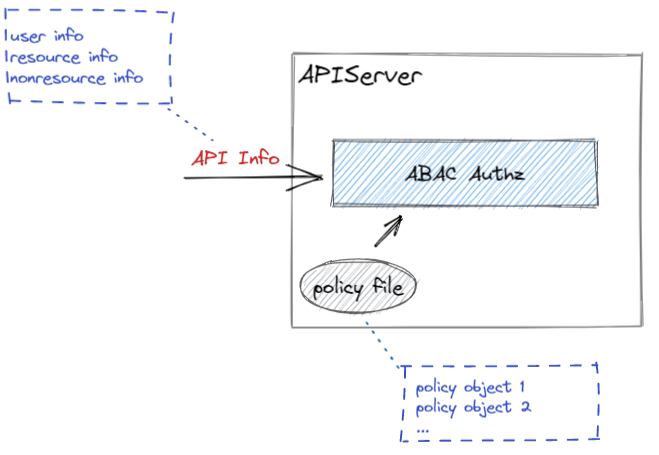
Policy 文件中的每一行是一个 JSON,也被称为 Policy Object。例如:
|
|
其中 apiVersion 与 kind 值都是固定的,在 spec 中描述详细的策略,包括:用户信息、资源信息、非资源信息。
- 用户信息 - 表明该策略针对那个用户有效
- user - 用户名
- group - 用户组
- 资源信息 - 用户有权限操作的资源
- apiGroup - 能够访问的 API 组,例如 apps
- namespace - 能够访问资源的 namespace
- resource - 能够访问的资源类型,例如 pod
- 非资源信息 - 用户有权限访问的非资源路径
- nonResourcePath - 能够请求的 URL 路径
- readonly - 为 true 表示只允许 GET 请求
收到请求后,会读取请求中的相关信息,然后根据 Policy 文件中的每个 Policy Object,逐条进行匹配。
如果任一一条匹配成功,那么这个请求就通过了鉴权。
3.2.2 开启
配置 APIServer 启动参数 --authorization-mode=ABAC 表明使用 ABAC 鉴权模块,使用参数 --authorization-policy-file=${file_path} 指定 Policy 文件的路径。
当需要修改 Policy 文件时,需要重新启动 APIServer 来重新加载。
3.2.3 示例
用户 alice 有任何资源的任何操作权限:
|
|
kubelet 可以读取任何 Pod:
|
|
未身份认证的用户(匿名请求)可以对所有非资源路径进行只读请求。
|
|
kube-system 命名空间下的 ServiceAccount default 有任何的操作权限。ServiceAccount 本质上是特殊的用户,见 ServiceAccount Token。
|
|
3.3 鉴权模块 RBAC
参考 RBAC 授权机制。
3.4 鉴权模块 Webhook
APIServer 也支持基于 Webhook 的回调鉴权机制,APIServer 会向 Webhook 服务进行鉴权。
3.4.1 鉴权原理
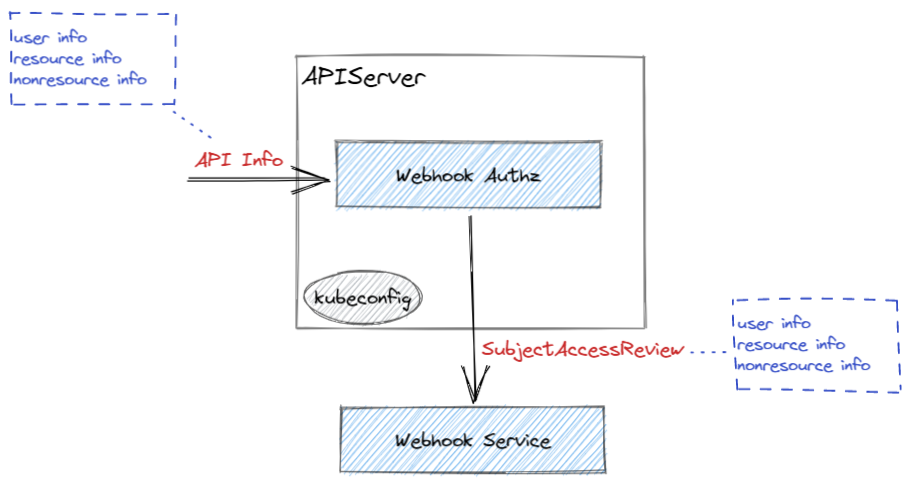
首先,依旧需要一个配置文件 kubeconfig 格式的配置文件给 APIServer,以描述 APIServer 如何访问 Webhook 服务:
|
|
-
clusters字段表明了如何访问 Webhook 服务:certificate-authority- 验证 Webhook 服务证书使用的 CA 证书;server- 发送认证请求的地址;
-
users字段表明 APIServer 使用的证书相关配置:client-certificate- Client 证书;client-key- Client 私钥;
-
contexts相关用于支持在多个 Webhook 验证中切换使用。
当开始鉴权时,APIServer 会发送一个 HTTP Post 请求给 Webhook 服务,来对请求进行鉴权。
发送的请求的内容为 JSON 格式的 SubjectAccessReview 消息。
|
|
Webhook 服务会回复相同的 SubjectAccessReview 消息,其中填充了 status 字段来表明鉴权结果。如下示例,有三种结果:
|
|
3.4.2 开启
配置 APIServer 启动参数 --authorization-mode=Webhook 表明使用 Webhook 鉴权模块,使用 --authorization-webhook-config-file=${file_path} 来指定 Webhook 服务的配置文件。
3.5 鉴权模块 AlwaysDeny AlwaysAllow
AlwaysDeny 表明所有请求都拒绝(没有啥意义),AlwaysAllow 表示所有请求都允许。
3.5.1 开启
配置 APIServer 启动参数 --authorization-mode=AlwaysAllow 表明使用 AlwaysAllow 鉴权模块。
4 测试访问权限
使用 kubectl auth can-i 可以测试 API 鉴权。该命令会发送 SelfSubjectAccessReview API 请求来确认当前的用户是否可以执行给定的操作。
|
|
使用改命令与 User impersonation 配置,可以测试某个用户是否有权限执行操作。
|
|
外部服务也可以通过发送 SubjectAccessReview 请求来测试访问权限。
参考
- 官方文档:用户认证
- 官方文档:鉴权概述
- Blog:Kubernetes 认证机制